Ch.14-Psych. Disorders
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
... What is the effect of labeling psychological disorders? It biases your perception of the patient’s behavior After you know the diagnosis (label) even normal behavior is seen as a symptom of that diagnosis. ...
So that explains the voices
... These disorders are marked by the loss of functioning of a specific body part but have no physiological cause. ...
... These disorders are marked by the loss of functioning of a specific body part but have no physiological cause. ...
2. Personality Disorders
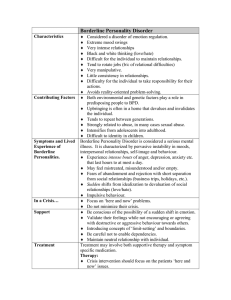
... She plans everything sown to the last detail and becomes very upset if things don’t work out the way she has planned. In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been ste ...
... She plans everything sown to the last detail and becomes very upset if things don’t work out the way she has planned. In the past 9 months Andrew has been fired by three different employers. He was unreliable and often missed work, and each employer finally let him go when they found he had been ste ...
MBBS Psychiatry - Newcastle University Blogging Service
... stem from early relationships in childhood, and be understood in terms of personality development or may be a product of genetic/ biological predisposition. High trait anxiety will mean that an individual is particularly vulnerable to experiencing high state anxiety in stressful situations. The perc ...
... stem from early relationships in childhood, and be understood in terms of personality development or may be a product of genetic/ biological predisposition. High trait anxiety will mean that an individual is particularly vulnerable to experiencing high state anxiety in stressful situations. The perc ...
Anxiety - CBE Home
... • All of these disorders can lead to panic attacks, which look and feel like a heart attack with shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, shakiness and sweating. They can be very frightening but they only last a short time and are ...
... • All of these disorders can lead to panic attacks, which look and feel like a heart attack with shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, shakiness and sweating. They can be very frightening but they only last a short time and are ...
Recent revisions to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
... Disorders (DSM‐5) with revisions to the criteria for the diagnosis and classification of mental disorders. These revisions are reflected in the content lists for the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior (PSBB) section of the MCAT2015 exam. Some of the revisions may not ye ...
... Disorders (DSM‐5) with revisions to the criteria for the diagnosis and classification of mental disorders. These revisions are reflected in the content lists for the Psychological, Social, and Biological Foundations of Behavior (PSBB) section of the MCAT2015 exam. Some of the revisions may not ye ...
Should nonpharmacological treatments of anxiety be considered
... nonpharmacological treatments involving exposure and cognitive strategies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, have been proven to do exactly that. So, should the nonpharmacological treatment of anxiety systematically be considered first? Empirical evidence and best practices indicate that it shou ...
... nonpharmacological treatments involving exposure and cognitive strategies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, have been proven to do exactly that. So, should the nonpharmacological treatment of anxiety systematically be considered first? Empirical evidence and best practices indicate that it shou ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Medical Model • 1800s medical model emerges, replaces “evil” cause of mental illness • Medical Model: A mental illness needs to be diagnosed on the basis of its symptoms and can be treated • Biopsychosocial approach: today’s psychologists say that all behavior (normal or disordered) arises from int ...
... Medical Model • 1800s medical model emerges, replaces “evil” cause of mental illness • Medical Model: A mental illness needs to be diagnosed on the basis of its symptoms and can be treated • Biopsychosocial approach: today’s psychologists say that all behavior (normal or disordered) arises from int ...
Anxiety Disorders
... • The disorder may begin in childhood or adolescence, • onset is not uncommon after age 20. • Depressive symptoms are common • numerous somatic complaints may also be a part of the clinical picture. • Generalized anxiety disorder tends to be chronic • frequent stress-related exacerbations and fluct ...
... • The disorder may begin in childhood or adolescence, • onset is not uncommon after age 20. • Depressive symptoms are common • numerous somatic complaints may also be a part of the clinical picture. • Generalized anxiety disorder tends to be chronic • frequent stress-related exacerbations and fluct ...
Stress Management - Truman State University
... University Counseling Services Free and confidential counseling to Truman students ...
... University Counseling Services Free and confidential counseling to Truman students ...
Chapter12
... 1 in 5 adults suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year 45 million Americans suffer Mental illness ranks 2nd in terms of burden of disease in the U.S. Depression is leading cause of lost years of healthy life for women worldwide Gender differences exist ...
... 1 in 5 adults suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year 45 million Americans suffer Mental illness ranks 2nd in terms of burden of disease in the U.S. Depression is leading cause of lost years of healthy life for women worldwide Gender differences exist ...
understanding and managing anxiety 2016
... dying, numbness, chills or hot flashes. These same symptoms also can be caused by caffeine consumption, amphetamines an overactive thyroid, abnormal heart rhythms, and other heart abnormalities. Separation anxiety disorder: Developmentally inappropriate and excessive fear or anxiety concerning sep ...
... dying, numbness, chills or hot flashes. These same symptoms also can be caused by caffeine consumption, amphetamines an overactive thyroid, abnormal heart rhythms, and other heart abnormalities. Separation anxiety disorder: Developmentally inappropriate and excessive fear or anxiety concerning sep ...
5lies we believe about anxiety
... people with anxiety. Studies indicate that a genre of therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly ...
... people with anxiety. Studies indicate that a genre of therapy called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY (PAT …
... may be due to wide range of medical conditions, e.g., thyroid and other endocrine abnormalities, cardiac conditions, hypoglycemia, brain lesions treatment is best directed at underlying condition ...
... may be due to wide range of medical conditions, e.g., thyroid and other endocrine abnormalities, cardiac conditions, hypoglycemia, brain lesions treatment is best directed at underlying condition ...
Abnormal Psychology
... ◦ Person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, heart palpatations, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
... ◦ Person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, heart palpatations, choking, or other frightening sensations. ...
Chapter 10: Mental Disorders What Are Mental Disorders?
... hopelessness, and sadness (more than a few weeks) Common during teen years when new challenges, responsibilities, and pressures can pile up and seem overpowering. Could lead to alienation (feeling isolated and separated from everyone else). When painful feelings go unchecked over long periods, ...
... hopelessness, and sadness (more than a few weeks) Common during teen years when new challenges, responsibilities, and pressures can pile up and seem overpowering. Could lead to alienation (feeling isolated and separated from everyone else). When painful feelings go unchecked over long periods, ...