1 Electrons in Atoms
... ionic bond : also called the electrovalent or heteropolar bond is and interaction between two ionized atoms. ionization energy : energy required to remove an electron from an atom. electron affinity : the energy available or attractive potential energy of an atom to attract an electron. covalent bon ...
... ionic bond : also called the electrovalent or heteropolar bond is and interaction between two ionized atoms. ionization energy : energy required to remove an electron from an atom. electron affinity : the energy available or attractive potential energy of an atom to attract an electron. covalent bon ...
energy levels
... energy levels in an atom – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
... energy levels in an atom – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... • Extensively studied by atomic theorists such as Bohr. • High energy sparks cause hydrogen gas molecules (H-H) to break apart suddenly, with some electrons in higher energy levels than would be expected normally. • As the electrons fall back to their ground states, energy is ...
... • Extensively studied by atomic theorists such as Bohr. • High energy sparks cause hydrogen gas molecules (H-H) to break apart suddenly, with some electrons in higher energy levels than would be expected normally. • As the electrons fall back to their ground states, energy is ...
Light - UDChemistry
... momentum of an electron simultaneously • The only way to know anything about an electron is to shoot it with a photon • The photon alters the position and/or momentum in an unpredictable manner, so the original position and momentum remain unknown. ...
... momentum of an electron simultaneously • The only way to know anything about an electron is to shoot it with a photon • The photon alters the position and/or momentum in an unpredictable manner, so the original position and momentum remain unknown. ...
BCIT Fall 2012 Chem 3615 Exam #2
... Section II: Short answer calculations do not need to be shown (16 points total). ...
... Section II: Short answer calculations do not need to be shown (16 points total). ...
Introduction to quantum mechanics
... Quantum mechanics is the study of mechanical systems whose dimensions are close to the atomic scale. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics with wide applications. Quantum theory generalizes classical mechanics to provide accurate descriptions for many previously unexplained phenomena ...
... Quantum mechanics is the study of mechanical systems whose dimensions are close to the atomic scale. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics with wide applications. Quantum theory generalizes classical mechanics to provide accurate descriptions for many previously unexplained phenomena ...
TAP 534- 3: Annihilation and pair production: bubble chamber pictures
... to four pairs of pions ( and ). These curve in opposite directions in the magnetic field. To think about: ...
... to four pairs of pions ( and ). These curve in opposite directions in the magnetic field. To think about: ...
Ch 5 Electrons in Atoms
... 2. Describe the structure of atoms according to the Rutherford atomic model 3. Compare each of the following scientists concept of the atom: Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr 4. Of the three subatomic particles, identify which determines the element and which can be lost/gained and the atom still be ...
... 2. Describe the structure of atoms according to the Rutherford atomic model 3. Compare each of the following scientists concept of the atom: Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr 4. Of the three subatomic particles, identify which determines the element and which can be lost/gained and the atom still be ...
Quantum Number, n. - Lyndhurst Schools
... Equation gives rise to ‘Orbitals.’ These orbitals provide the electron density distributed about the nucleus. Orbitals are described by quantum numbers. ...
... Equation gives rise to ‘Orbitals.’ These orbitals provide the electron density distributed about the nucleus. Orbitals are described by quantum numbers. ...
I. Waves & Particles
... shines on the metal Hmm… (For a given metal, no electrons were emitted if the light’s frequency was below a certain minimum – why did light have to be of a minimum frequency?) ...
... shines on the metal Hmm… (For a given metal, no electrons were emitted if the light’s frequency was below a certain minimum – why did light have to be of a minimum frequency?) ...
Homework Set 1
... any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) classical Bohr orbit. d. Using the Bohr theory, calculate the ionization energi ...
... any system is the most in need of a quantum description.) c. Taking λ/r ≤ 0.1 as the (arbitrary) cut-off when classical mechanics begins to be valid as Bohr’s quantum number n increases, calculate the lowest (smallest n) classical Bohr orbit. d. Using the Bohr theory, calculate the ionization energi ...
e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... Atomic Structure The results of many experiments collectively suggest that all matter is made up of small, indivisible units which have a unique identity. Study of chemistry suggests a number of elementary substances (elements) that show unique chemical behavior. These elements are made up of ident ...
... Atomic Structure The results of many experiments collectively suggest that all matter is made up of small, indivisible units which have a unique identity. Study of chemistry suggests a number of elementary substances (elements) that show unique chemical behavior. These elements are made up of ident ...
PPA6_Lecture_Ch_27
... Photons passing through matter can undergo the following interactions: 1. Photoelectric effect: photon is completely absorbed, electron is ejected 2. Photon may be totally absorbed by electron, but not have enough energy to eject it; the electron moves into an excited state 3. The photon can scatter ...
... Photons passing through matter can undergo the following interactions: 1. Photoelectric effect: photon is completely absorbed, electron is ejected 2. Photon may be totally absorbed by electron, but not have enough energy to eject it; the electron moves into an excited state 3. The photon can scatter ...
Notes-17
... When an atom or molecule is exposed to an electromagnetic field, it can undergo energy and momentum exchange with the photon field, i.e., it can absorb or emit radiations. To describe the electromagnetic field using the concept of photons, one has to use quantum electrodynamics (QED) where the elect ...
... When an atom or molecule is exposed to an electromagnetic field, it can undergo energy and momentum exchange with the photon field, i.e., it can absorb or emit radiations. To describe the electromagnetic field using the concept of photons, one has to use quantum electrodynamics (QED) where the elect ...
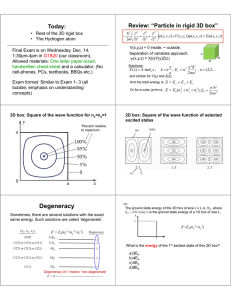
Degeneracy
... – Why? Fits to spectral lines of Hydrogen – Problem: No reason for fixed energy levels Structure doesn’t fit physics ...
... – Why? Fits to spectral lines of Hydrogen – Problem: No reason for fixed energy levels Structure doesn’t fit physics ...
The Lippmann-Schwinger equation reads ψk(x) = φk(x) + ∫ dx G0(x
... (One should remember that this is only true for elastic scattering, while in the general case a factor kf /ki must be introduced). Common approximations to the exact expression for the scattering amplitude are briefly enumerated. • Born approximation means first-order approximation in the potential ...
... (One should remember that this is only true for elastic scattering, while in the general case a factor kf /ki must be introduced). Common approximations to the exact expression for the scattering amplitude are briefly enumerated. • Born approximation means first-order approximation in the potential ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.



















![L 33 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003217156_1-265c5a519e2bca3f33717b4abd842898-300x300.png)
![L 34 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008622077_1-047a8df5b8f51427a7d951942e25e95f-300x300.png)