Chapter 16
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
... societal norms or the usual minimum standards for social conduct, culturally specific. 2. Mood disorder is a major disturbance in mood or emotion, such as depression or mania or bipolarity. 3. Schizophrenia means having a split personality 4. Everyone who experiences the same traumatic event will ex ...
Chapter 16-Psychotherapy - Department of Psychology
... happened during all or part of the trip? Found that you can’t remember whether or not you have just done something or perhaps had just thought about doing it? Realized when you are listening to someone talk that you didn’t hear part or all of what the person said? ...
... happened during all or part of the trip? Found that you can’t remember whether or not you have just done something or perhaps had just thought about doing it? Realized when you are listening to someone talk that you didn’t hear part or all of what the person said? ...
Mental Illness review
... Environment plays a large part in psychological development May be in addition to or in combination with genetic predisposition and brain chemistry ...
... Environment plays a large part in psychological development May be in addition to or in combination with genetic predisposition and brain chemistry ...
Psych Revision Notes
... Night-waking and severe sleep problems are relatively common Illness, stress and maternal depression contribute Management by behavioural techniques Medication is seldom used Outbursts are common and peak in year 2 of life Causes include frustration over speech delay, difficulties in par ...
... Night-waking and severe sleep problems are relatively common Illness, stress and maternal depression contribute Management by behavioural techniques Medication is seldom used Outbursts are common and peak in year 2 of life Causes include frustration over speech delay, difficulties in par ...
Abnormal Psychology
... particular action. • Obsession about dirt and germs may lead to compulsive hand washing. ...
... particular action. • Obsession about dirt and germs may lead to compulsive hand washing. ...
Mood Disorders
... thoughts and memories of their ordeal and feel emotionally numb, especially with people they were once close to. They may experience sleep problems, feel detached or numb, or be easily startled. ...
... thoughts and memories of their ordeal and feel emotionally numb, especially with people they were once close to. They may experience sleep problems, feel detached or numb, or be easily startled. ...
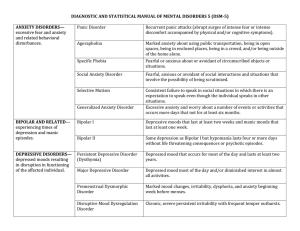
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
Document
... Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma. Numbing of general responsiveness Persistent increased arousal (problems sleeping, irritability/anger, hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, etc.) All symptoms must last more than 1 month. ...
... Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma. Numbing of general responsiveness Persistent increased arousal (problems sleeping, irritability/anger, hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, etc.) All symptoms must last more than 1 month. ...
Psychological Disorders
... History of diverse physical complaints for which there is NO organic basis Long medical history of treatments for minor physical ailments ...
... History of diverse physical complaints for which there is NO organic basis Long medical history of treatments for minor physical ailments ...
Abnormal Psychology - West Essex High School
... particular action. • Obsession about dirt and germs may lead to compulsive hand washing. ...
... particular action. • Obsession about dirt and germs may lead to compulsive hand washing. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... humans or other animals, specifically how, when and where they occur. – Epidemiological studies can never prove causation – Incidence = new cases of a condition which occur during a specified period – Prevalence = cases (both new and existing) of a condition observed at a point in time or during a p ...
... humans or other animals, specifically how, when and where they occur. – Epidemiological studies can never prove causation – Incidence = new cases of a condition which occur during a specified period – Prevalence = cases (both new and existing) of a condition observed at a point in time or during a p ...
Psyc 213: Abnormal Psychology
... 7. Briefly describe PTSD. Provide an example of an experience that may result in PTSD and identify the various symptoms that may accompany this disorder. 8. While some professionals believe that multiple personalities are real and more common than previously thought, others believe that the conditio ...
... 7. Briefly describe PTSD. Provide an example of an experience that may result in PTSD and identify the various symptoms that may accompany this disorder. 8. While some professionals believe that multiple personalities are real and more common than previously thought, others believe that the conditio ...
Chapter 14, Psych Disorders
... feelings of anxiety that are caused by an experience so traumatic that it would produce stress in almost anyone. • Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of stimuli associated w/trauma, sleep disturbances, & irritability. They can occur six months or more after the traumatic event, and t ...
... feelings of anxiety that are caused by an experience so traumatic that it would produce stress in almost anyone. • Symptoms include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of stimuli associated w/trauma, sleep disturbances, & irritability. They can occur six months or more after the traumatic event, and t ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... • Physical complaints without a clear medical cause and severe anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious illness • Medical reassurance does not seem to help • Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders ...
... • Physical complaints without a clear medical cause and severe anxiety focused on the possibility of having a serious illness • Medical reassurance does not seem to help • Comorbidity with anxiety and mood disorders ...
AP Psych 15 sq AP Psych-Psychological Disorders-SQ
... 1. What is abnormal behavior? Cite the main components that typically enter into diagnoses of abnormal behavior. 2. What effects do psychiatric labeling have on social and self-perceptions? 3. What is a phobia, and what are the three major types of phobias? 4. Differentiate between obsessions and co ...
... 1. What is abnormal behavior? Cite the main components that typically enter into diagnoses of abnormal behavior. 2. What effects do psychiatric labeling have on social and self-perceptions? 3. What is a phobia, and what are the three major types of phobias? 4. Differentiate between obsessions and co ...
Anxiety and Children
... Anxiety disorders are among the most common Psychiatric disorders affecting children and adolescents Anxiety disorders tend to have an early onset in childhood and adolescents and run a chronic course well into adulthood Anxiety symptoms may worsen over time (kindling, Physiological effects and lear ...
... Anxiety disorders are among the most common Psychiatric disorders affecting children and adolescents Anxiety disorders tend to have an early onset in childhood and adolescents and run a chronic course well into adulthood Anxiety symptoms may worsen over time (kindling, Physiological effects and lear ...
Slide 1
... A. Excessive anxiety and worry occurring more days than not for at least 6 months, about a number of events B. The person finds it difficult to control the worry C. The anxiety and worry are associated with 3 or more of the following symptoms ...
... A. Excessive anxiety and worry occurring more days than not for at least 6 months, about a number of events B. The person finds it difficult to control the worry C. The anxiety and worry are associated with 3 or more of the following symptoms ...