Meteorological Support to the Air Force Eastern Test Range
... rological facility. In addition to the conven tional rawinsonde upper air observation equipment and surface observing systems, three of the land stations are equipped to make meteorological rocket observations on a routine basis. Two of the three ship board stations are also equipped to launch met ...
... rological facility. In addition to the conven tional rawinsonde upper air observation equipment and surface observing systems, three of the land stations are equipped to make meteorological rocket observations on a routine basis. Two of the three ship board stations are also equipped to launch met ...
7 Science Learner`s Material Unit 4 – Earth and Space Module 2
... can we not see auroras in the Philippines? The upper limit of our atmosphere is the exosphere. This layer of the atmosphere merges into space. Satellites are stationed in this area, 500 km to 1000 km from Earth. To summarize what has been discussed: More than three quarters of Earth’s atmosphere is ...
... can we not see auroras in the Philippines? The upper limit of our atmosphere is the exosphere. This layer of the atmosphere merges into space. Satellites are stationed in this area, 500 km to 1000 km from Earth. To summarize what has been discussed: More than three quarters of Earth’s atmosphere is ...
Chapter 12: Air Section 1: What Causes Air Pollution Clean air
... A pH number is a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is. The lower the pH, the more acidic the substance is. The higher the pH the more basic a substance is. Pure water has a pH of 7. Natural rain is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide dissolves into the precipitation forming carbonic aci ...
... A pH number is a measure of how acidic or basic a substance is. The lower the pH, the more acidic the substance is. The higher the pH the more basic a substance is. Pure water has a pH of 7. Natural rain is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide dissolves into the precipitation forming carbonic aci ...
SCIENCE OF SUN PHOTOMETRY
... definition of PAR is not precise, because different kinds of plants respond to different parts of the solar spectrum. However, PAR is generally considered to include just the visible part of the solar spectrum between 400 and 700 nm. Thus, a PAR detector is similar to a pyranometer, but with its spe ...
... definition of PAR is not precise, because different kinds of plants respond to different parts of the solar spectrum. However, PAR is generally considered to include just the visible part of the solar spectrum between 400 and 700 nm. Thus, a PAR detector is similar to a pyranometer, but with its spe ...
national unit specification: general information
... reviewing and evaluation (SCQF level 5) skills. These skills are also further developed as the candidate builds a knowledge of the large scale meteorological and oceanographic processes. Communication (Reading and Writing at SCQF level 5) skills are developed and Using Information Technology (SCQF l ...
... reviewing and evaluation (SCQF level 5) skills. These skills are also further developed as the candidate builds a knowledge of the large scale meteorological and oceanographic processes. Communication (Reading and Writing at SCQF level 5) skills are developed and Using Information Technology (SCQF l ...
introduction to synoptic meteorology введение в синоптическую
... velop. At the same time the processes within thinner layer, nearest to the ground surface, such as airflows streamlining a building, do not signifi cantly affect weather conditions. Hence the vertical scale of the atmos pheric weather forming processes, which are considered in synoptic me teorolo ...
... velop. At the same time the processes within thinner layer, nearest to the ground surface, such as airflows streamlining a building, do not signifi cantly affect weather conditions. Hence the vertical scale of the atmos pheric weather forming processes, which are considered in synoptic me teorolo ...
Unit Test Study Guide
... 10.What fact about Earth’s atmosphere best explains this data? a. As altitude increases in the atmosphere, temperature changes from layer to layer. b. At higher altitudes, there is less air pushing down from above, which decreases the pressure. ...
... 10.What fact about Earth’s atmosphere best explains this data? a. As altitude increases in the atmosphere, temperature changes from layer to layer. b. At higher altitudes, there is less air pushing down from above, which decreases the pressure. ...
STORM TROOPERS
... Tornado Alley. A quick search of the Internet, provides you with the following information on Tornado Alley. The American Meteorology Society's Glossary of Weather and Climate defines Tornado Alley as: "The area of the United States in which tornadoes are most frequent. It encompasses the great lowl ...
... Tornado Alley. A quick search of the Internet, provides you with the following information on Tornado Alley. The American Meteorology Society's Glossary of Weather and Climate defines Tornado Alley as: "The area of the United States in which tornadoes are most frequent. It encompasses the great lowl ...
H8-Isr-str
... station in Qeqertarsuaq (Godhavn), since 1957 a station in Narsarsuaq, and since 1966 an ionosonde station in Qaanaaq (Thule). More recently these stations have been upgrades to use modern Digisondes. The ionosondes/ digisondes measures the electron content in the upper atmosphere, a parameter of gr ...
... station in Qeqertarsuaq (Godhavn), since 1957 a station in Narsarsuaq, and since 1966 an ionosonde station in Qaanaaq (Thule). More recently these stations have been upgrades to use modern Digisondes. The ionosondes/ digisondes measures the electron content in the upper atmosphere, a parameter of gr ...
Chapter 3 The vertical structure of the atmosphere
... (including us) from the damaging effects of this radiation. The stratosphere, as its name suggests, is highly stratified, poorly mixed (stratus meaning layered) with long residence times for particles ejected into it (for example by volcanos) from the troposphere below. It is close to radiative equil ...
... (including us) from the damaging effects of this radiation. The stratosphere, as its name suggests, is highly stratified, poorly mixed (stratus meaning layered) with long residence times for particles ejected into it (for example by volcanos) from the troposphere below. It is close to radiative equil ...
On the physics of droughts presentation
... In the simple GCM the basis functions are represented by a constant and half-cycle sine waves with varying periods (wavelengths). The constant represents the average conditions of temperature and water vapor content, whereas the sine waves model the weather disturbances. For their wavelengths on the ...
... In the simple GCM the basis functions are represented by a constant and half-cycle sine waves with varying periods (wavelengths). The constant represents the average conditions of temperature and water vapor content, whereas the sine waves model the weather disturbances. For their wavelengths on the ...
J1.2 WHERE AND WHY DOES SPACE WEATHER OCCUR?
... magnetic field and atmosphere, and our location in the solar system. As a practical matter, space weather often means a disturbed situation, whereas space environment usually refers to normal or background conditions. Space weather is created by electromagnetic energy from the Sun and by the Sun’s o ...
... magnetic field and atmosphere, and our location in the solar system. As a practical matter, space weather often means a disturbed situation, whereas space environment usually refers to normal or background conditions. Space weather is created by electromagnetic energy from the Sun and by the Sun’s o ...
Environmental Chemistry (Air)
... a) What are the dominant natural and anthropogenic sources? b) What is the current level of CO2 in the atmosphere (in ppmV und in %vol)? c) What is the average annual rate of the CO2 increase? d) Why does the atmospheric CO2 concentration show a seasonal variability? e) How large is the total atmosp ...
... a) What are the dominant natural and anthropogenic sources? b) What is the current level of CO2 in the atmosphere (in ppmV und in %vol)? c) What is the average annual rate of the CO2 increase? d) Why does the atmospheric CO2 concentration show a seasonal variability? e) How large is the total atmosp ...
Wind Measuring - WindCom Messtechnik
... box. Meteorological measurements In connection with questions of the air-pollution control it is around the respective climate conditions to grasp required, also the physical condition of the atmosphere exactly to be able determine. To this it requires the measuring of a variety of meteorological pa ...
... box. Meteorological measurements In connection with questions of the air-pollution control it is around the respective climate conditions to grasp required, also the physical condition of the atmosphere exactly to be able determine. To this it requires the measuring of a variety of meteorological pa ...
doc - UA Atmospheric Sciences
... Note that the warmer the atmosphere is, the larger H is which causes pressure to decay more slowly with altitude. At lower temperatures, H is smaller and pressure decays more rapidly with altitude. Pressure height as a thermometer: Therefore, accurately measuring the height of a pressure surface can ...
... Note that the warmer the atmosphere is, the larger H is which causes pressure to decay more slowly with altitude. At lower temperatures, H is smaller and pressure decays more rapidly with altitude. Pressure height as a thermometer: Therefore, accurately measuring the height of a pressure surface can ...
The Ramdas layer
... temperature minimum (LTM)’ develops, in which a local minimum in the vertical temperature profile occurs a few decimeters above the ground. The LTM was first observed by Ramdas and Ramanathan in 1932, and has been variously referred to as the Ramdas layer, the Ramdas paradox, the elevated temperatur ...
... temperature minimum (LTM)’ develops, in which a local minimum in the vertical temperature profile occurs a few decimeters above the ground. The LTM was first observed by Ramdas and Ramanathan in 1932, and has been variously referred to as the Ramdas layer, the Ramdas paradox, the elevated temperatur ...
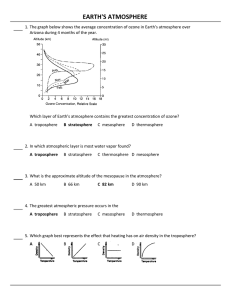
earth`s atmosphere
... The atmosphere is a shell of gases surrounding most of the Earth. The atmosphere's altitude is less than the depth of the ocean. The atmosphere is more dense than the hydrosphere but less dense than the ...
... The atmosphere is a shell of gases surrounding most of the Earth. The atmosphere's altitude is less than the depth of the ocean. The atmosphere is more dense than the hydrosphere but less dense than the ...
Wind and Clouds - pkms.poteau.k12.ok.us
... 2nd– Face that direction – the direction behind you will be what? To your left is west and to your right is east. 3rd– Then feel which way the wind is coming from – wet your finger if you have too! 4th– A south wind usually means that warmer weather is on the way soon. A north wind usually means tha ...
... 2nd– Face that direction – the direction behind you will be what? To your left is west and to your right is east. 3rd– Then feel which way the wind is coming from – wet your finger if you have too! 4th– A south wind usually means that warmer weather is on the way soon. A north wind usually means tha ...
Insolation and Temperature
... Earth and its atmosphere equals the total amount of terrestrial radiation returned to space) 2. global energy budget: annual balance between incoming and outgoing radiation for the entire globe B. Earth’s energy budget (using 100 units to represent total insolation at top of atmosphere) (Fig 4-17) 1 ...
... Earth and its atmosphere equals the total amount of terrestrial radiation returned to space) 2. global energy budget: annual balance between incoming and outgoing radiation for the entire globe B. Earth’s energy budget (using 100 units to represent total insolation at top of atmosphere) (Fig 4-17) 1 ...
Chapter 4: Insolation and Temperature
... Earth and its atmosphere equals the total amount of terrestrial radiation returned to space) 2. global energy budget: annual balance between incoming and outgoing radiation for the entire globe B. Earth’s energy budget (using 100 units to represent total insolation at top of atmosphere) (Fig 4-17) 1 ...
... Earth and its atmosphere equals the total amount of terrestrial radiation returned to space) 2. global energy budget: annual balance between incoming and outgoing radiation for the entire globe B. Earth’s energy budget (using 100 units to represent total insolation at top of atmosphere) (Fig 4-17) 1 ...
Eastern Africa
... own bulletins. Also, these bulletins represent the expert knowledge of the individual countries and can be used to assess extreme events and disasters in a historical perspective especially when an archive of bulletins are present. ...
... own bulletins. Also, these bulletins represent the expert knowledge of the individual countries and can be used to assess extreme events and disasters in a historical perspective especially when an archive of bulletins are present. ...
Samantha Fiani Report - Charter Township of Union
... collision of gas molecules. Air pressure is measured with a mercury barometer, which was invented in 1643 by a former student of Galileo, Torricelli (Lutgens & Tarbuck, 2007). He described the atmosphere as, “a vast ocean of air that exerts pressure on us and all things about us (Lutgens & Tarbuck, ...
... collision of gas molecules. Air pressure is measured with a mercury barometer, which was invented in 1643 by a former student of Galileo, Torricelli (Lutgens & Tarbuck, 2007). He described the atmosphere as, “a vast ocean of air that exerts pressure on us and all things about us (Lutgens & Tarbuck, ...
Chapter_I_Understand..
... The molecules in a gas are bouncing around like hyperactive kids on a chocolate diet. All this scurrying about causes them to knock into their neighbors and ricochet off in random fashion. If the molecules encounter a solid they leave some energy behind as they hit the solid. In fact, this exchange ...
... The molecules in a gas are bouncing around like hyperactive kids on a chocolate diet. All this scurrying about causes them to knock into their neighbors and ricochet off in random fashion. If the molecules encounter a solid they leave some energy behind as they hit the solid. In fact, this exchange ...
IM_08 - earthjay science
... turbulent mixing near the surface usually produce good visibility, cumuliform clouds, and showers of rain or snow. On the other hand, when the air mass is warmer than the surface below, the lower layers are chilled by contact with the cold earth. Warm air above cooler air produces a stable lapse rat ...
... turbulent mixing near the surface usually produce good visibility, cumuliform clouds, and showers of rain or snow. On the other hand, when the air mass is warmer than the surface below, the lower layers are chilled by contact with the cold earth. Warm air above cooler air produces a stable lapse rat ...
© 2008 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted.... reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for...
... grid of ASOS 1-min surface observations and NOAA RUC model data are used in making this product. Broad access to the FAA networked ASOS 1-min observation data stream needs to be made operational as soon as possible. ...
... grid of ASOS 1-min surface observations and NOAA RUC model data are used in making this product. Broad access to the FAA networked ASOS 1-min observation data stream needs to be made operational as soon as possible. ...
Weather

Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Weather, seen from an anthropological perspective, is something all humans in the world constantly experience through their senses, at least while being outside. There are socially and scientifically constructed understandings of what weather is, what makes it change, the effect it has on humans in different situations, etc. Therefore, weather is something people often communicate about.Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather generally refers to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the statistics of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, ""weather"" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.Weather is driven by air pressure (temperature and moisture) differences between one place and another. These pressure and temperature differences can occur due to the sun angle at any particular spot, which varies by latitude from the tropics. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the jet stream. Weather systems in the mid-latitudes, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by instabilities of the jet stream flow. Because the Earth's axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane, sunlight is incident at different angles at different times of the year. On Earth's surface, temperatures usually range ±40 °C (−40 °F to 100 °F) annually. Over thousands of years, changes in Earth's orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thus influencing long-term climate and global climate change.Surface temperature differences in turn cause pressure differences. Higher altitudes are cooler than lower altitudes due to differences in compressional heating. Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a future time and a given location. The system is a chaotic system; so small changes to one part of the system can grow to have large effects on the system as a whole. Human attempts to control the weather have occurred throughout human history, and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have modified weather patterns.Studying how the weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth. A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter's Great Red Spot, is an anticyclonic storm known to have existed for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies. A star's corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.