anatomical terms and terminoogy
... assumption that the person is standing erect, and the parts of the body are described in relation to some imaginary planes. ...
... assumption that the person is standing erect, and the parts of the body are described in relation to some imaginary planes. ...
1 NOTES: Respiratory System, Chapter 22 and Digestive System
... • Contain open pores that • Connect adjacent alveoli • Allow air pressure throughout the lung to be equalized • House alveolar macrophages that keep alveolar surfaces sterile 47. Fig. 22.9 c pg. 816 48 Lungs • Occupy all of the thoracic cavity except the mediastinum • Root: site of vascular and bron ...
... • Contain open pores that • Connect adjacent alveoli • Allow air pressure throughout the lung to be equalized • House alveolar macrophages that keep alveolar surfaces sterile 47. Fig. 22.9 c pg. 816 48 Lungs • Occupy all of the thoracic cavity except the mediastinum • Root: site of vascular and bron ...
Cnidaria
... • Single Body Cavity diploblastic (two membranes: ectoderm/endoderm) used for digestion and respiration ...
... • Single Body Cavity diploblastic (two membranes: ectoderm/endoderm) used for digestion and respiration ...
Position in Animal Kingdom
... Both phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora make up the radiate animals. Biradial symmetry is radial symmetry limited to two planes that create mirror images. Other eumetazoans have bilateral symmetry or their radial symmetry is derived from a bilateral ancestor. Neither Cnidaria nor Ctenophora have ...
... Both phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora make up the radiate animals. Biradial symmetry is radial symmetry limited to two planes that create mirror images. Other eumetazoans have bilateral symmetry or their radial symmetry is derived from a bilateral ancestor. Neither Cnidaria nor Ctenophora have ...
Orientating ourselves
... is tipping the pelvis backwards, or posterior (see table below). The opposite, rolling the pelvis out to increase the space between the wall and the lower back. This position, very commonly seen in dancers, is called anterior pelvis (tipped forwards). ...
... is tipping the pelvis backwards, or posterior (see table below). The opposite, rolling the pelvis out to increase the space between the wall and the lower back. This position, very commonly seen in dancers, is called anterior pelvis (tipped forwards). ...
Workshop: The Evolution of Animalia
... gonocoel and haemocoel (and open circulatory system) convergent, due to common ancestry, or due simply to similar action of homeotic genes during development? The answer is not yet known. When morphological/ontogenetic data and molecular data suggest conflicting hypotheses of evolutionary relationsh ...
... gonocoel and haemocoel (and open circulatory system) convergent, due to common ancestry, or due simply to similar action of homeotic genes during development? The answer is not yet known. When morphological/ontogenetic data and molecular data suggest conflicting hypotheses of evolutionary relationsh ...
study guide unit 3
... What is the foramen ovale called in adults? Fossa ovalis What is the connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta? Ductus arteriosus What is the name for the venous vessel leading to the liver? Hepatic portal vein (not hepatic vein!) A portal system is a ________ system within the ________s ...
... What is the foramen ovale called in adults? Fossa ovalis What is the connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta? Ductus arteriosus What is the name for the venous vessel leading to the liver? Hepatic portal vein (not hepatic vein!) A portal system is a ________ system within the ________s ...
Block Dissection
... be opened and the mucosal surface inspected before it is removed by dissecting along a plane between it and the bladder or uterus anteriorly. It may be separated first and then the mucosa inspected later after it is opened. In males, the peritoneum here is now lifted to expose the seminal vesicles. I ...
... be opened and the mucosal surface inspected before it is removed by dissecting along a plane between it and the bladder or uterus anteriorly. It may be separated first and then the mucosa inspected later after it is opened. In males, the peritoneum here is now lifted to expose the seminal vesicles. I ...
Axial Skeleton (cont.)
... – Mid and largest portion, formed by 4 bones that fuse after puberty. – Side notches articulate w/ 2nd to 7th ribs ...
... – Mid and largest portion, formed by 4 bones that fuse after puberty. – Side notches articulate w/ 2nd to 7th ribs ...
Human Anatomy - Fisiokinesiterapia
... pectoral girdle consists of bones that hold the upper limbs in place pelvic girdle consists of bones that hold the lower limbs in place ...
... pectoral girdle consists of bones that hold the upper limbs in place pelvic girdle consists of bones that hold the lower limbs in place ...
Lower Respiratory Tract Anatomy - Scottish Universities Medical
... of several lymph ducts, known as the cisterna chyli, which drains the abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs. The thoracic duct enters the thorax posterior to the aorta through the diaphragm, and traverses superiorly through the posterior mediastinum to the right of the midline. It then ...
... of several lymph ducts, known as the cisterna chyli, which drains the abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs. The thoracic duct enters the thorax posterior to the aorta through the diaphragm, and traverses superiorly through the posterior mediastinum to the right of the midline. It then ...
Hieronymus Bosch Madman or Medical Analyst
... Collects and preserves physical evidence that will later be processed at the crime lab. Many officers also being train in the proper collection of evidence. ...
... Collects and preserves physical evidence that will later be processed at the crime lab. Many officers also being train in the proper collection of evidence. ...
Physical Evidence
... • Physical evidence is any material either in gross or trace quantities that can establish through scientific examination and analysis that a crime has been committed. • Examination of physical evidence conducted for identification or comparison purposes • Identification is to determine the physical ...
... • Physical evidence is any material either in gross or trace quantities that can establish through scientific examination and analysis that a crime has been committed. • Examination of physical evidence conducted for identification or comparison purposes • Identification is to determine the physical ...
Bones of the Axial Skeleton Notes
... Coccyx- tailbone- 4 (or for some 3-5) vert fused together, articulates superiorly with sacrum nearly useless- sometimes babies are born with it unusually long, doc snips Intervertebral discs- are cushion-like pads between vertebral bodies- to absorb shock and allow spine to flex and extend and b ...
... Coccyx- tailbone- 4 (or for some 3-5) vert fused together, articulates superiorly with sacrum nearly useless- sometimes babies are born with it unusually long, doc snips Intervertebral discs- are cushion-like pads between vertebral bodies- to absorb shock and allow spine to flex and extend and b ...
Biological Psychology
... You are about to scrape away part of the medial face of one of your brain halves. Choose your half wisely. If your cut is off center, be certain that the structures we are interested in are still in the half you choose to scrape, they don't lie far from the midline. The most caudal part of the forni ...
... You are about to scrape away part of the medial face of one of your brain halves. Choose your half wisely. If your cut is off center, be certain that the structures we are interested in are still in the half you choose to scrape, they don't lie far from the midline. The most caudal part of the forni ...
THALAMUS
... Forms the upper part of lateral wall of 3rd ventricle interthalamic mass (adhesion) ...
... Forms the upper part of lateral wall of 3rd ventricle interthalamic mass (adhesion) ...
A Litigation Primer On The Respiratory System
... quickly if breathing stops. Respiratory System, Chapter 7, Advanced Anatomy and Physiology for ICD10-CM/PCS, Contexo/Medio, 2010. Working in tandem with the circulatory system, this gaseous exchange occurs when air enters the body through the nose or mouth and travels down the trachea. Air then en ...
... quickly if breathing stops. Respiratory System, Chapter 7, Advanced Anatomy and Physiology for ICD10-CM/PCS, Contexo/Medio, 2010. Working in tandem with the circulatory system, this gaseous exchange occurs when air enters the body through the nose or mouth and travels down the trachea. Air then en ...
ABFO Model of Curricular Topics for Forensic Odontology I
... vary and therefore so will the amount of time and weight that is afforded to this subject. ...
... vary and therefore so will the amount of time and weight that is afforded to this subject. ...
RE-ORDERED New CHAPTER 1 FOR CD.WPD
... Anatomists have special terms for discussing where things are positioned in the body. These terms enable one to describe unequivocally the location of lesion, or where to place a stethoscope, or where to feel for a tumor in a patient whether that person is standing, sitting, lying, or upside down. T ...
... Anatomists have special terms for discussing where things are positioned in the body. These terms enable one to describe unequivocally the location of lesion, or where to place a stethoscope, or where to feel for a tumor in a patient whether that person is standing, sitting, lying, or upside down. T ...
Axial - gaskinsanatomy
... What are the names of the 5 groups of vertebrae and how many are in each group? Cervical ...
... What are the names of the 5 groups of vertebrae and how many are in each group? Cervical ...
Unit 2 Study Outline
... Establishes the judge as the “gatekeeper” where the judge decides on whether or not evidence is admissible in court. In Daubert, the Court stated that evidence based on innovative or unusual scientific knowledge may be admitted only after it has been established that the evidence is reliable and sci ...
... Establishes the judge as the “gatekeeper” where the judge decides on whether or not evidence is admissible in court. In Daubert, the Court stated that evidence based on innovative or unusual scientific knowledge may be admitted only after it has been established that the evidence is reliable and sci ...
The Skeletal System
... bizarre means of moving about. Hominids after Ardi all walked upright as we do, but Ardi’s feet, pelvis, legs and hands suggest she was a biped on the ground but a quadruped when moving about the trees. All previously known hominids—members of our ancestral lineage—walked upright on two legs, like ...
... bizarre means of moving about. Hominids after Ardi all walked upright as we do, but Ardi’s feet, pelvis, legs and hands suggest she was a biped on the ground but a quadruped when moving about the trees. All previously known hominids—members of our ancestral lineage—walked upright on two legs, like ...
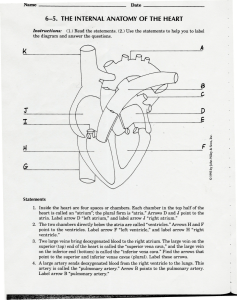
6-5. THE INTERNAL`ANATOMYOF THE HEART
... veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blood leaving the left atrium flows into the left ventricle. When it closes, it prevent ...
... veins are called "pulmonary veins." Find the arrow that points to the pulmonary veins. Label that arrow "pulmonary veins." 7. The bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle. When it opens, blood leaving the left atrium flows into the left ventricle. When it closes, it prevent ...
ANIMAL BIOLOGY (1604) LABORATORY Week of
... • Body perforated by numerous pores for water flow Scypha: longitudinal and cross-section slides (Figs. 5.1, 5.2) Identify the following structures: • Apopyles • Canals • Choanocytes ...
... • Body perforated by numerous pores for water flow Scypha: longitudinal and cross-section slides (Figs. 5.1, 5.2) Identify the following structures: • Apopyles • Canals • Choanocytes ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.