MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF INTERNAL ILIAC ARTERY
... pedicled on the ilio-lumbar artery, a branch of posterior division of internal iliac artery, is being used as a reliable bone flap. A severe and potentially lethal complication in pelvic injuries is arterial bleeding commonly involving the branches of internal iliac artery, namely, the lateral sacra ...
... pedicled on the ilio-lumbar artery, a branch of posterior division of internal iliac artery, is being used as a reliable bone flap. A severe and potentially lethal complication in pelvic injuries is arterial bleeding commonly involving the branches of internal iliac artery, namely, the lateral sacra ...
Veins 1 Head and Thoracic Veins
... 3. intercostal vein 3. inferior vena cava 5. superior vena cava Select and arrange the veins in the order blood passes through them going from the esophagus to the heart. ...
... 3. intercostal vein 3. inferior vena cava 5. superior vena cava Select and arrange the veins in the order blood passes through them going from the esophagus to the heart. ...
C- Spine Adult vs pediatric - Calgary Emergency Medicine
... infections in children (first is peritonsillar abscesses which account for up to 50% of the deep neck infections) ...
... infections in children (first is peritonsillar abscesses which account for up to 50% of the deep neck infections) ...
Blood supply of Head and neck
... Formed by the union of maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein. Leaving parotid gland divides into anterior branch and posterior branch. Anterior branch joins facial vein. Posterior branch joins posterior auricular vein to form ...
... Formed by the union of maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein. Leaving parotid gland divides into anterior branch and posterior branch. Anterior branch joins facial vein. Posterior branch joins posterior auricular vein to form ...
C- Spine Adult vs pediatric
... infections in children (first is peritonsillar abscesses which account for up to 50% of the deep neck infections) ...
... infections in children (first is peritonsillar abscesses which account for up to 50% of the deep neck infections) ...
Variant origin of thyrolingual trunk from left common carotid artery
... from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left arise from the aortic arch in the thoracic region. The cervical portion of common carotids resembles each other very closely. The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia. ...
... from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left arise from the aortic arch in the thoracic region. The cervical portion of common carotids resembles each other very closely. The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia. ...
Anatomy of the Abdomen and pelvis
... problems with the notes or if you notice any errors. I don't promise to respond to all emails but I'll do my best. For the Anatomy of The Abdomen and Pelvis notes I used a mixture of Gray's, Netter's and Clinically Orientated Anatomy. In addition some detail is taken from Instant Anatomy for android ...
... problems with the notes or if you notice any errors. I don't promise to respond to all emails but I'll do my best. For the Anatomy of The Abdomen and Pelvis notes I used a mixture of Gray's, Netter's and Clinically Orientated Anatomy. In addition some detail is taken from Instant Anatomy for android ...
Erdogan, Persistent left superior vena cava.qxp
... pacemaker implantation and for cardiac surgery. The PLSVC is often found during surgery or catheterization due to the low frequency of presence of some diagnostic signs on the conventional chest X-rays (11, 24, 28, 29). Some researchers have proposed some diagnostic features which include the wideni ...
... pacemaker implantation and for cardiac surgery. The PLSVC is often found during surgery or catheterization due to the low frequency of presence of some diagnostic signs on the conventional chest X-rays (11, 24, 28, 29). Some researchers have proposed some diagnostic features which include the wideni ...
Long Head of Biceps: More than a starting point?
... ¤ Ultrasound cannot visualise the anchor of the long head of biceps to the labrum..potentially missing pathology as it cannot be visualised.. ¤ Difficult to conclude on the quality of imaging devices used, and the experience level of clinicians. ...
... ¤ Ultrasound cannot visualise the anchor of the long head of biceps to the labrum..potentially missing pathology as it cannot be visualised.. ¤ Difficult to conclude on the quality of imaging devices used, and the experience level of clinicians. ...
Veins supplying Head and Neck
... Formed by the union of maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein. Leaving parotid gland divides into anterior branch and posterior branch. Anterior branch joins facial vein. Posterior branch joins posterior auricular vein to form ...
... Formed by the union of maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein. Leaving parotid gland divides into anterior branch and posterior branch. Anterior branch joins facial vein. Posterior branch joins posterior auricular vein to form ...
View PDF
... greater trochanter.16 These vessels have definitive anatomical landmarks without much variation, which makes them useful for designing flaps. The quadrilobed superior gluteal artery perforator flap was designed as follows. A superior gluteal artery perforator was located on one side of the sacrococc ...
... greater trochanter.16 These vessels have definitive anatomical landmarks without much variation, which makes them useful for designing flaps. The quadrilobed superior gluteal artery perforator flap was designed as follows. A superior gluteal artery perforator was located on one side of the sacrococc ...
vascular-technology-lecture-22-venous-gross
... superficial femoral vein) when passes through adductor hiatus in lower thigh ...
... superficial femoral vein) when passes through adductor hiatus in lower thigh ...
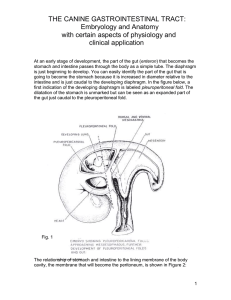
caninegastrointesttract
... Is there a difference between obstruction of the small intestine vs. obstruction of the large? Obstruction of the descending colon and rectum may not be detected for weeks; unless the owner checks the animal’s passage of stool or, being observant, notes the enlarging abdomen. Signs of obstruction o ...
... Is there a difference between obstruction of the small intestine vs. obstruction of the large? Obstruction of the descending colon and rectum may not be detected for weeks; unless the owner checks the animal’s passage of stool or, being observant, notes the enlarging abdomen. Signs of obstruction o ...
The peritoneal cavity
... inflammation of the peritoneum which is called as peritonitis. The infected fluid may tend to collect in the most dependent area of the peritoneal cavity in supine position, these areas are pelvis and the right subphrenic space. In such condition the patient complains of pain in the shoulder. Peri ...
... inflammation of the peritoneum which is called as peritonitis. The infected fluid may tend to collect in the most dependent area of the peritoneal cavity in supine position, these areas are pelvis and the right subphrenic space. In such condition the patient complains of pain in the shoulder. Peri ...
Soft Tissue Coverage in Abdominal Wall Reconstruction
... coverage, the next option is to consider a regional flap. Regional flaps are pedicled flaps based on a dominant axial blood supply that can be delivered into the abdominal wall to support tissue perfusion in the flap’s new location. Regional pedicled flaps are harvested from adjacent anatomic areas ...
... coverage, the next option is to consider a regional flap. Regional flaps are pedicled flaps based on a dominant axial blood supply that can be delivered into the abdominal wall to support tissue perfusion in the flap’s new location. Regional pedicled flaps are harvested from adjacent anatomic areas ...
Mediastinum
... 1- Esophagus (passes at the neck to thorax to the abdomen) 2- Thoracic aorta (from arch of aorta) 3- Thoracic duct (left lymphatic) starts at the abdomen and then it will go up. 4- Sympathetic trunks (extending from the base of the skull then on both sides of the vertebral column and end at the tip ...
... 1- Esophagus (passes at the neck to thorax to the abdomen) 2- Thoracic aorta (from arch of aorta) 3- Thoracic duct (left lymphatic) starts at the abdomen and then it will go up. 4- Sympathetic trunks (extending from the base of the skull then on both sides of the vertebral column and end at the tip ...
ARTERIES OF THE HEAD AND NECK
... v. Anastomoses of the facial artery are very numerous not only with the vessel of the opposite side but also with the internal carotid and in the neck with the lingual and ascending pharyngeal arteries. In the face, it anastomoses with branches of the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries. vi. ...
... v. Anastomoses of the facial artery are very numerous not only with the vessel of the opposite side but also with the internal carotid and in the neck with the lingual and ascending pharyngeal arteries. In the face, it anastomoses with branches of the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries. vi. ...
abberrant patterns of branching of external carotid artery
... Common carotid arteries (CCA) are the largest bilateral arteries of the head and neck. CCA of both sides divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at intervertebral disc level between the third and fourth cervical vertebrae into external and internal carotid arteries (Takenoshita, 1983).Ex ...
... Common carotid arteries (CCA) are the largest bilateral arteries of the head and neck. CCA of both sides divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at intervertebral disc level between the third and fourth cervical vertebrae into external and internal carotid arteries (Takenoshita, 1983).Ex ...
Module 2A
... because of the fruit of the poisonous tree doctrine. Exculpatory evidence can establish the innocence of a ...
... because of the fruit of the poisonous tree doctrine. Exculpatory evidence can establish the innocence of a ...
036.001.124
... If the palatal mucosa is very thick and covers the safety wire holes of the distractor, place the safety wires in the distractor before the distractor body is placed in the footplates. Distractor placement – The hard palate cleft or alveolar cleft is likely to open if the scar is disrupted by the di ...
... If the palatal mucosa is very thick and covers the safety wire holes of the distractor, place the safety wires in the distractor before the distractor body is placed in the footplates. Distractor placement – The hard palate cleft or alveolar cleft is likely to open if the scar is disrupted by the di ...
Fractures of the body of the talus in the sagittal plane
... S U M M A R Y Fractures of the body of the talus in the sagittal plane are very rare. The definition, however, is unclear. We therefore reviewed nine cases of this type of fracture in our series. The rate of occurrence was 4.6% of major talar fractures. Analysis of radiographs revealed a characteris ...
... S U M M A R Y Fractures of the body of the talus in the sagittal plane are very rare. The definition, however, is unclear. We therefore reviewed nine cases of this type of fracture in our series. The rate of occurrence was 4.6% of major talar fractures. Analysis of radiographs revealed a characteris ...
Anatomy Exam 3 Outline Lecture 16 – Pelvis and Perineum
... vi. Thin tunica albuginea (very thin) forms on surface of ovary to separate follicles from surface epithelium vii. Important to form this thin single cell layer around ovary because at some point these will have to mature and rupture through the surface; if there is a thick tunica albuginea, you wou ...
... vi. Thin tunica albuginea (very thin) forms on surface of ovary to separate follicles from surface epithelium vii. Important to form this thin single cell layer around ovary because at some point these will have to mature and rupture through the surface; if there is a thick tunica albuginea, you wou ...
Major arteries
... 5. Pulsations felt at the lower border of the mandible are in : A. Superficial temporal artery. B. Common carotid artery. C.Maxillary artery. D. Facial artery. 6. The internal iliac artery supplies: ...
... 5. Pulsations felt at the lower border of the mandible are in : A. Superficial temporal artery. B. Common carotid artery. C.Maxillary artery. D. Facial artery. 6. The internal iliac artery supplies: ...
Arteries of the Head and Neck
... • Common carotid artery: – The right artery arise from the brachiocephalic artery and the left from the arch of the aorta. – Runs upward and back and divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage into two terminal branches the external and internal arteries ...
... • Common carotid artery: – The right artery arise from the brachiocephalic artery and the left from the arch of the aorta. – Runs upward and back and divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage into two terminal branches the external and internal arteries ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.