Version
... personality can be very dangerous too, however, quick medical help is necessary. Other mental health issues Yes, a person who is suffering from DID, may also suffer from other various mental illness, including- high degree of depression, silence, anxiety, distress, and such sort of patients may harm ...
... personality can be very dangerous too, however, quick medical help is necessary. Other mental health issues Yes, a person who is suffering from DID, may also suffer from other various mental illness, including- high degree of depression, silence, anxiety, distress, and such sort of patients may harm ...
Mental Disorders
... This is a collection of diseases that severely affect the brain and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available ...
... This is a collection of diseases that severely affect the brain and thinking processes. These people have difficulty thinking rationally and their judgments are impaired. Living their daily life becomes very, very difficult. However, for even the worst of these disorders there is treatment available ...
available now #2
... • Review the DSM-5 changes to mood disorder diagnostic criteria • Discuss differential diagnosis of depressive disorders • Introduce new pharmacological agents for treatment of depressive disorders and strategies for their use • Discuss the use of diagnostic testing in the treatment of mood disorder ...
... • Review the DSM-5 changes to mood disorder diagnostic criteria • Discuss differential diagnosis of depressive disorders • Introduce new pharmacological agents for treatment of depressive disorders and strategies for their use • Discuss the use of diagnostic testing in the treatment of mood disorder ...
personality disorders histrionic personality disorder
... behaviour. The individual may also behave in a sexually provocative and flirtatious manner towards others, even if the individual does not have a sexual interest or attraction towards the person, and this behaviour is often socially and professionally inappropriate. They may also consider relationsh ...
... behaviour. The individual may also behave in a sexually provocative and flirtatious manner towards others, even if the individual does not have a sexual interest or attraction towards the person, and this behaviour is often socially and professionally inappropriate. They may also consider relationsh ...
Mood Disorders
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
... Major Depressive Disorder Depression is the “common cold” of psychological disorders. In a year, 5.8% of men and 9.5% of women report depression worldwide (WHO, 2002). ...
Electrode Placement for Chest Leads, V1 to V6
... 2.Diminished interest or pleasure in all or most activities 3.Significant change in weight or appetite (continued) ...
... 2.Diminished interest or pleasure in all or most activities 3.Significant change in weight or appetite (continued) ...
Slide 1
... syndrome do not develop a psychotic disorder, but 20-40% do so within 1 year Advantages of early intervention and hope for recovery: describe high level of functioning now associated with psychosis ...
... syndrome do not develop a psychotic disorder, but 20-40% do so within 1 year Advantages of early intervention and hope for recovery: describe high level of functioning now associated with psychosis ...
E1, PTSD: Impact on Everyday Activities
... Horses are used as tools for military veterans to gain self-understanding and emotional growth ...
... Horses are used as tools for military veterans to gain self-understanding and emotional growth ...
Case Report A Novel Study of Comorbidity
... traits, rather than a personality disorder per se, seem more likely in these disorders, and they tend to resemble the cluster C category of disorders in DSM-IV [1, 2]. Schizoaffective disorder is episodic in which both affective and schizophrenic symptoms are prominent within the same episode of ill ...
... traits, rather than a personality disorder per se, seem more likely in these disorders, and they tend to resemble the cluster C category of disorders in DSM-IV [1, 2]. Schizoaffective disorder is episodic in which both affective and schizophrenic symptoms are prominent within the same episode of ill ...
Perspectives on Psychological Disorders
... • and perhaps excessive guilt or feelings of worthlessness. ...
... • and perhaps excessive guilt or feelings of worthlessness. ...
ANXIETY DISORDERS - Wikispaces
... Major Depressive disorder (unipolar depression)- the common cold of psychology. DSM criteria is more than 2 weeks of hopelessness, worthlessness, fatigue, and/or change of appetite, sleeping pattern. Women are 2 times more likely to get. Dysthymic Disorder mild depression 2 years or more Bipolar dis ...
... Major Depressive disorder (unipolar depression)- the common cold of psychology. DSM criteria is more than 2 weeks of hopelessness, worthlessness, fatigue, and/or change of appetite, sleeping pattern. Women are 2 times more likely to get. Dysthymic Disorder mild depression 2 years or more Bipolar dis ...
Young Adults with Bipolar Disorder
... Considered good workers during their manic episodes, and often don’t want to take medications because it reduces their “production” Often seen as school failures, occupational problems, and poor relationship partners First episode of a male is typically mania, females first episode is most oft ...
... Considered good workers during their manic episodes, and often don’t want to take medications because it reduces their “production” Often seen as school failures, occupational problems, and poor relationship partners First episode of a male is typically mania, females first episode is most oft ...
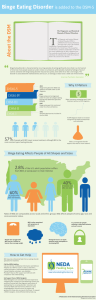
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
Bipolar Disorder: A Biopsychosocial Overview
... Bipolar disorder characterized by a hypersensitivity in the wanting circuit ...
... Bipolar disorder characterized by a hypersensitivity in the wanting circuit ...
a severe mood disorder characterized by major
... Having close biological relatives who were diagnosed with depression increases your chances of becoming depressed. Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression ...
... Having close biological relatives who were diagnosed with depression increases your chances of becoming depressed. Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression ...
PSYCHOLOGY MID-TERM REVIEW GUIDE
... 44. What is disrupted when we experience “jet lag?” 45. In the very beginning, what did psychology focus on? 46. In the first half of the 20th century, what did psychology shift its focus to? 47. What is cognitive analysis? 48. What are hallucinations? 49. Which machine is used to measure brainwaves ...
... 44. What is disrupted when we experience “jet lag?” 45. In the very beginning, what did psychology focus on? 46. In the first half of the 20th century, what did psychology shift its focus to? 47. What is cognitive analysis? 48. What are hallucinations? 49. Which machine is used to measure brainwaves ...
Overview of Mental Illness PowerPoint
... combination of psychosocial supports (e.g. family involvement, work or school support, psychotherapy and self-management strategies) and medications (to reduce symptom intensity). Unfortunately, fewer than one-third of adults and one-half of children with diagnosed mental health disorders receive ...
... combination of psychosocial supports (e.g. family involvement, work or school support, psychotherapy and self-management strategies) and medications (to reduce symptom intensity). Unfortunately, fewer than one-third of adults and one-half of children with diagnosed mental health disorders receive ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 38 garber edits
... Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms ...
... Formerly called manic-depressive disorder. An alternation between depression and mania signals bipolar disorder. Depressive Symptoms ...
DSM5 Diagnostic Criteria
... A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple context, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive; see text): 1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approa ...
... A. Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple context, as manifested by the following, currently or by history (examples are illustrative, not exhaustive; see text): 1. Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, ranging, for example, from abnormal social approa ...
Psychiatric illnesses in Children and Adolescents: types and treatment
... avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort (such as schoolwork or homework) difficulty organizing tasks and activities fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in schoolwork, work, or other activities Can’t sustain attention i ...
... avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort (such as schoolwork or homework) difficulty organizing tasks and activities fails to give close attention to details or makes careless mistakes in schoolwork, work, or other activities Can’t sustain attention i ...
Notes 3-13
... • Acute onset • Reversible • Hallucinations, illusions, misperceptions • Abnormal EEG ...
... • Acute onset • Reversible • Hallucinations, illusions, misperceptions • Abnormal EEG ...
- National Affairs
... DSM to which their title refers is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, a weighty tome currently in its fourth incarnation and therefore known as DSM-IV for short. Produced and published by the American Psychiatric Association, it is supposed to bring sonqe order to the bewilde ...
... DSM to which their title refers is the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, a weighty tome currently in its fourth incarnation and therefore known as DSM-IV for short. Produced and published by the American Psychiatric Association, it is supposed to bring sonqe order to the bewilde ...
Mental Health Nursing II NURS 2310
... frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at same developmental level Hyperactivity = excessive psychomotor activity that may be purposeful or aimless, accompanied by physical movements that are usually more rapid than normal Impulsitivity = acting without reflection and with ...
... frequent and severe than is typically observed in individuals at same developmental level Hyperactivity = excessive psychomotor activity that may be purposeful or aimless, accompanied by physical movements that are usually more rapid than normal Impulsitivity = acting without reflection and with ...
File
... disorganized speech and behaviors. It is relatively rare (0.5-1%) of the population of the world. ...
... disorganized speech and behaviors. It is relatively rare (0.5-1%) of the population of the world. ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.