Chapter_001 (1)
... • Homeostasis: The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment in response to a changing environment • Homeostatic mechanisms help maintain homeostasis. • Homeostatic imbalance is associated with various disorders. ...
... • Homeostasis: The body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment in response to a changing environment • Homeostatic mechanisms help maintain homeostasis. • Homeostatic imbalance is associated with various disorders. ...
Animal classification
... Though all members of Animalia are multicellular, all of them do not exhibit the same pattern of organisation of cells. For example, in sponges, the cells are arranged as loose cell aggregates, i.e., they exhibit cellular level of organisation. Some division of labour (activities) occur among the ce ...
... Though all members of Animalia are multicellular, all of them do not exhibit the same pattern of organisation of cells. For example, in sponges, the cells are arranged as loose cell aggregates, i.e., they exhibit cellular level of organisation. Some division of labour (activities) occur among the ce ...
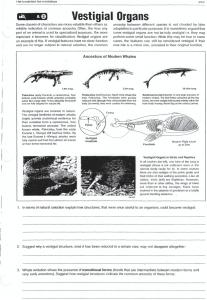
Vestigial Organs
... In all snakes (far left), one lobe of the lung is vestigial (there is not sufficient room in the narrow body cavity for it). In some snakes there are also vestiges of the pelvic girdle and hind limbs of their walking ancestors. Like all ratites, kiwis (left) are flightless. However, more than in oth ...
... In all snakes (far left), one lobe of the lung is vestigial (there is not sufficient room in the narrow body cavity for it). In some snakes there are also vestiges of the pelvic girdle and hind limbs of their walking ancestors. Like all ratites, kiwis (left) are flightless. However, more than in oth ...
Regions of Body
... III. The Chemical Composition and Physical Properties of Bone Living bones are plastic organs with organic and inorganic components. The organic material gives the bones resilience and toughness; the inorganic salts give them hardness and rigidity. The physical properties of the bones depend upon t ...
... III. The Chemical Composition and Physical Properties of Bone Living bones are plastic organs with organic and inorganic components. The organic material gives the bones resilience and toughness; the inorganic salts give them hardness and rigidity. The physical properties of the bones depend upon t ...
Cnidarian Observations
... 2. Hydras have a variety of reproductive structures, both sexual (spermaries, slightly pointed bumps, eggs or ovaries, broad low mounds, or embryos, like attached balls) and asexual (buds, like miniature Hydras attached to the body). If your hydra has these structures, (Q2) describe them on your WS. ...
... 2. Hydras have a variety of reproductive structures, both sexual (spermaries, slightly pointed bumps, eggs or ovaries, broad low mounds, or embryos, like attached balls) and asexual (buds, like miniature Hydras attached to the body). If your hydra has these structures, (Q2) describe them on your WS. ...
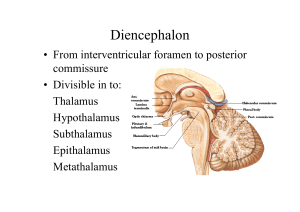
Diencephalon
... • Receives fibres from stria medullares, habenular nuclei & post. Com. • Inhibits gonadal function. • After 16 yrs., calcerous bodies present which are visible in skull x-rays. • Identification & position of pineal gland in skull films. ...
... • Receives fibres from stria medullares, habenular nuclei & post. Com. • Inhibits gonadal function. • After 16 yrs., calcerous bodies present which are visible in skull x-rays. • Identification & position of pineal gland in skull films. ...
Intro to Forensics and Types of Evidence
... pathologist and is appointed by the governing body of the area. There are 400 forensic pathologists throughout the U.S. § A coroner is an elected official who usually has no special medical training. In four states, the coroner is a medical doctor. ...
... pathologist and is appointed by the governing body of the area. There are 400 forensic pathologists throughout the U.S. § A coroner is an elected official who usually has no special medical training. In four states, the coroner is a medical doctor. ...
ANNELID LAB Phylum Annelida Class Oligochaeta 1. Lumbricus
... segments and formed on the plan of a tubular jacket of muscle surrounding a fluid-filled coelom. Although lacking a rigid internal skeleton. annelids can use the hydrostatic pressure of coelomic fruit, acted upon by the muscular body wall, as a "fluid skeleton," aiding in extension and flexing of th ...
... segments and formed on the plan of a tubular jacket of muscle surrounding a fluid-filled coelom. Although lacking a rigid internal skeleton. annelids can use the hydrostatic pressure of coelomic fruit, acted upon by the muscular body wall, as a "fluid skeleton," aiding in extension and flexing of th ...
forensic science chapter 1 notes
... < The word forensics means to verbally debate in public. < Forensic science is the application of science to matters of law. It applies the knowledge and technology of science for the definition and enforcement of such laws. < Each year science merges more closely with civil and criminal law as gove ...
... < The word forensics means to verbally debate in public. < Forensic science is the application of science to matters of law. It applies the knowledge and technology of science for the definition and enforcement of such laws. < Each year science merges more closely with civil and criminal law as gove ...
1 CLASS 1X BIOLOGY PLANT TISSUES Definition of tissue Tissues
... 1. The connective tissue is concerned with connecting the parts of the body. As such it can connect bones to each other, muscles to bones, bind tissues and give support to the various parts of the body by forming a packing around organs so that they do not get displaced by body movements. 2. Fluid ...
... 1. The connective tissue is concerned with connecting the parts of the body. As such it can connect bones to each other, muscles to bones, bind tissues and give support to the various parts of the body by forming a packing around organs so that they do not get displaced by body movements. 2. Fluid ...
The Female Reproductive Cycle
... cervical ca risk factors: frequent cervical inflammation HPV starting sex activity @ early age multiple pregnancies/early 1st pregnancy unprotected intercourse smoking multiple sex partners ...
... cervical ca risk factors: frequent cervical inflammation HPV starting sex activity @ early age multiple pregnancies/early 1st pregnancy unprotected intercourse smoking multiple sex partners ...
Checklist for Breast Examination
... f)Examination of the floor of the mouth : -Asked the patient to open the mouth and to put the tip of the tongue on the roof of the mouth and to bend the head slightly backwards. -Inspected the floor of the mouth and the undersurface of the tongue -Did bimanual palpation for any visible swelling g)Ex ...
... f)Examination of the floor of the mouth : -Asked the patient to open the mouth and to put the tip of the tongue on the roof of the mouth and to bend the head slightly backwards. -Inspected the floor of the mouth and the undersurface of the tongue -Did bimanual palpation for any visible swelling g)Ex ...
Chapter 17
... 19. The evolution of motile adults in primitive chordates could have resulted from __________ (which is the development of sexual maturity in the larval body form). A) protandry B) paedomorphosis C) parthenogenesis D) viviparity E) hermaphroditism 20. Terrestrial vertebrates made their appearance ap ...
... 19. The evolution of motile adults in primitive chordates could have resulted from __________ (which is the development of sexual maturity in the larval body form). A) protandry B) paedomorphosis C) parthenogenesis D) viviparity E) hermaphroditism 20. Terrestrial vertebrates made their appearance ap ...
Venous Dilatation Seen on Routine Mammography
... include the following: the internal thoracic-superior-inferior epigastric veins on the left; the lateral thoracicsuperficial epigastric veins on the right; the anterior and posterior intercostal veins; the azygos-accessory hemiazygos-hemiazygos veins; the jugular veins; the vertebral plexus; and th ...
... include the following: the internal thoracic-superior-inferior epigastric veins on the left; the lateral thoracicsuperficial epigastric veins on the right; the anterior and posterior intercostal veins; the azygos-accessory hemiazygos-hemiazygos veins; the jugular veins; the vertebral plexus; and th ...
Tissue level - Cloudfront.net
... Planes - imaginary flat surfaces that pass through the body Sagittal plane - a vertical plane that divides the body or organ into left and right parts Midsagittal (median) plane - divides the body or organ into equal left and right parts Frontal plane - divides the body or organ into front and back ...
... Planes - imaginary flat surfaces that pass through the body Sagittal plane - a vertical plane that divides the body or organ into left and right parts Midsagittal (median) plane - divides the body or organ into equal left and right parts Frontal plane - divides the body or organ into front and back ...
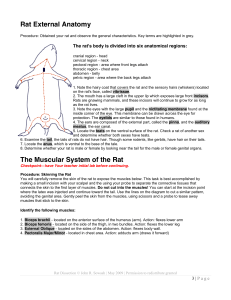
Rat External Anatomy The Muscular System of the Rat
... connects the skin to the first layer of muscles. Do not cut into the muscles! You can start at the incision point where the latex was injected and continue toward the tail. Use the lines on the diagram to cut a similar pattern, avoiding the genital area. Gently peel the skin from the muscles, using ...
... connects the skin to the first layer of muscles. Do not cut into the muscles! You can start at the incision point where the latex was injected and continue toward the tail. Use the lines on the diagram to cut a similar pattern, avoiding the genital area. Gently peel the skin from the muscles, using ...
Earthworm Dissection
... Examine your earthworm and determine the dorsal and ventral sides. Locate the two openings on the ventral surface of the earthworm. The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts. The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal ...
... Examine your earthworm and determine the dorsal and ventral sides. Locate the two openings on the ventral surface of the earthworm. The openings toward the anterior of the worm are the sperm ducts. The openings near the clitellum are the genital setae. Locate the dark line that runs down the dorsal ...
File
... deduced from a well-recognized scientific principle or discovery, the thing from which the deduction is made must be sufficiently established to have gained general acceptance in a particular field in which it belongs. ...
... deduced from a well-recognized scientific principle or discovery, the thing from which the deduction is made must be sufficiently established to have gained general acceptance in a particular field in which it belongs. ...
body contour program
... Cellulite can be described as a condition of uneven deposits of fat, water, and wastes that have become trapped in connective tissues of the body, just below the skin’s surface. Cellulite occurs primarily in the hips, knees, upper thighs, abdomen, buttocks and upper arms. Studies of cellulite found ...
... Cellulite can be described as a condition of uneven deposits of fat, water, and wastes that have become trapped in connective tissues of the body, just below the skin’s surface. Cellulite occurs primarily in the hips, knees, upper thighs, abdomen, buttocks and upper arms. Studies of cellulite found ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.