Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... a. Accessory route for transmission of discrete signals from the motor cortex to the spinal cord ...
... a. Accessory route for transmission of discrete signals from the motor cortex to the spinal cord ...
Telencephalon/Cerebral Cortex Thelencephalon consists of
... cortico-spinal (pyramidal) tract, cortico-bulbar, cortico-pontine tract. Colleteral axons of these cells also connect to striatum and thalamus. Layer 6 – Heterogeneous cellular elements and is thus called polymorphic layer. These neurons contribute to corticothalamic tract. This layer blends into th ...
... cortico-spinal (pyramidal) tract, cortico-bulbar, cortico-pontine tract. Colleteral axons of these cells also connect to striatum and thalamus. Layer 6 – Heterogeneous cellular elements and is thus called polymorphic layer. These neurons contribute to corticothalamic tract. This layer blends into th ...
extra pyramidal system
... it originates from the red nucleus which is present in the tegmentum of mid brain. Then these cross over to the opposite side and descend through the pons, medulla oblongata to enter the lateral white column of spinal cord and it terminates onto the motor neurons in the ventral horn of spinal cord a ...
... it originates from the red nucleus which is present in the tegmentum of mid brain. Then these cross over to the opposite side and descend through the pons, medulla oblongata to enter the lateral white column of spinal cord and it terminates onto the motor neurons in the ventral horn of spinal cord a ...
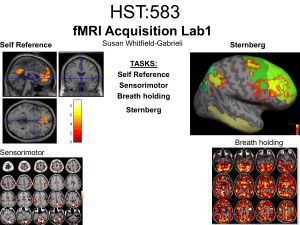
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
Lecture 2
... Interspecies Comparisons Figure H shows the macaque monkey visual areas morphed onto human cortex based on the placement of sulcal landmarks (Van Essen et al., 2001) Can we assume humans are just morphed monkeys? In some areas the human cortical surface area is slightly larger than in the macaque ( ...
... Interspecies Comparisons Figure H shows the macaque monkey visual areas morphed onto human cortex based on the placement of sulcal landmarks (Van Essen et al., 2001) Can we assume humans are just morphed monkeys? In some areas the human cortical surface area is slightly larger than in the macaque ( ...
Lecture 10
... cerebral cortex - (gray matter) surface, cell bodies cerebral tracts - (white matter) beneath, axons gyri/convolutions - ridges of cortex fissures - deep grooves/valleys between gyri sulci - shallow grooves/valleys between gyri longitudinal fissure - divide right/left hemispheres corpus callosum - t ...
... cerebral cortex - (gray matter) surface, cell bodies cerebral tracts - (white matter) beneath, axons gyri/convolutions - ridges of cortex fissures - deep grooves/valleys between gyri sulci - shallow grooves/valleys between gyri longitudinal fissure - divide right/left hemispheres corpus callosum - t ...
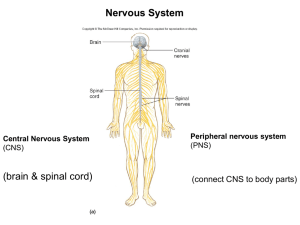
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... matter, composed of fiber tracts (bundles of nerve fibers), carrying impulses to and from the cortex • corpus callosum is a very large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres • the basal nuclei are made from gray matter and are located deep within the white matter • they help the motor corte ...
... matter, composed of fiber tracts (bundles of nerve fibers), carrying impulses to and from the cortex • corpus callosum is a very large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres • the basal nuclei are made from gray matter and are located deep within the white matter • they help the motor corte ...
GeneralOrganizationoftheNervousSystem(1)
... segment. Note that unlike the brain, where the cell bodies are on the surface, the spinal gray matter is in the center and the white matter consisting of axons is on the outside. ...
... segment. Note that unlike the brain, where the cell bodies are on the surface, the spinal gray matter is in the center and the white matter consisting of axons is on the outside. ...
Abbreviated 11-15
... P type = (also known as beta or midget ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting details in vision. M type = (also known as alpha or parasol ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting motion. nonM-nonP type =are a diverse group of cell types that make up the rema ...
... P type = (also known as beta or midget ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting details in vision. M type = (also known as alpha or parasol ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting motion. nonM-nonP type =are a diverse group of cell types that make up the rema ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... to the hand to patterns of activity that are necessary for activating the muscles and moving the limb. Slide 6. Some cells in M1 have a discharge that correlates with forces produced by arm muscles. In this experiment, a constant torque was applied to elbow and shoulder joints of the monkey’s arm. T ...
... to the hand to patterns of activity that are necessary for activating the muscles and moving the limb. Slide 6. Some cells in M1 have a discharge that correlates with forces produced by arm muscles. In this experiment, a constant torque was applied to elbow and shoulder joints of the monkey’s arm. T ...
Motor system - Brain Facts
... Many neurons are active in relation to movements in the posterior parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the s ...
... Many neurons are active in relation to movements in the posterior parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the s ...
BOX 30.8 THE ROLE OF THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS IN
... You are sitting astride your bicycle at an intersection and just about to press down on the pedal when all of a sudden a motorist runs the light. This requires the rapid cancellation of an initiated action. Recent studies suggest that rapid stopping of this kind is implemented by a “hyperdirect” pat ...
... You are sitting astride your bicycle at an intersection and just about to press down on the pedal when all of a sudden a motorist runs the light. This requires the rapid cancellation of an initiated action. Recent studies suggest that rapid stopping of this kind is implemented by a “hyperdirect” pat ...
UNIT XI
... • Excess neurons at birth • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later ...
... • Excess neurons at birth • Axons that do not connect or connect with wrong type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... motor neuron and muscle fibers it innervates (motor unit) Connection between an Alpha motor neuron and skeletal muscle occurs at the neuromuscular junction located at the middle of the muscle. This synapse allows nerve impulses to be transmitted so he muscle contracts and movement occurs. Alpha Moto ...
... motor neuron and muscle fibers it innervates (motor unit) Connection between an Alpha motor neuron and skeletal muscle occurs at the neuromuscular junction located at the middle of the muscle. This synapse allows nerve impulses to be transmitted so he muscle contracts and movement occurs. Alpha Moto ...
The Nervous System
... Mollusca: ranges from simple nervous system to relatively complex systems that rival those of mammals Arthropoda: cerebral ganglion (brain!); sense organs concentrated on head Echinodermata: decentralized nervous; no brain but have ganglia along radial nerves in some species; sensory neurons within ...
... Mollusca: ranges from simple nervous system to relatively complex systems that rival those of mammals Arthropoda: cerebral ganglion (brain!); sense organs concentrated on head Echinodermata: decentralized nervous; no brain but have ganglia along radial nerves in some species; sensory neurons within ...
Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortex
... The influence of M1 in generating muscle contractions has been studied using primarily two methods: stimulation and recording. We have already discussed the finding by Sherrington and Penfield that M1 required the least amount of stimulating current to generate muscular contractions. Asanuma and his ...
... The influence of M1 in generating muscle contractions has been studied using primarily two methods: stimulation and recording. We have already discussed the finding by Sherrington and Penfield that M1 required the least amount of stimulating current to generate muscular contractions. Asanuma and his ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
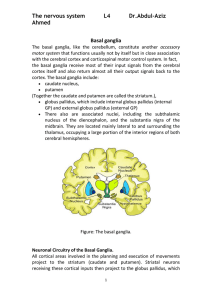
... putamen from sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by the cerebral cortex via this feedback loop. ...
... putamen from sensory, motor, and association areas of the cortex. • Processing and integration occurs w/i the nuclei and then info is sent from the globus pallidus to the motor cortex via the thalamus. • The basal nuclei alter motor commands issued by the cerebral cortex via this feedback loop. ...
control of movement by the CNS - motor neurons found in anterior
... premotor (area 6), motor (area 4), posterior parietal (areas 5 and 7) somatotopic organization... regional ‘concentric’ plan around distal foci (fingers, toes) - distal-axial gradient distal muscles tend to be deep in central sulcus while axial closer to premotor cortex - multiple representation sin ...
... premotor (area 6), motor (area 4), posterior parietal (areas 5 and 7) somatotopic organization... regional ‘concentric’ plan around distal foci (fingers, toes) - distal-axial gradient distal muscles tend to be deep in central sulcus while axial closer to premotor cortex - multiple representation sin ...
Slide 1
... mammals. Comparative studies of extant mammals reveal cortical areas that are widespread across mammalian clades, suggesting that they have been retained from early mammalian ancestors. A. Dorsal view of the brain with cortical areas indicated. B. Lateral view. C. View of cortex after it has been se ...
... mammals. Comparative studies of extant mammals reveal cortical areas that are widespread across mammalian clades, suggesting that they have been retained from early mammalian ancestors. A. Dorsal view of the brain with cortical areas indicated. B. Lateral view. C. View of cortex after it has been se ...
ppt file
... Specify world space constraints that one or more parts of the skeleton must achieve Solve for joint angles to achieve these Good for meeting world space constraints, but movement flow can be a problem Most skeletons are highly redundant, so problem is underconstrained ...
... Specify world space constraints that one or more parts of the skeleton must achieve Solve for joint angles to achieve these Good for meeting world space constraints, but movement flow can be a problem Most skeletons are highly redundant, so problem is underconstrained ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... Target location and hand position are computed by posterior parietal cortex cells in terms of vectors with respect to fixation point. These visual cues are represented with neurons that have receptive fields. Proprioceptive information from the arm, head, and eyes are used to estimate hand position ...
... Target location and hand position are computed by posterior parietal cortex cells in terms of vectors with respect to fixation point. These visual cues are represented with neurons that have receptive fields. Proprioceptive information from the arm, head, and eyes are used to estimate hand position ...
Motor cortex

Motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.Classically the motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the dorsal precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus.