Lecture 3 Teaching notes
... the probability of occupation of a quantum state is A exp(-E/kT) ? The answer is clearly no. A grows to be very big at low temperatures, but the Pauli exclusion principle says that the occupation of a state can only be 0 or 1. So the Boltzmann distribution would violate this quantum principle. It ne ...
... the probability of occupation of a quantum state is A exp(-E/kT) ? The answer is clearly no. A grows to be very big at low temperatures, but the Pauli exclusion principle says that the occupation of a state can only be 0 or 1. So the Boltzmann distribution would violate this quantum principle. It ne ...
Do your homework on a separate piece of paper, or
... 12. How does the concept of the photon explain 4)? Kinetic energy depends on the energy of each photon, not how many photons are hitting the metal. 13. How does the concept of the photon explain 5)? Because the kinetic energy is dependent on the energy of the photon, and because the photon’s energy ...
... 12. How does the concept of the photon explain 4)? Kinetic energy depends on the energy of each photon, not how many photons are hitting the metal. 13. How does the concept of the photon explain 5)? Because the kinetic energy is dependent on the energy of the photon, and because the photon’s energy ...
Winter 2008 Physics 315 / 225
... Component of E along transmission axis is transmitted After a Polaroid sheet the direction of E is along the transmission axis ...
... Component of E along transmission axis is transmitted After a Polaroid sheet the direction of E is along the transmission axis ...
Lecture 17: Bohr Model of the Atom
... hydrogen to develop a quantum model for H. • Central idea: electron circles the “nucleus” in only certain allowed circular orbitals. • Bohr postulates that there is Coulombic attraction between e- and nucleus. However, classical physics is unable to explain why an H atom doesn’t simply collapse. ...
... hydrogen to develop a quantum model for H. • Central idea: electron circles the “nucleus” in only certain allowed circular orbitals. • Bohr postulates that there is Coulombic attraction between e- and nucleus. However, classical physics is unable to explain why an H atom doesn’t simply collapse. ...
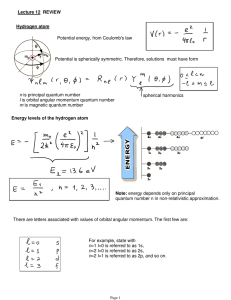
Lecture 12: Review.
... interactions of electrons with the quantized electromagnetic field. In QED, a quantized radiation field in the lowest-energy state of NOT the one with ZERO electromagnetic fields, but there exist zero-point oscillations. Then, there are non-zero electromagnetic fields that are present even in the ab ...
... interactions of electrons with the quantized electromagnetic field. In QED, a quantized radiation field in the lowest-energy state of NOT the one with ZERO electromagnetic fields, but there exist zero-point oscillations. Then, there are non-zero electromagnetic fields that are present even in the ab ...
n = 2. - Cloudfront.net
... sends photons into the crystal. This sends some atoms into a higher energy state, electrons drop into lower energy levels releasing more photons. ...
... sends photons into the crystal. This sends some atoms into a higher energy state, electrons drop into lower energy levels releasing more photons. ...
École Doctorale de Physique de la Région Parisienne
... antiferromagnet-normal metal transition. Near such a quantum phase transition the system develops an SU(2) order parameter, which characterizes the mixture of superconductivity with a charge density wave. The resulting states, which completely differ from the original antiferromagnetic state, are de ...
... antiferromagnet-normal metal transition. Near such a quantum phase transition the system develops an SU(2) order parameter, which characterizes the mixture of superconductivity with a charge density wave. The resulting states, which completely differ from the original antiferromagnetic state, are de ...
TALK - ECM
... The coupling constants and the field, time and wave number scales depend on T and the RG parameter s=log[/k] ...
... The coupling constants and the field, time and wave number scales depend on T and the RG parameter s=log[/k] ...
Chemistry 1 Practice Final Exam - Tutor
... n = 2, l = 1, ml = 1 : n = 4, l = 2, ml = -2 : n = 3, l = 1, ml = 2 : n = 2, l = 2, ml = -1 ...
... n = 2, l = 1, ml = 1 : n = 4, l = 2, ml = -2 : n = 3, l = 1, ml = 2 : n = 2, l = 2, ml = -1 ...
Schrodinger_Uncertainty
... interfere?” • One way to interpret this is to consider that while it is not possible to specify in advance where a particular electron will hit the screen after passing through one or the other slit, one can predict the probability of it hitting at a certain location. • Bright fringes correspond to ...
... interfere?” • One way to interpret this is to consider that while it is not possible to specify in advance where a particular electron will hit the screen after passing through one or the other slit, one can predict the probability of it hitting at a certain location. • Bright fringes correspond to ...
Schwennesen Fundamental Particles and the Physics of the
... rotation; thus, if an observer saw a particle rotating clockwise, the particle’s angular momentum would be directed away from this observer [6, p. 30]. Angular momentum came to be identified as an intrinsic aspect of fundamental particles through experiments testing the Zeeman effect, in which a mag ...
... rotation; thus, if an observer saw a particle rotating clockwise, the particle’s angular momentum would be directed away from this observer [6, p. 30]. Angular momentum came to be identified as an intrinsic aspect of fundamental particles through experiments testing the Zeeman effect, in which a mag ...
Kvantfysik Lecture Notes No. 4x
... Z, that is the charge of the nucleus, was unknown before Moseley’s work. In fact, Moseley could see gaps along the lines at Z = 43, 61 and 75, allowing him to predict the existence of these elements. (Note that L and K in the figure refer to the Lα line and the Kα line. The Kα and Lα are actually pa ...
... Z, that is the charge of the nucleus, was unknown before Moseley’s work. In fact, Moseley could see gaps along the lines at Z = 43, 61 and 75, allowing him to predict the existence of these elements. (Note that L and K in the figure refer to the Lα line and the Kα line. The Kα and Lα are actually pa ...
Quantum numbers
... why do halogens (X) form X2 in the gas phase? why do the alkali metals (Li, Na, ….) do so too? ...
... why do halogens (X) form X2 in the gas phase? why do the alkali metals (Li, Na, ….) do so too? ...
Physics 30 Lesson 34 – Quantum Mechanics
... function. While quantum mechanics is a highly successful mathematical model, it is not easily visualized as a physical model. Schrödinger’s model describes the electrons belonging to an atom in terms of four quantum numbers (see below) from which the wave function for each electron can be calculated ...
... function. While quantum mechanics is a highly successful mathematical model, it is not easily visualized as a physical model. Schrödinger’s model describes the electrons belonging to an atom in terms of four quantum numbers (see below) from which the wave function for each electron can be calculated ...
Quantum electrodynamics

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.In technical terms, QED can be described as a perturbation theory of the electromagnetic quantum vacuum. Richard Feynman called it ""the jewel of physics"" for its extremely accurate predictions of quantities like the anomalous magnetic moment of the electron and the Lamb shift of the energy levels of hydrogen.