strange_quarks_nucleon
... individual quark contributions to the electric charge radii of the baryon octet, we obtain an accurate determination of the strange electric charge radius of the proton. While this analysis provides a value for GsE(Q2 = 0.1GeV2) in agreement with the best current data, the theoretical error is compa ...
... individual quark contributions to the electric charge radii of the baryon octet, we obtain an accurate determination of the strange electric charge radius of the proton. While this analysis provides a value for GsE(Q2 = 0.1GeV2) in agreement with the best current data, the theoretical error is compa ...
Development of a Space-charge-sensing System
... Fig. 4 shows an example of the burst sound wave and the integrated electric field changes when the distances between the loud speaker and the bottom of the electrode are, respectively, 1, 1.5 and 2 meters. In the E-field waveforms, the beginning time of the E-field rise and its peak time are marked ...
... Fig. 4 shows an example of the burst sound wave and the integrated electric field changes when the distances between the loud speaker and the bottom of the electrode are, respectively, 1, 1.5 and 2 meters. In the E-field waveforms, the beginning time of the E-field rise and its peak time are marked ...
Scientific Notation Numbers
... DESCO INDUSTRIES, INC. EMPLOYEE OWNED Scientific Notation Numbers The display of numbers in floating point form. The number (mantissa) is always equal to or greater than one and less than 10, and the base is ...
... DESCO INDUSTRIES, INC. EMPLOYEE OWNED Scientific Notation Numbers The display of numbers in floating point form. The number (mantissa) is always equal to or greater than one and less than 10, and the base is ...
Lecture 3
... In the real material, we expect the electrons to be moving randomly even in zero electric field due to thermal energy. However, they will have an average, or drift velocity along the field direction. ...
... In the real material, we expect the electrons to be moving randomly even in zero electric field due to thermal energy. However, they will have an average, or drift velocity along the field direction. ...
Physics (Sample Paper 2)
... A pot of very cold water (0 C) is placed on a stove with the burner adjusted for maximum heat. It is found that the water just begins to boil after 3.0 min. How much longer will it take the water to completely boil away? A 1.6 min B 3.6 min C 16 min D 18 min E 19 min ...
... A pot of very cold water (0 C) is placed on a stove with the burner adjusted for maximum heat. It is found that the water just begins to boil after 3.0 min. How much longer will it take the water to completely boil away? A 1.6 min B 3.6 min C 16 min D 18 min E 19 min ...
Syllabus - Course ON-LINE
... enable them to be available to take the final exam on the scheduled date (For example, please ensure that plane tickets purchased by or for you are for flights after, not before or on the day of the final.). Do not bring your cellular phones and pocket calculators to the exam rooms. ...
... enable them to be available to take the final exam on the scheduled date (For example, please ensure that plane tickets purchased by or for you are for flights after, not before or on the day of the final.). Do not bring your cellular phones and pocket calculators to the exam rooms. ...
Electric charge
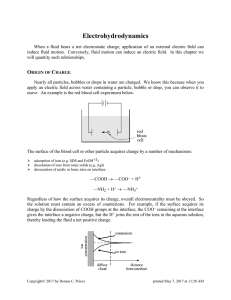
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Positively charged substances are repelled from other positively charged substances, but attracted to negatively charged substances; negatively charged substances are repelled from negative and attracted to positive. An object is negatively charged if it has an excess of electrons, and is otherwise positively charged or uncharged. The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), although in electrical engineering it is also common to use the ampere-hour (Ah), and in chemistry it is common to use the elementary charge (e) as a unit. The symbol Q is often used to denote charge. The early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still very accurate if quantum effects do not need to be considered.The electric charge is a fundamental conserved property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interaction. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. The interaction between a moving charge and an electromagnetic field is the source of the electromagnetic force, which is one of the four fundamental forces (See also: magnetic field).Twentieth-century experiments demonstrated that electric charge is quantized; that is, it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, approximately equal to 6981160200000000000♠1.602×10−19 coulombs (except for particles called quarks, which have charges that are integer multiples of e/3). The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e. The study of charged particles, and how their interactions are mediated by photons, is called quantum electrodynamics.