First life fish reptiles mammals
... • Geologic time is divided according to types of life • These divisions often occur from mass extinctions, examples of which include: – Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction killed dinosaurs – Triassic-Jurassic extinction (22% of marine families) – Permian-Triassic extinction (95% of all species) ...
... • Geologic time is divided according to types of life • These divisions often occur from mass extinctions, examples of which include: – Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction killed dinosaurs – Triassic-Jurassic extinction (22% of marine families) – Permian-Triassic extinction (95% of all species) ...
PPT NOTES_AP Biology Chapter 25 Notes
... • Characteristics of the _____________ planet and its atmosphere. • How ___________ and _______________ tested the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis and what they learned. • Methods used to __________________ fossils and rocks. • Evidence for _____________________________. • How continental drift can explai ...
... • Characteristics of the _____________ planet and its atmosphere. • How ___________ and _______________ tested the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis and what they learned. • Methods used to __________________ fossils and rocks. • Evidence for _____________________________. • How continental drift can explai ...
File - Bruner science
... Close analysis of rocks around the world suggests that the continents were all _________. ...
... Close analysis of rocks around the world suggests that the continents were all _________. ...
Name: June Proficiency Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Honors
... A rock is either older or younger than rocks nearby. Scientists determine the relative order in which rock layers were deposited. 14. What is absolute-age dating? More precise than relative-age dating; scientists use radioactive decay, a natural clocklike process in rocks to learn its age in year. 1 ...
... A rock is either older or younger than rocks nearby. Scientists determine the relative order in which rock layers were deposited. 14. What is absolute-age dating? More precise than relative-age dating; scientists use radioactive decay, a natural clocklike process in rocks to learn its age in year. 1 ...
UNIT 2, CHAPTER 5:
... 2. Unstable radioactive isotopes used to date rock are called the _________________ and the stable material produced by its decay is called the _______________________. By comparing the relative amount of these materials, the age of the rock can be determined. The more ____________________ material ...
... 2. Unstable radioactive isotopes used to date rock are called the _________________ and the stable material produced by its decay is called the _______________________. By comparing the relative amount of these materials, the age of the rock can be determined. The more ____________________ material ...
2/21/2014
... •Several, not necessarily mutually exclusive, explanations have been proposed to account for this change: an asteroid impact in what is now the Caribbean sea; slow changes in climate due to continental drift ; and massive volcanic activity in India during the late Cretaceous that contributed to cool ...
... •Several, not necessarily mutually exclusive, explanations have been proposed to account for this change: an asteroid impact in what is now the Caribbean sea; slow changes in climate due to continental drift ; and massive volcanic activity in India during the late Cretaceous that contributed to cool ...
Vocabulary Chapter 14
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
The evolution of Life in the History of Earth
... Introduction Principles p of Geology gy & Palaeontology ...
... Introduction Principles p of Geology gy & Palaeontology ...
Practice Q`s Earth History What is the estimated age of the earth
... In fact 4700 years is the half life of the C14 isotope. Why isn’t this a useful isotope to measure the age of rocks? Does the half-life of a radioactive isotope change? How can the age of a fossil be determined? The most reliable method of dating absolute age of rocks is: a. superposition b. rates o ...
... In fact 4700 years is the half life of the C14 isotope. Why isn’t this a useful isotope to measure the age of rocks? Does the half-life of a radioactive isotope change? How can the age of a fossil be determined? The most reliable method of dating absolute age of rocks is: a. superposition b. rates o ...
Earth Science Chapter 21: Fossils and the Rock Record Chapter
... Fossils are the evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals. They provide evidence of the past existence of a wide variety of life forms, most of which have become extinct. The fossil record also provides evidence that populations have undergone change throughout time in response to changes ...
... Fossils are the evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals. They provide evidence of the past existence of a wide variety of life forms, most of which have become extinct. The fossil record also provides evidence that populations have undergone change throughout time in response to changes ...
14 The History of Life
... . They determine the relative age of rocks , which compares the sequence of rock ...
... . They determine the relative age of rocks , which compares the sequence of rock ...
Important Steps in the Development of Geology…
... published a book “Theory of the Earth with Proof and Illustrations”, and this became the foundation of modern geology. Hutton proposed his theory of uniformitarianism, stating that: The earth was very old, and not formed by catastrophes alone. The earth was a great internal heat machine (hence t ...
... published a book “Theory of the Earth with Proof and Illustrations”, and this became the foundation of modern geology. Hutton proposed his theory of uniformitarianism, stating that: The earth was very old, and not formed by catastrophes alone. The earth was a great internal heat machine (hence t ...
History of the Disciplines
... Hutton explains that the present is the key to the past • The earth is dynamic, so as rocks are eroded and weathered, so are there new rocks are created. • Therefore, the geologic process observe today were at work in the past… even the distant past. HOWEVER – those processes may have happened at di ...
... Hutton explains that the present is the key to the past • The earth is dynamic, so as rocks are eroded and weathered, so are there new rocks are created. • Therefore, the geologic process observe today were at work in the past… even the distant past. HOWEVER – those processes may have happened at di ...
the rock record - Sardis Secondary
... Other Use of Fossils • Indicators of past climate • coral reefs today are only found in shallow, warm water. When a rock containing fossil coral is found, we can assume the area was once warm and shallow water • Oil exploration and microfossils • Microfossil: fossils so tiny that you need a microsco ...
... Other Use of Fossils • Indicators of past climate • coral reefs today are only found in shallow, warm water. When a rock containing fossil coral is found, we can assume the area was once warm and shallow water • Oil exploration and microfossils • Microfossil: fossils so tiny that you need a microsco ...
28 - KaterinaCLHSportfolio
... Original preservation: Describes a fossil with soft and hard parts that have undergone very little change since the organisms death. 8. Absolute-age dating: Method that enables scientists to determine that actual age of certain rocks and other objects. Relative-age dating: To determine how many year ...
... Original preservation: Describes a fossil with soft and hard parts that have undergone very little change since the organisms death. 8. Absolute-age dating: Method that enables scientists to determine that actual age of certain rocks and other objects. Relative-age dating: To determine how many year ...
Earth Science EOG Review
... What is the benefit of absolute age? Gives the most precise measurement (when possible) ...
... What is the benefit of absolute age? Gives the most precise measurement (when possible) ...
Ch 14 Notes - OCPS TeacherPress
... Radioactive dating is the method used to determine the age of the earth and of fossils. Clues in Rocks A fossil is any preserved evidence of an organism. Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a ch ...
... Radioactive dating is the method used to determine the age of the earth and of fossils. Clues in Rocks A fossil is any preserved evidence of an organism. Examples of fossils include bones, shells, and impressions of dead organisms left in rocks. Most organisms decompose before they have a ch ...
Book F Chapter 3 Section 4
... The fossil record offers only a ____________ ___________ of the history of life on Earth. ...
... The fossil record offers only a ____________ ___________ of the history of life on Earth. ...
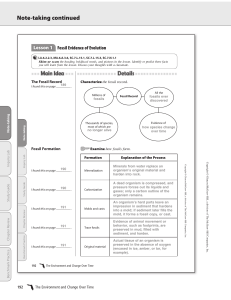
Note-taking continued
... Relate types of fossils found in different rock layers to the geologic time scale. ...
... Relate types of fossils found in different rock layers to the geologic time scale. ...
Chapter 5 Section 1 Geologic History
... are usually the oldest, and the top layers are usually the youngest. • Scientists can use the order of rock layers to determine the relative age of objects within the layers. ...
... are usually the oldest, and the top layers are usually the youngest. • Scientists can use the order of rock layers to determine the relative age of objects within the layers. ...
A Trip Through Geologic Time
... – tell about what an organism ate • unchanged fossils – amber, tar pits ...
... – tell about what an organism ate • unchanged fossils – amber, tar pits ...
History of paleontology

The history of paleontology traces the history of the effort to understand the history of life on Earth by studying the fossil record left behind by living organisms. Since it is concerned with understanding living organisms of the past paleontology can be considered to be a field of biology, but its historical development has been closely tied to geology and the effort to understand the history of the Earth itself.In ancient times Xenophanes (570-480 BC), Herodotus (484-425 BC), Eratosthenes (276-194 BC), and Strabo (64 BC-24 AD), wrote about fossils of marine organisms indicating that land was once under water. During the Middle Ages, fossils were discussed by the Persian naturalist, Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna in Europe), in The Book of Healing (1027), which proposed a theory of petrifying fluids that Albert of Saxony would elaborate on in the 14th century. The Chinese naturalist Shen Kuo (1031–1095) would propose a theory of climate change based on evidence from petrified bamboo.In early modern Europe, the systematic study of fossils emerged as an integral part of the changes in natural philosophy that occurred during the Age of Reason. The nature of fossils and their relationship to life in the past became better understood during the 17th and 18th centuries, and at the end of the 18th century the work of Georges Cuvier ended a long running debate about the reality of extinction and led to the emergence of paleontology, in association with comparative anatomy, as a scientific discipline. The expanding knowledge of the fossil record also played an increasing role in the development of geology, particularly stratigraphy.In 1822 the word ""paleontology"" was invented by the editor of a French scientific journal to refer to the study of ancient living organisms through fossils, and the first half of the 19th century saw geological and paleontological activity become increasingly well organized with the growth of geologic societies and museums and an increasing number of professional geologists and fossil specialists. This contributed to a rapid increase in knowledge about the history of life on Earth, and progress towards definition of the geologic time scale largely based on fossil evidence. As knowledge of life's history continued to improve, it became increasingly obvious that there had been some kind of successive order to the development of life. This would encourage early evolutionary theories on the transmutation of species. After Charles Darwin published Origin of Species in 1859, much of the focus of paleontology shifted to understanding evolutionary paths, including human evolution, and evolutionary theory.The last half of the 19th century saw a tremendous expansion in paleontological activity, especially in North America. The trend continued in the 20th century with additional regions of the Earth being opened to systematic fossil collection, as demonstrated by a series of important discoveries in China near the end of the 20th century. Many transitional fossils have been discovered, and there is now considered to be abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. The last few decades of the 20th century saw a renewed interest in mass extinctions and their role in the evolution of life on Earth. There was also a renewed interest in the Cambrian explosion that saw the development of the body plans of most animal phyla. The discovery of fossils of the Ediacaran biota and developments in paleobiology extended knowledge about the history of life back far before the Cambrian.