15-Thoracic Wall
... Joined to Brachial plexus, by a branch that is equivalent to lateral cutaenous branch. • 2nd Intercostal nerve: Joined to the medial cutaenous nerve of the arm, by a branch called Intercostobrachial nerve ( corresponds to lateral cutaenous branch) In Angina pectoris & myocardial infarction pain refe ...
... Joined to Brachial plexus, by a branch that is equivalent to lateral cutaenous branch. • 2nd Intercostal nerve: Joined to the medial cutaenous nerve of the arm, by a branch called Intercostobrachial nerve ( corresponds to lateral cutaenous branch) In Angina pectoris & myocardial infarction pain refe ...
Case Report Internal Occipital Crest Misalignment with Internal
... The posterior cranial fossa is posteriorly enclosed by the occipital bone. Internal occipital crest and internal occipital protuberance are prominent anatomical landmarks of the floor of the midsagittal plane of posterior cranial cavity. The internal occipital protuberance is identified as an elevat ...
... The posterior cranial fossa is posteriorly enclosed by the occipital bone. Internal occipital crest and internal occipital protuberance are prominent anatomical landmarks of the floor of the midsagittal plane of posterior cranial cavity. The internal occipital protuberance is identified as an elevat ...
CARCINOMA OF THE RECTUM
... Carcinoma rectum can occur in early life, though the common age is above 55 years. Early cases are free from symptoms, so patients do not come for advice for more than six months. • 1.Bleeding Bleeding is often slight and occurs at end of defaecation, resembling haemorrhoids. Haemorrhoids can coe ...
... Carcinoma rectum can occur in early life, though the common age is above 55 years. Early cases are free from symptoms, so patients do not come for advice for more than six months. • 1.Bleeding Bleeding is often slight and occurs at end of defaecation, resembling haemorrhoids. Haemorrhoids can coe ...
TRIFURCATION OF POSTERIOR DIVISION OF INTERNAL ILIAC
... CASE REPORT DISCUSSION: The first attempt made by Jastschinski 1891[4] in Polish subjects to classify the variations in the origin of parietal branches into three categories as a) large caliber vessels (Superior Gluteal, Inferior Gluteal & Internal Pudendal arteries) b) Medium caliber vessels (Obtu ...
... CASE REPORT DISCUSSION: The first attempt made by Jastschinski 1891[4] in Polish subjects to classify the variations in the origin of parietal branches into three categories as a) large caliber vessels (Superior Gluteal, Inferior Gluteal & Internal Pudendal arteries) b) Medium caliber vessels (Obtu ...
anterior abdominal wall and inguinal area
... (2) lower free margin of the posterior lamella is called the arcuate line or linea semicircularis at the level of L4 4. inferior part a. below the level of L4 there is only an anterior lamella that consists of the aponeuroses of all three abdominal muscles b. above the pubic bone, the aponeuroses in ...
... (2) lower free margin of the posterior lamella is called the arcuate line or linea semicircularis at the level of L4 4. inferior part a. below the level of L4 there is only an anterior lamella that consists of the aponeuroses of all three abdominal muscles b. above the pubic bone, the aponeuroses in ...
PDF file - Via Medica Journals
... urinary bladder function, pelvic organs atrophy and degeneration of the acetabular bone remains insufficient. ...
... urinary bladder function, pelvic organs atrophy and degeneration of the acetabular bone remains insufficient. ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Female Pelvis - Figure B
... of the surgeon, “spaces” are empty [45]. They are only filled with loose connective tissue and neither contain large vessels nor nerves. Some years ago, we already proposed dropping the term “space” and speaking of compartments instead, taking into account that a compartment may be filled by different ...
... of the surgeon, “spaces” are empty [45]. They are only filled with loose connective tissue and neither contain large vessels nor nerves. Some years ago, we already proposed dropping the term “space” and speaking of compartments instead, taking into account that a compartment may be filled by different ...
Accuracy of the physical examination in evaluating pleural effusion
... Since other conditions such as consolidation of the lung and atelectasis can also be associated with dullness to percussion, some authors advocate percussion in the lateral supine position to detect a shift in the dullness that would indicate movement of fluid in the chest.25 The sensitivity of comp ...
... Since other conditions such as consolidation of the lung and atelectasis can also be associated with dullness to percussion, some authors advocate percussion in the lateral supine position to detect a shift in the dullness that would indicate movement of fluid in the chest.25 The sensitivity of comp ...
pdf
... Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are pro ...
... Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are pro ...
Blunt Force Traumatic Injuries of the Chest
... the mediastinum. This is primarily due to the fact the most common cause of a widen mediastinum is aortic rupture. We will also discuss the mechanisms of chest injury. II. Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Thorax A. Overview: The thorax forms the upper part of the trunk, being separated from the lower ...
... the mediastinum. This is primarily due to the fact the most common cause of a widen mediastinum is aortic rupture. We will also discuss the mechanisms of chest injury. II. Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Thorax A. Overview: The thorax forms the upper part of the trunk, being separated from the lower ...
Vessels of Lower Abdomen, Thigh, and Leg
... Follow the Descending Abdominal Aorta downward (inferiorly) to where it splits forming an upside-down “Y”. Each arm of the “Y” is the Common Iliac Artery. However, not all of each arm is the Common Iliac. About 1/3 away from the split, a vessel comes off and goes inferior. This vessel is the Interna ...
... Follow the Descending Abdominal Aorta downward (inferiorly) to where it splits forming an upside-down “Y”. Each arm of the “Y” is the Common Iliac Artery. However, not all of each arm is the Common Iliac. About 1/3 away from the split, a vessel comes off and goes inferior. This vessel is the Interna ...
Dissection of Anterior Abdominal Wall
... symphysis, cutting around the umbilicus. Then incise the skin 1 inch above the pubis symphysis laterally over to and a little above the iliac crest to the midaxillary line on both sides. Reflect the skin from the midline anteriorlly to the midaxillary line, leaving the superficial fascia on the ante ...
... symphysis, cutting around the umbilicus. Then incise the skin 1 inch above the pubis symphysis laterally over to and a little above the iliac crest to the midaxillary line on both sides. Reflect the skin from the midline anteriorlly to the midaxillary line, leaving the superficial fascia on the ante ...
Chapt 1 pgs 1-17
... the success of TV shows such as CSI and NCIS, forensic science has been thrust into the mainstream media and entered into the homes of America’s youth. Also inundating our culture is the use of forensic science to solve real-life criminal investigations. Shows such as A&E’s Forensic Files and Tru Cr ...
... the success of TV shows such as CSI and NCIS, forensic science has been thrust into the mainstream media and entered into the homes of America’s youth. Also inundating our culture is the use of forensic science to solve real-life criminal investigations. Shows such as A&E’s Forensic Files and Tru Cr ...
Dorsal hand coverage
... fasciocutaneous flaps. The lateral arm flap [19,20,25-27] is sometimes limited by its short pedicle and the scapular flap [20] requires a change of position during the operation, hindering a two-team approach. Compared to these flaps, the anterolateral thigh flap has numerous advantages: simultaneo ...
... fasciocutaneous flaps. The lateral arm flap [19,20,25-27] is sometimes limited by its short pedicle and the scapular flap [20] requires a change of position during the operation, hindering a two-team approach. Compared to these flaps, the anterolateral thigh flap has numerous advantages: simultaneo ...
1. The boundaries of the perineum include all the following except
... muscles. This is found only in females; the male homolog for this structure is the central tendinous point. Frenulum is a word that refers to a small fold, and there are two in the female perineum, so this isn't even specific enough to be a good answer. The frenulum of the clitoris is a structure ly ...
... muscles. This is found only in females; the male homolog for this structure is the central tendinous point. Frenulum is a word that refers to a small fold, and there are two in the female perineum, so this isn't even specific enough to be a good answer. The frenulum of the clitoris is a structure ly ...
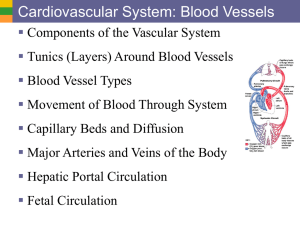
4 BloodVessels
... A simple “tube heart” develops in the embryo and pumps by the fourth week The heart becomes a four-chambered organ by the end of seven weeks Few structural changes occur after the seventh week Congential heart defects sometimes arise ...
... A simple “tube heart” develops in the embryo and pumps by the fourth week The heart becomes a four-chambered organ by the end of seven weeks Few structural changes occur after the seventh week Congential heart defects sometimes arise ...
Chapter 5 The Human Body
... – Superior and inferior – Superficial and deep – Ventral and dorsal – Palmar and plantar – Apex ...
... – Superior and inferior – Superficial and deep – Ventral and dorsal – Palmar and plantar – Apex ...
(MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination
... It lies in retrocaecal recess in 65% of subjects It has a nerve supply from the 10th thoracic spinal segment The Appendicular artery enters the mesoappendix by crossing infront of terminal ileum The Appendicular vein drains into the iliocolic vein The Appendicular lymph nodes drains finally in the s ...
... It lies in retrocaecal recess in 65% of subjects It has a nerve supply from the 10th thoracic spinal segment The Appendicular artery enters the mesoappendix by crossing infront of terminal ileum The Appendicular vein drains into the iliocolic vein The Appendicular lymph nodes drains finally in the s ...
triangles of the neck
... In bilateral incomplete paralysis, the cords come together, stridor is intense and tracheotomy may become essential. WHY loss of voice must always be regarded as an warning symptom requiring careful investigation. Thyroid malignancy or malignant lymph nodes in neck may damaged the either RLN. The le ...
... In bilateral incomplete paralysis, the cords come together, stridor is intense and tracheotomy may become essential. WHY loss of voice must always be regarded as an warning symptom requiring careful investigation. Thyroid malignancy or malignant lymph nodes in neck may damaged the either RLN. The le ...
major arteries of the head and neck
... The neck is supplied by arteries other than the carotids. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. From this trunk, several vessels arise, which go on to supply the neck. The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery. It supplies the t ...
... The neck is supplied by arteries other than the carotids. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. From this trunk, several vessels arise, which go on to supply the neck. The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery. It supplies the t ...
Document
... part of duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, vermiform appendix, transverse and sigmoid colons, spleen and ovary ...
... part of duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, vermiform appendix, transverse and sigmoid colons, spleen and ovary ...
Pelvic Viscera
... The course of the ureters is much the same as for males. In females, the ureters travels medial to the origin of the uterine artery, travelling to the ischial spine – where the uterine vessels pass superior to ureters. They then travel lateral to the fornix of the vagina entering the bladder inferom ...
... The course of the ureters is much the same as for males. In females, the ureters travels medial to the origin of the uterine artery, travelling to the ischial spine – where the uterine vessels pass superior to ureters. They then travel lateral to the fornix of the vagina entering the bladder inferom ...
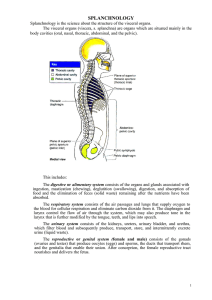
2. Splanchnology
... The parodontium are composed of periodontium, alveola dentis, gums, cementum, which surrounding the teeth. The periodontium consists of the supporting soft and hard dental tissues between and including portions of the tooth and the alveolar bone. The periodontium serves to support the tooth in its r ...
... The parodontium are composed of periodontium, alveola dentis, gums, cementum, which surrounding the teeth. The periodontium consists of the supporting soft and hard dental tissues between and including portions of the tooth and the alveolar bone. The periodontium serves to support the tooth in its r ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.