22 questions - ReviewEarthScience.com
... A sandstone layer is found tilted at an angle of 75D from the horizontal. What probably caused this 75D tilt? A) The sediments that formed this sandstone layer were originally deposited at a 75D tilt. B) Nearly all sandstone layers are formed from winddeposited sands. C) This sandstone layer has rec ...
... A sandstone layer is found tilted at an angle of 75D from the horizontal. What probably caused this 75D tilt? A) The sediments that formed this sandstone layer were originally deposited at a 75D tilt. B) Nearly all sandstone layers are formed from winddeposited sands. C) This sandstone layer has rec ...
Grade 6 Curriculum Map - Bibb County School District
... specifically identify the expectations for student learning for the Bibb County School District. This curriculum is expected to be followed by all teachers to ensure that learning goals are met for all students and state standards. ...
... specifically identify the expectations for student learning for the Bibb County School District. This curriculum is expected to be followed by all teachers to ensure that learning goals are met for all students and state standards. ...
Chapter 25 The History of Life on Earth 25.3 Key Events in Life`s
... prokaryotes, mitochonrida & plastids replicate by a splitting process that’s similar to prokaryotes’, each of these organelles contain a single circular DNA molecule that’s like that of bacteria, they have cell machinery needed to transcribe & translate their DNA into proteins In terms of size, RN ...
... prokaryotes, mitochonrida & plastids replicate by a splitting process that’s similar to prokaryotes’, each of these organelles contain a single circular DNA molecule that’s like that of bacteria, they have cell machinery needed to transcribe & translate their DNA into proteins In terms of size, RN ...
Study Guide for Geology Exam 2016
... In December 2004, an earthquake registering 9.0 on the Richter scale was recorded off the coast of Sumatra. What is a common secondary effect of this type of earthquake? ...
... In December 2004, an earthquake registering 9.0 on the Richter scale was recorded off the coast of Sumatra. What is a common secondary effect of this type of earthquake? ...
File
... Fossils: 11. What are fossils? 12. List at least 3 ways they are formed or found 13. Draw a diagram showing how the fossils of a bird would be found if they were 10 years old, 25 years old, and 50 years old 14. What does the term geological history refer to? 15. What makes a petrified fossil special ...
... Fossils: 11. What are fossils? 12. List at least 3 ways they are formed or found 13. Draw a diagram showing how the fossils of a bird would be found if they were 10 years old, 25 years old, and 50 years old 14. What does the term geological history refer to? 15. What makes a petrified fossil special ...
Essay- choose ONE
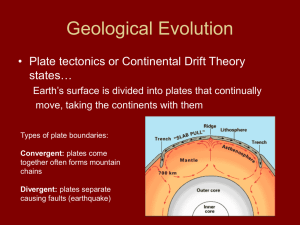
... ___The theory that states all continents were once a part of one giant landmass, split apart and slowly moved to there present positions. ___The theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle is broken up into sections. ___The process that explains how continents move and where new crust is made. ...
... ___The theory that states all continents were once a part of one giant landmass, split apart and slowly moved to there present positions. ___The theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle is broken up into sections. ___The process that explains how continents move and where new crust is made. ...
© UKRIGS Education Project: Earth Science On-Site
... Examine evidence and interpret data about how organisms and species have changed over time. Suggest reasons why species may become extinct. C1 Topic 3, Using Chemical Reactions To Make New Materials. ...
... Examine evidence and interpret data about how organisms and species have changed over time. Suggest reasons why species may become extinct. C1 Topic 3, Using Chemical Reactions To Make New Materials. ...
Fossils - Our eclass community
... • When crystals of thorium and potassium in the soil are irradiated, part of the radiation is released in the form of light and the rest is trapped in the crystal lattice of the material to be dated (e.g. pottery or stone). • When the material is heated, the stored energy is released as light, the s ...
... • When crystals of thorium and potassium in the soil are irradiated, part of the radiation is released in the form of light and the rest is trapped in the crystal lattice of the material to be dated (e.g. pottery or stone). • When the material is heated, the stored energy is released as light, the s ...
Maddison & Omee
... can't be recycled. We know that it is a non-renewable resource. The bad news is that prices for fossil fuels such as gas, coal and oil are rising due to fact that fossil fuel is polluting the environment and other main things. We need to stop polluting the environment, and ...
... can't be recycled. We know that it is a non-renewable resource. The bad news is that prices for fossil fuels such as gas, coal and oil are rising due to fact that fossil fuel is polluting the environment and other main things. We need to stop polluting the environment, and ...
The geological time scale divides Earth`s history into units from its
... baby named Dima is pictured in situ near Kirgiljach River in northeast Siberia. ...
... baby named Dima is pictured in situ near Kirgiljach River in northeast Siberia. ...
Earths History Presentation
... • Radioactive decay occurs when the nuclei of unstable atoms break down, changing the original atoms into atoms of another element. • The rate of radioactive decay is measured in terms of half-life. – Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half the atoms of a substance to decay into another el ...
... • Radioactive decay occurs when the nuclei of unstable atoms break down, changing the original atoms into atoms of another element. • The rate of radioactive decay is measured in terms of half-life. – Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half the atoms of a substance to decay into another el ...
Chapter 15
... • Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms – Traced partly from the fossil record – Also inferred from morphological and ...
... • Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a group of organisms – Traced partly from the fossil record – Also inferred from morphological and ...
Questions for the fifth quiz
... Which sedimentary rocks were the most difficult for Smith to differentiate? What were conditions like in England (Somerset) during the Lower and Middle Jurassic? What was the name of the Sea? Smith began to realize that the stones may have the same color, chemistry, and grain size, but that …… Did h ...
... Which sedimentary rocks were the most difficult for Smith to differentiate? What were conditions like in England (Somerset) during the Lower and Middle Jurassic? What was the name of the Sea? Smith began to realize that the stones may have the same color, chemistry, and grain size, but that …… Did h ...
EarthViewer Questions
... Biological Events 9. When was the Cambrian Explosion? ___________________________________________________ a. What % of the atmosphere was Oxygen (O2)? ________________________________ b. What % of the atmosphere is O2 today? ...
... Biological Events 9. When was the Cambrian Explosion? ___________________________________________________ a. What % of the atmosphere was Oxygen (O2)? ________________________________ b. What % of the atmosphere is O2 today? ...
Introduction to stratigraphy
... Biostratigraphy = using fossils to establish age equivalency 1. zones or biozones - the time interval between the first and last appearance of a fossil or fossils 2. position within evolutionary lineages - for traits that change gradually over time you can tell the age of the fossil-bearing rock la ...
... Biostratigraphy = using fossils to establish age equivalency 1. zones or biozones - the time interval between the first and last appearance of a fossil or fossils 2. position within evolutionary lineages - for traits that change gradually over time you can tell the age of the fossil-bearing rock la ...
Geo Vocab Puzzle
... Across 1.plant having its seeds enclosed in an ovary; a flowering plant 3.method of dating geological or archeological specimens by determining the relative proportions of particular radioactive isotopes present in a sample. 7.subdivision of a period 10.is a system of chronological measurement that ...
... Across 1.plant having its seeds enclosed in an ovary; a flowering plant 3.method of dating geological or archeological specimens by determining the relative proportions of particular radioactive isotopes present in a sample. 7.subdivision of a period 10.is a system of chronological measurement that ...
How Do You Study the Past? (The Rock Record: Absolute
... there is no lead present • U-238 can be used to date rocks formed in the early Earth 4. Carbon 14 • When an organism is alive, it’s C-14 is continuously replaced • When that organism dies, the C-14 decays to nitrogen and it does not get replaced • C-14 can be used to date geologic events involving o ...
... there is no lead present • U-238 can be used to date rocks formed in the early Earth 4. Carbon 14 • When an organism is alive, it’s C-14 is continuously replaced • When that organism dies, the C-14 decays to nitrogen and it does not get replaced • C-14 can be used to date geologic events involving o ...
How Do You Study the Past? (The Rock Record: Absolute
... 3. Other Means of Determining Relative Age a. Correlation • Used to date rock layers that are far apart from each other • Geologists examine rocks for distinctive fossils and features to help identify and date them b. Inclusions • If a rock contains fragments of another rock, then the rock that is ...
... 3. Other Means of Determining Relative Age a. Correlation • Used to date rock layers that are far apart from each other • Geologists examine rocks for distinctive fossils and features to help identify and date them b. Inclusions • If a rock contains fragments of another rock, then the rock that is ...
II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? I. What is a Fossil
... 3. Other Means of Determining Relative Age a. Correlation • Used to date rock layers that are far apart from each other • Geologists examine rocks for distinctive fossils and features to help identify and date them b. Inclusions • If a rock contains fragments of another rock, then the rock tha ...
... 3. Other Means of Determining Relative Age a. Correlation • Used to date rock layers that are far apart from each other • Geologists examine rocks for distinctive fossils and features to help identify and date them b. Inclusions • If a rock contains fragments of another rock, then the rock tha ...
Earth Science, 10th edition Chapter 10: Geologic Time I. Historical
... 1. Half-life – the time for one-half of the radioactive nuclei to decay 2. Requires a closed system 3. Cross-checks are used for accuracy 4. Complex procedure 5. Yields numerical dates D. Carbon-14 dating 1. Half-life of only 5730 years 2. Used to date very recent events ...
... 1. Half-life – the time for one-half of the radioactive nuclei to decay 2. Requires a closed system 3. Cross-checks are used for accuracy 4. Complex procedure 5. Yields numerical dates D. Carbon-14 dating 1. Half-life of only 5730 years 2. Used to date very recent events ...
Part A KEY - Belmont Secondary Home Page
... A conglomerate along the California coast contains pieces of basalt which have been dated as 18 million years old. How should we interpret this age? A. It represents the time that the clasts of the conglomerate accumulated at the surface. B. It represents the time that the clasts of the conglomerate ...
... A conglomerate along the California coast contains pieces of basalt which have been dated as 18 million years old. How should we interpret this age? A. It represents the time that the clasts of the conglomerate accumulated at the surface. B. It represents the time that the clasts of the conglomerate ...
Note Taking Guide Continental Drift Powerpoint
... Do Scientists now have additional evidence to support Wegner’s theory? YES/NO (Circle one) Follow Up Questions: 1. What is the significance of finding fossil remains of Mesosaurs and Lystrosaurs on separate continents? ...
... Do Scientists now have additional evidence to support Wegner’s theory? YES/NO (Circle one) Follow Up Questions: 1. What is the significance of finding fossil remains of Mesosaurs and Lystrosaurs on separate continents? ...
Continental Drift Theory
... Fossil Fuel in Antarctica • Tropical plant remains (coal deposits) found in Antarctica – this is evidence that Antarctica was once much warmer and much closer to the equator, since tropical plants don’t grow in Antarctica today ...
... Fossil Fuel in Antarctica • Tropical plant remains (coal deposits) found in Antarctica – this is evidence that Antarctica was once much warmer and much closer to the equator, since tropical plants don’t grow in Antarctica today ...
History of paleontology

The history of paleontology traces the history of the effort to understand the history of life on Earth by studying the fossil record left behind by living organisms. Since it is concerned with understanding living organisms of the past paleontology can be considered to be a field of biology, but its historical development has been closely tied to geology and the effort to understand the history of the Earth itself.In ancient times Xenophanes (570-480 BC), Herodotus (484-425 BC), Eratosthenes (276-194 BC), and Strabo (64 BC-24 AD), wrote about fossils of marine organisms indicating that land was once under water. During the Middle Ages, fossils were discussed by the Persian naturalist, Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna in Europe), in The Book of Healing (1027), which proposed a theory of petrifying fluids that Albert of Saxony would elaborate on in the 14th century. The Chinese naturalist Shen Kuo (1031–1095) would propose a theory of climate change based on evidence from petrified bamboo.In early modern Europe, the systematic study of fossils emerged as an integral part of the changes in natural philosophy that occurred during the Age of Reason. The nature of fossils and their relationship to life in the past became better understood during the 17th and 18th centuries, and at the end of the 18th century the work of Georges Cuvier ended a long running debate about the reality of extinction and led to the emergence of paleontology, in association with comparative anatomy, as a scientific discipline. The expanding knowledge of the fossil record also played an increasing role in the development of geology, particularly stratigraphy.In 1822 the word ""paleontology"" was invented by the editor of a French scientific journal to refer to the study of ancient living organisms through fossils, and the first half of the 19th century saw geological and paleontological activity become increasingly well organized with the growth of geologic societies and museums and an increasing number of professional geologists and fossil specialists. This contributed to a rapid increase in knowledge about the history of life on Earth, and progress towards definition of the geologic time scale largely based on fossil evidence. As knowledge of life's history continued to improve, it became increasingly obvious that there had been some kind of successive order to the development of life. This would encourage early evolutionary theories on the transmutation of species. After Charles Darwin published Origin of Species in 1859, much of the focus of paleontology shifted to understanding evolutionary paths, including human evolution, and evolutionary theory.The last half of the 19th century saw a tremendous expansion in paleontological activity, especially in North America. The trend continued in the 20th century with additional regions of the Earth being opened to systematic fossil collection, as demonstrated by a series of important discoveries in China near the end of the 20th century. Many transitional fossils have been discovered, and there is now considered to be abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. The last few decades of the 20th century saw a renewed interest in mass extinctions and their role in the evolution of life on Earth. There was also a renewed interest in the Cambrian explosion that saw the development of the body plans of most animal phyla. The discovery of fossils of the Ediacaran biota and developments in paleobiology extended knowledge about the history of life back far before the Cambrian.