Class 22
... Each type of atom produces unique set of colors. Discussion: Given that we now know that light comes quantized in photons with energy E=hc/λ= hf. What do these observations imply about electrons in atoms? Student suggestions: a. b. c. d. e. ...
... Each type of atom produces unique set of colors. Discussion: Given that we now know that light comes quantized in photons with energy E=hc/λ= hf. What do these observations imply about electrons in atoms? Student suggestions: a. b. c. d. e. ...
Free Electron Laser
... • Holography was discovered in 1947 by Hungarian physicist Dennis Gabor (Hungarian name: Gábor Dénes) (1900–1979), work for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1971. It was made possible by pioneering work in the field of physics by other scientists like Mieczysław Wolfke who resolved te ...
... • Holography was discovered in 1947 by Hungarian physicist Dennis Gabor (Hungarian name: Gábor Dénes) (1900–1979), work for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1971. It was made possible by pioneering work in the field of physics by other scientists like Mieczysław Wolfke who resolved te ...
A simple proof of Born`s rule for statistical interpretation of quantum
... based on intuition that light quanta and matter must behave in a similar manner and wave function might be analogous to electric field. In his Nobel lecture [3], Born stated, “Again an idea of Einstein’s gave me the lead. He had tried to make the duality of particles - light quanta or photons - and ...
... based on intuition that light quanta and matter must behave in a similar manner and wave function might be analogous to electric field. In his Nobel lecture [3], Born stated, “Again an idea of Einstein’s gave me the lead. He had tried to make the duality of particles - light quanta or photons - and ...
Name
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
5.1 Worksheet File
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
... Electron Configurations An electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The aufbau principle says that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first. According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each orbital can contain at most two electrons. The two electrons must ...
ppt - UCSC Bayesian Data Analysis Workshop
... runs that with high probability trigger the detectors that fired – non-parametric representation of the distribution that allows for tracking of multiple hypotheses ...
... runs that with high probability trigger the detectors that fired – non-parametric representation of the distribution that allows for tracking of multiple hypotheses ...
Chapter 6
... electron in a hydrogen atom is 240pm The size of an isolated H atom is about 240 pm This leads to an uncertainty in the location of the electron ...
... electron in a hydrogen atom is 240pm The size of an isolated H atom is about 240 pm This leads to an uncertainty in the location of the electron ...
Chapter 9 The Atom - Bakersfield College
... explained by the electromagnetic theory of light. Albert Einstein developed the quantum theory of light in ...
... explained by the electromagnetic theory of light. Albert Einstein developed the quantum theory of light in ...
Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity Magnetism and
... 4. Hund’s Rule must be obeyed: most stable arrangement of electrons is that with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. Orbitals are filled one electron at a time until all orbitals of a subshell contain one electron, then any remaining electrons are added to complete the shell. Electron Configur ...
... 4. Hund’s Rule must be obeyed: most stable arrangement of electrons is that with the maximum number of unpaired electrons. Orbitals are filled one electron at a time until all orbitals of a subshell contain one electron, then any remaining electrons are added to complete the shell. Electron Configur ...
Cyclotron radiation
... An electron moves in the xy plane under the action of a constant and uniform magnetic field B = B0 ẑ. Assume the motion to be non-relativistic and the initial velocity to have modulus v (≪ c). a) Characterize the radiation emitted by the electron, specifying its frequency and its polarization along ...
... An electron moves in the xy plane under the action of a constant and uniform magnetic field B = B0 ẑ. Assume the motion to be non-relativistic and the initial velocity to have modulus v (≪ c). a) Characterize the radiation emitted by the electron, specifying its frequency and its polarization along ...
Fermions
... Sometimes we will use this convention when highlighting the spinor indices in products - ie. a, b etc with no raising or lowering convention (they will appear up or down, wherever convenient). Having defined a scalar quantity we can define the Dirac action µ LD = ψ̄a (iγab ∂µ − m × 1ab )ψb , µ which ...
... Sometimes we will use this convention when highlighting the spinor indices in products - ie. a, b etc with no raising or lowering convention (they will appear up or down, wherever convenient). Having defined a scalar quantity we can define the Dirac action µ LD = ψ̄a (iγab ∂µ − m × 1ab )ψb , µ which ...
L 34 Modern Physics [1]
... • In the classical picture, the electrons in atoms orbit around the nucleus just as the planets orbit around the Sun. • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose al ...
... • In the classical picture, the electrons in atoms orbit around the nucleus just as the planets orbit around the Sun. • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose al ...
Ch27CTans
... (FE = qE) and begins moving upward. Once it starts moving, it feels a force due to the Bfield. If velocity is up, and B is out of the page, the right-hand-rule gives a force, due to the B-field, to the right. The same is true when the E-field is down and the B-field is down. This force due to the li ...
... (FE = qE) and begins moving upward. Once it starts moving, it feels a force due to the Bfield. If velocity is up, and B is out of the page, the right-hand-rule gives a force, due to the B-field, to the right. The same is true when the E-field is down and the B-field is down. This force due to the li ...
Electromagnetic Radiation
... Radiation-form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Electromagnetic Spectrum-ordered arrangement by wavelength or frequency for all forms of electromagnetic radiation. ...
... Radiation-form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space. Electromagnetic Spectrum-ordered arrangement by wavelength or frequency for all forms of electromagnetic radiation. ...
4-1. 1 - Riverside Local Schools
... 1. The PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when… 2. Light was known to be a form of energy, capable of… 3. Scientists couldn’t explain why the light had to be of a minimum frequency in order for the… LIGHT AS PARTICLES (pg. 93-94) 1. Max Planck suggested that an obj ...
... 1. The PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when… 2. Light was known to be a form of energy, capable of… 3. Scientists couldn’t explain why the light had to be of a minimum frequency in order for the… LIGHT AS PARTICLES (pg. 93-94) 1. Max Planck suggested that an obj ...
Chapter 1 Atoms Properties of Matter Intensive vs. Extensive
... Chapter 1 Atoms Properties of Matter o Intensive vs. Extensive, physical vs. chemical Chemical Change Physical Change Mixtures and Pure Substances Elements and Compounds o Group or Family o Period or Row o Metals o Nonmetals o Metalloids Chapter 2 Scientific Method SI Units of Measur ...
... Chapter 1 Atoms Properties of Matter o Intensive vs. Extensive, physical vs. chemical Chemical Change Physical Change Mixtures and Pure Substances Elements and Compounds o Group or Family o Period or Row o Metals o Nonmetals o Metalloids Chapter 2 Scientific Method SI Units of Measur ...
Chemistry Name______________________________________
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
Shapes of the Charge Clouds
... visible objects. •Therefore… we cannot tell exactly where an e- is at any given time or how it got there. •We CAN predict the position of the e- ...
... visible objects. •Therefore… we cannot tell exactly where an e- is at any given time or how it got there. •We CAN predict the position of the e- ...
[2011 question paper]
... ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger equation for the time-evolution of the above particle and find its stationary states and their energies. (e) Suppose a particle in the above initial state ψ(x, t = 0) evolves in time acco ...
... ∆x = hx2 i − hxi2 in the above initial gaussian wave packet state. (d) Write down the free particle Schrödinger equation for the time-evolution of the above particle and find its stationary states and their energies. (e) Suppose a particle in the above initial state ψ(x, t = 0) evolves in time acco ...
Statistical laws
... §1 Statistical laws of macroscopic matter Statistical laws In classic physics, the motion of a single particle will obey Newton’s law. If the initial position and velocity are known, we can predict its position at any time by solving the Newton equation of motions. A macroscopic body has a large ...
... §1 Statistical laws of macroscopic matter Statistical laws In classic physics, the motion of a single particle will obey Newton’s law. If the initial position and velocity are known, we can predict its position at any time by solving the Newton equation of motions. A macroscopic body has a large ...
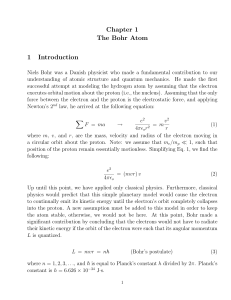
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
... physics would predict that this simple planetary model would cause the electron to continually emit its kinetic energy until the electron’s orbit completely collapses into the proton. A new assumption must be added to this model in order to keep the atom stable, otherwise, we would not be here. At t ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.











![L 34 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001537103_1-dca58a96feb57d01fab60ba8bdd791ec-300x300.png)








![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)