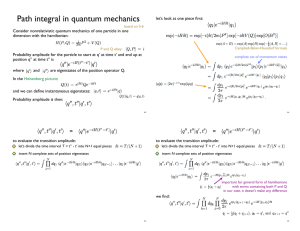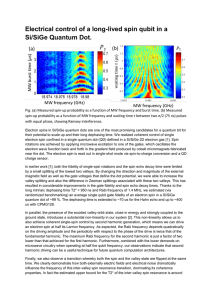
Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a
... ground state, introduces a substantial non-linearity in our system [2]. This non-linearity allows us to also achieve coherent single-spin control by second harmonic generation, which means we can drive an electron spin at half its Larmor frequency. As expected, the Rabi frequency depends quadratical ...
... ground state, introduces a substantial non-linearity in our system [2]. This non-linearity allows us to also achieve coherent single-spin control by second harmonic generation, which means we can drive an electron spin at half its Larmor frequency. As expected, the Rabi frequency depends quadratical ...
$doc.title
... - Classical model, failure at low temperature, Einstein model Black Body radiation (introduction) ...
... - Classical model, failure at low temperature, Einstein model Black Body radiation (introduction) ...
Quantum Zeno Effect, Anti Zeno Effect and the Quantum recurrence theorem
... *Side note 1 - if we hadn’t taken cm = 1/N we would have gotten an ellipsoid instead of a sphere, yet our results still would have been valid, as explained in [1]. P *Side note 2 - taking N to be finitie is justified by the fact that |cm |2 = 1, thus we can find N for which this sum (truncated at N) ...
... *Side note 1 - if we hadn’t taken cm = 1/N we would have gotten an ellipsoid instead of a sphere, yet our results still would have been valid, as explained in [1]. P *Side note 2 - taking N to be finitie is justified by the fact that |cm |2 = 1, thus we can find N for which this sum (truncated at N) ...
Physical problem for Nonlinear Equations:General
... This is the era of nanotechnology. Humans now have the ability to manipulate things in the nanometer range, even single electrons. This has opened up exciting new directions in the design of computer where computations are performed by manipulating single electrons – the ultimate limit in electronic ...
... This is the era of nanotechnology. Humans now have the ability to manipulate things in the nanometer range, even single electrons. This has opened up exciting new directions in the design of computer where computations are performed by manipulating single electrons – the ultimate limit in electronic ...
PDF
... This is the era of nanotechnology. Humans now have the ability to manipulate things in the nanometer range, even single electrons. This has opened up exciting new directions in the design of computer where computations are performed by manipulating single electrons – the ultimate limit in electronic ...
... This is the era of nanotechnology. Humans now have the ability to manipulate things in the nanometer range, even single electrons. This has opened up exciting new directions in the design of computer where computations are performed by manipulating single electrons – the ultimate limit in electronic ...
1 The Photoelectric Effect 2 Line Spectra and Energy Levels
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
Chapter 28 notes
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
... Rutherford scattering : alpha particles projected onto atoms and the resulting deflection. scintillation: momentary flash caused by a particle being absorbed and re-emitted by certain materials. Geiger counter : a device commonly used to detect radiation. nucleus: positively charged, dense core of t ...
Questions and Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and wh ...
... experiment when detectors are used to determine which slit an electron is passing through? How do researchers explain this? 2. When the electrons are observed, what interpretations do researchers suggest causes the electrons to travel the way they do? Which interpretation do you think is true and wh ...
Toffoli gate
... via a single measurement Once converted to classical information, quantum information cannot be recovered ...
... via a single measurement Once converted to classical information, quantum information cannot be recovered ...
5.4 Quantum Devices Energy Levels in a Single Quantum Well
... We have used periodic boundary conditions for this case, which is physically sensible for large crystals. The wave functions are propagating plane waves in this case. It is, however, more common and sensible to use fixed boundary conditions, especially for small dimensions. The wave functions then a ...
... We have used periodic boundary conditions for this case, which is physically sensible for large crystals. The wave functions are propagating plane waves in this case. It is, however, more common and sensible to use fixed boundary conditions, especially for small dimensions. The wave functions then a ...
photoelectric effect Work function
... in 1927 for his discovery and explanation of the change in the wavelength of X rays when they collide with electrons in metals. Compton, a younger brother of the physicist Karl T. Compton, who was President of MIT, received his doctorate from Princeton University in 1916 and became head of the depar ...
... in 1927 for his discovery and explanation of the change in the wavelength of X rays when they collide with electrons in metals. Compton, a younger brother of the physicist Karl T. Compton, who was President of MIT, received his doctorate from Princeton University in 1916 and became head of the depar ...
Document
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
Chapter 5
... In 1896 Antoine Becquerel discovered that certain elements decomposed to form other elements by emitting radiation. There are three types of radiation alpha () particle which is a He+2 ion beta () particle which is an egamma () ray which is made up of high energy and has no charge ...
... In 1896 Antoine Becquerel discovered that certain elements decomposed to form other elements by emitting radiation. There are three types of radiation alpha () particle which is a He+2 ion beta () particle which is an egamma () ray which is made up of high energy and has no charge ...
Possible Topics for the Final Project Taken with slight modification
... 18. The Zeeman effect in weak, intermediate and strong magnetic fields. 19. The Lamb shift in hydrogen — evidence that relativistic quantum mechanics must be replaced by quantum field theory. 20. The non-relativistic quark model of the proton, neutron and related particles. 21. Isospin — a quantum s ...
... 18. The Zeeman effect in weak, intermediate and strong magnetic fields. 19. The Lamb shift in hydrogen — evidence that relativistic quantum mechanics must be replaced by quantum field theory. 20. The non-relativistic quark model of the proton, neutron and related particles. 21. Isospin — a quantum s ...
Periodic Table
... lines up with applied field. • Values from –l to l • Lz is with respect to field ...
... lines up with applied field. • Values from –l to l • Lz is with respect to field ...
Chemistry 354 - Homework Set IV
... mass of a hydrogen atom; the mass of Haystacks Calhoun (erstwhile professional wrestler); the distance between the n = 1 and n = 2 energy levels of an electron in a one-dimensional box of length 1 nm; and finally, the speed of light. Make a table of these numbers, and note that the “atomic-scale” qu ...
... mass of a hydrogen atom; the mass of Haystacks Calhoun (erstwhile professional wrestler); the distance between the n = 1 and n = 2 energy levels of an electron in a one-dimensional box of length 1 nm; and finally, the speed of light. Make a table of these numbers, and note that the “atomic-scale” qu ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.