Unit 8, Abnormal Psychology
... Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
... Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. ...
Chapter 16
... Children can be diagnosed with “adult” anxiety disorders (e.g., MDD, OCD, GAD) Specific symptoms may differ from adults Some symptoms may be absent due to children’s developmental differences Difficulty in obtaining reliable information due to problems with self-reports ...
... Children can be diagnosed with “adult” anxiety disorders (e.g., MDD, OCD, GAD) Specific symptoms may differ from adults Some symptoms may be absent due to children’s developmental differences Difficulty in obtaining reliable information due to problems with self-reports ...
LA.rce Classifying Psychological Disorders
... a parent. Even the routine behavior of taking notes was misinterpreted as a symptom. Labels matter. When people in another experiment watched videotaped interviews, those told the interviewees were job applicants perceived them as normal (Langer et al., 1974,1980). Those who thought they were watchi ...
... a parent. Even the routine behavior of taking notes was misinterpreted as a symptom. Labels matter. When people in another experiment watched videotaped interviews, those told the interviewees were job applicants perceived them as normal (Langer et al., 1974,1980). Those who thought they were watchi ...
Mood Disorders - Shoreline Community College
... – Involuntary movements of the tongue and face (tardive dyskinesia) – Not everyone responds ...
... – Involuntary movements of the tongue and face (tardive dyskinesia) – Not everyone responds ...
Griggs Chapter 10: Abnormal Psychology
... ◦ This includes biological, behavioral, cognitive, and social/cultural factors ...
... ◦ This includes biological, behavioral, cognitive, and social/cultural factors ...
Antisocial Personality Disorder
... • They probably inherited tendencies & it is in their genes. • Biological factors such as abnormal chemistry in the nervous system & parts of the brain. • Nurture: • Or they got it from their environment & life situations such as troubled children who have problems at home. ...
... • They probably inherited tendencies & it is in their genes. • Biological factors such as abnormal chemistry in the nervous system & parts of the brain. • Nurture: • Or they got it from their environment & life situations such as troubled children who have problems at home. ...
Panic Disorder - Cloudfront.net
... situations), Specific Phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an obsession about contamination), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (e.g., in response to stimuli associated with a severe stressor), or Separation A ...
... situations), Specific Phobia (e.g., on exposure to a specific phobic situation), Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (e.g., on exposure to dirt in someone with an obsession about contamination), Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (e.g., in response to stimuli associated with a severe stressor), or Separation A ...
職場心理衛生
... features Types –marked and persistent fear and avoidance of specific stimulus Situation interfere significantly with person’s life Excessive or unrealistic ANS arousal ...
... features Types –marked and persistent fear and avoidance of specific stimulus Situation interfere significantly with person’s life Excessive or unrealistic ANS arousal ...
Describe dissociative disorders in general several
... briefly explaining two such disorders. (one or two paragraphs) How was factor analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorde ...
... briefly explaining two such disorders. (one or two paragraphs) How was factor analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorde ...
Mood disorders ( affective disorders )
... the biological amines, noradrenaline (dopamine) and serotonin - neurotransmitters most implicated in the pathophysiology of mood disorders neuroendocrine dysregulation (alteration of hypothalamic-hypophysis-adrenal and hypothalamic-thyreoid axis) 2. Genetic factors 3. Psychosocial factors 4. Oth ...
... the biological amines, noradrenaline (dopamine) and serotonin - neurotransmitters most implicated in the pathophysiology of mood disorders neuroendocrine dysregulation (alteration of hypothalamic-hypophysis-adrenal and hypothalamic-thyreoid axis) 2. Genetic factors 3. Psychosocial factors 4. Oth ...
Abnormal Psychology
... disorders, and treatment methods within clinical psychology. The course will emphasize the application of scientific research to identifying and treating psychological disorders across a range of theoretical approaches. Course Prerequisite PSY 200 or 201 Course Outcomes Upon completion of the course ...
... disorders, and treatment methods within clinical psychology. The course will emphasize the application of scientific research to identifying and treating psychological disorders across a range of theoretical approaches. Course Prerequisite PSY 200 or 201 Course Outcomes Upon completion of the course ...
Abnormal Psych2014 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Ex: having visions or communicating with the dead is not commonplace in the US o The behavior is irrational Terms Associated with Abnormal Behavior o Insane used by uneducated people to mean psychological disorders in general Insane is not a medical term it is a legal term differentiating t ...
... Ex: having visions or communicating with the dead is not commonplace in the US o The behavior is irrational Terms Associated with Abnormal Behavior o Insane used by uneducated people to mean psychological disorders in general Insane is not a medical term it is a legal term differentiating t ...
Studying Psychological Disorders Studying Psychological Disorders
... Personality Disorder: inflexible, maladaptive personality traits that cause significant impairment of social and occupational functioning Types of personality disorders: Antisocial Personality Disorder Borderline Personality Disorder ...
... Personality Disorder: inflexible, maladaptive personality traits that cause significant impairment of social and occupational functioning Types of personality disorders: Antisocial Personality Disorder Borderline Personality Disorder ...
Abnormal Psychology
... which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no psychological basis can be found ...
... which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no psychological basis can be found ...
has
... College students are very at risk for depression and suicide. If you or someone you know is battling with feelings of suicide please refer them to a ...
... College students are very at risk for depression and suicide. If you or someone you know is battling with feelings of suicide please refer them to a ...
Chapter Summary/Lecture Organizer I. STUDYING
... failing to recall or identify past experiences (dissociative amnesia), by leaving home and wandering off (dissociative fugue), or by developing completely separate personalities (dissociative identity disorder DID or multiple personality disorder). There is considerable ...
... failing to recall or identify past experiences (dissociative amnesia), by leaving home and wandering off (dissociative fugue), or by developing completely separate personalities (dissociative identity disorder DID or multiple personality disorder). There is considerable ...
RAPID REVIEW The text chapter begins with a series of vivid real
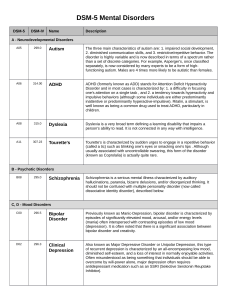
... mental retardation. Axis III includes an assessment of any physical disorders that affect a person psychologically. Axis IV consists of problems in a person’s environment that may be affecting his or her psychological functioning, and Axis V is an assessment of a person’s overall (or global) level o ...
... mental retardation. Axis III includes an assessment of any physical disorders that affect a person psychologically. Axis IV consists of problems in a person’s environment that may be affecting his or her psychological functioning, and Axis V is an assessment of a person’s overall (or global) level o ...
Document
... and externalizing disorders. The second set of columns examines the utility for using the GAIN as a diagnostic screener to predict who is likely to get each diagnosis by a clinician. All are significant at p<.05 and have large positive odds ratio. ...
... and externalizing disorders. The second set of columns examines the utility for using the GAIN as a diagnostic screener to predict who is likely to get each diagnosis by a clinician. All are significant at p<.05 and have large positive odds ratio. ...
Psychiatric comorbidities in asperger syndrome and high functioning
... the manifestation and interpretation of these symptoms. Finally, we will propose some strategies to try to address these issues, and we will discuss therapeutic implications. Keywords: Asperger, High functioning autism, Comorbidities, Diagnostic challenges ...
... the manifestation and interpretation of these symptoms. Finally, we will propose some strategies to try to address these issues, and we will discuss therapeutic implications. Keywords: Asperger, High functioning autism, Comorbidities, Diagnostic challenges ...
Chapter 16 - IWS2.collin.edu
... can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which may include treatment in a psychiatric hospital ...
... can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured assumes that these “mental” illnesses can be diagnosed on the basis of their symptoms and cured through therapy, which may include treatment in a psychiatric hospital ...
hi low
... A. Preoccupation with the belief that one has a serious disease B. The preoccupation persists despite medical evaluation and reassurance C. Not delusional D. Distress or impairment E. Lasts at least 6 months ...
... A. Preoccupation with the belief that one has a serious disease B. The preoccupation persists despite medical evaluation and reassurance C. Not delusional D. Distress or impairment E. Lasts at least 6 months ...