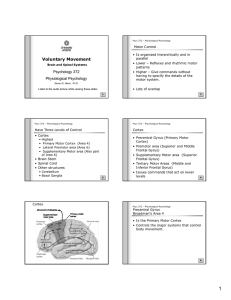
Motor systems
... corticospinal neurons active just before initiation of a movement; activity related to amount of force necessary to produce the movement; directionally-sensitive corticospinal neurons; higher-order motor cortex involved in calculating trajectories in space (probably in close communication with cereb ...
... corticospinal neurons active just before initiation of a movement; activity related to amount of force necessary to produce the movement; directionally-sensitive corticospinal neurons; higher-order motor cortex involved in calculating trajectories in space (probably in close communication with cereb ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Know the various cell types that are found in nervous tissue and their function • Identify and understand the function of the various parts of the central nervous system ...
... • Know the various cell types that are found in nervous tissue and their function • Identify and understand the function of the various parts of the central nervous system ...
Motor Systems - University of Sunderland
... Muscles • Muscles are springs and correct for errors. As for any spring, oscillation can be an issue, but the muscle controls it. The muscle thinks! • A muscle is made up of multiple muscle fibers—multinucleate cells in mammals that contain myosin and actin (elastic). These are excitable cells like ...
... Muscles • Muscles are springs and correct for errors. As for any spring, oscillation can be an issue, but the muscle controls it. The muscle thinks! • A muscle is made up of multiple muscle fibers—multinucleate cells in mammals that contain myosin and actin (elastic). These are excitable cells like ...
Our Ancient Laughing Brain
... When you try to tickle yourself, your cerebellum sends to your somatosensory cortex precise information on the position of the tickling target and therefore what sensation to expect. ...
... When you try to tickle yourself, your cerebellum sends to your somatosensory cortex precise information on the position of the tickling target and therefore what sensation to expect. ...
Lecture 5 Sensory and Motor Systems
... – Very little sensory information is used by the nervous system exactly as it is transduced. – High compression: many sensors, few neurons. – Preprocessing and feature extraction. – Allows the cortex to concentrate on recognition, planning and response. ...
... – Very little sensory information is used by the nervous system exactly as it is transduced. – High compression: many sensors, few neurons. – Preprocessing and feature extraction. – Allows the cortex to concentrate on recognition, planning and response. ...
primary motor cortex - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... muscles can do the same task) Sensorimotor programs may be stored in 2° motor cortex (SMC) Eg: You can sign your name with left or right hand. Signature is very similar and the SMC for preferred right hand is activated (even when left ...
... muscles can do the same task) Sensorimotor programs may be stored in 2° motor cortex (SMC) Eg: You can sign your name with left or right hand. Signature is very similar and the SMC for preferred right hand is activated (even when left ...
1 - U-System
... - Cortical areas project to other areas in same hemisphere (ipsilateral); to neighboring areas via short U-fibers that dip under one or two sulci; to faraway areas through longer association bundles (arcuate fasciculus is one that arcs above insula and interconnects anterior and posterior parts of a ...
... - Cortical areas project to other areas in same hemisphere (ipsilateral); to neighboring areas via short U-fibers that dip under one or two sulci; to faraway areas through longer association bundles (arcuate fasciculus is one that arcs above insula and interconnects anterior and posterior parts of a ...
Motor Systems - People Server at UNCW
... The premotor and supplementary motor ctx: “The sections” Stimulation= complex sequences of behavior (aimless behavior) ...
... The premotor and supplementary motor ctx: “The sections” Stimulation= complex sequences of behavior (aimless behavior) ...
Motor Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum
... B. Primary Motor Cortex (M1) 1. Located in precentral gyrus area of the frontal lobe 2. Somatatopically organized Note: primary motor cortex “map” is similar to primary sensory cortex “map” on the postcentral sulcus parietal cortex, except that cortical area on the motor cortex depends on precision ...
... B. Primary Motor Cortex (M1) 1. Located in precentral gyrus area of the frontal lobe 2. Somatatopically organized Note: primary motor cortex “map” is similar to primary sensory cortex “map” on the postcentral sulcus parietal cortex, except that cortical area on the motor cortex depends on precision ...
The Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy
... The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scaling movements or providing an ‘energy vigor’ term [9], 3) and as performing dimension reduction [1]. Recently, spiking neuron implementations of the WTA circuit model have b ...
... The basal ganglia has been characterized in several ways: 1) As a winner-take-all (WTA) circuit [5], 2) as responsible for scaling movements or providing an ‘energy vigor’ term [9], 3) and as performing dimension reduction [1]. Recently, spiking neuron implementations of the WTA circuit model have b ...
Chapter 3
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... • The cortex is much larger in mammals than in species that evolved earlier, such as fish and amphibians. • The cross section of the human brain shows how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
... • The cortex is much larger in mammals than in species that evolved earlier, such as fish and amphibians. • The cross section of the human brain shows how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
The Brain - Academic Computer Center
... Outlines the temporal lobe and separates it from the parietal and frontal lobes Regional Organization The Insula Lies deep to the temporal lobe and forms part of its floor Covered by portions of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes ...
... Outlines the temporal lobe and separates it from the parietal and frontal lobes Regional Organization The Insula Lies deep to the temporal lobe and forms part of its floor Covered by portions of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes ...
Ch. 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes
... • Three kinds of functional regions – Motor areas – voluntary movement – Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensations – Association areas – integrate different info for purposeful action ...
... • Three kinds of functional regions – Motor areas – voluntary movement – Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensations – Association areas – integrate different info for purposeful action ...
A1982NC82200001
... movement remain to be empirically resolved, the motor potentials provide a non-invasive index of cortical mechanisms involved in the initiation and control of human voluntary movement. Following the discovery of the scalp-recorded movement-related potentials in man, studies of single neurons in monk ...
... movement remain to be empirically resolved, the motor potentials provide a non-invasive index of cortical mechanisms involved in the initiation and control of human voluntary movement. Following the discovery of the scalp-recorded movement-related potentials in man, studies of single neurons in monk ...
The Brain The brain is responsible for everything we think, feel and
... Parietal Lobe: receives and processes sensory information from the body and other sensory areas in the brain; also involved in spatial perception and memory. The parietal lobe allows us to process and perceive the sensations of touch, temperature, pressure and pain. These sensations are processed in ...
... Parietal Lobe: receives and processes sensory information from the body and other sensory areas in the brain; also involved in spatial perception and memory. The parietal lobe allows us to process and perceive the sensations of touch, temperature, pressure and pain. These sensations are processed in ...
Slide ()
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... cingulate motor area > small contribution to pathways > movements associated with an emotional context ...
... cingulate motor area > small contribution to pathways > movements associated with an emotional context ...
Cerebellar system and diseases
... • Posterior lobes receive afferents from cortex through corticopontine pathways. • It projects to the cortex via the dentate nucleus. Its projections are to the cerebral cortex through nucleus ruber, thalamus. • In association with the differentiation of skeletal muscle this part is the largest in h ...
... • Posterior lobes receive afferents from cortex through corticopontine pathways. • It projects to the cortex via the dentate nucleus. Its projections are to the cerebral cortex through nucleus ruber, thalamus. • In association with the differentiation of skeletal muscle this part is the largest in h ...
Slide 1
... Sites controlling individual muscles are distributed over a wide area of motor cortex Muscle representations overlap in cortex Stimulation of single sites activates several muscles (diverging innervation) Many motor cortical neurons contribute to multijointed movements ...
... Sites controlling individual muscles are distributed over a wide area of motor cortex Muscle representations overlap in cortex Stimulation of single sites activates several muscles (diverging innervation) Many motor cortical neurons contribute to multijointed movements ...
f19c623c99fc721
... Note: All the three projects directly to the spinal cord via corticospinal tract. • Premotor and supplementary motor cortex also project to primary motor cortex and is involved in coordinating & planning complex sequences of movement (motor learning). ...
... Note: All the three projects directly to the spinal cord via corticospinal tract. • Premotor and supplementary motor cortex also project to primary motor cortex and is involved in coordinating & planning complex sequences of movement (motor learning). ...
Final review quiz
... In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmother cell”? True or False: A single cell in the brain can be uniquel ...
... In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmother cell”? True or False: A single cell in the brain can be uniquel ...
Cerebral Cortex and Corpus Callosum
... head than there are neurons for receiving sensory information about the trunk of the body and the legs. This is one reason why our face and head are more sensitive to touch than other parts of our body. ...
... head than there are neurons for receiving sensory information about the trunk of the body and the legs. This is one reason why our face and head are more sensitive to touch than other parts of our body. ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-30
... Medial Pathways – maintain posture Motor neurons in the ventral horn are organized medial = postural & lateral = voluntary (limb) Planning of motor activity occurs in the Premotor Cortex Primary Motor Cortex executes the Plan (pyramidal neurons) Pyramidal System Voluntary movement is initiated by py ...
... Medial Pathways – maintain posture Motor neurons in the ventral horn are organized medial = postural & lateral = voluntary (limb) Planning of motor activity occurs in the Premotor Cortex Primary Motor Cortex executes the Plan (pyramidal neurons) Pyramidal System Voluntary movement is initiated by py ...
Motor cortex

Motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.Classically the motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the dorsal precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus.