Chapter 12
... Psychoanalysis – problems from unresolved, unconscious clashes between internal desires & environmental pressures. Social-Cognitive – result of past learning & current situations. Humanistic – person’s natural tendency toward healthy growth is blocked by not being aware of or have the ability to exp ...
... Psychoanalysis – problems from unresolved, unconscious clashes between internal desires & environmental pressures. Social-Cognitive – result of past learning & current situations. Humanistic – person’s natural tendency toward healthy growth is blocked by not being aware of or have the ability to exp ...
AP Psych 15 sq AP Psych-Psychological Disorders-SQ
... 5. Describe four common features of PTSD. 6. How does psychoanalytic theory explain the development of anxiety disorders? What research supports this? 7. How do cognitive factors contribute to anxiety disorders, particularly panic disorder? What research supports these explanations? 8. Describe thre ...
... 5. Describe four common features of PTSD. 6. How does psychoanalytic theory explain the development of anxiety disorders? What research supports this? 7. How do cognitive factors contribute to anxiety disorders, particularly panic disorder? What research supports these explanations? 8. Describe thre ...
Lecture 2
... contact with reality, and of emotional responsiveness. Delusions and hallucinations (especially of voices) are usual features, and the person may feel that thoughts, sensations and actions are controlled by or shared with others. The person may become socially withdrawn and lose energy. No single ca ...
... contact with reality, and of emotional responsiveness. Delusions and hallucinations (especially of voices) are usual features, and the person may feel that thoughts, sensations and actions are controlled by or shared with others. The person may become socially withdrawn and lose energy. No single ca ...
Mental Health and our Faithful Response
... • Stigma (“I don’t want people to know that I’m in therapy.” “I have problems, but I’m not crazy.”) • Misunderstanding (“Just try harder.” “Look on the brighter side.” “I’ve got the blues, but I don’t think I’m depressed”. “I don’t want to use medication as a crutch.”) • Neglect (“I don’t want to pa ...
... • Stigma (“I don’t want people to know that I’m in therapy.” “I have problems, but I’m not crazy.”) • Misunderstanding (“Just try harder.” “Look on the brighter side.” “I’ve got the blues, but I don’t think I’m depressed”. “I don’t want to use medication as a crutch.”) • Neglect (“I don’t want to pa ...
The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
... let me know whether I’ve succeeded and how I could improve on your evaluation form and Facebook. ...
... let me know whether I’ve succeeded and how I could improve on your evaluation form and Facebook. ...
Document
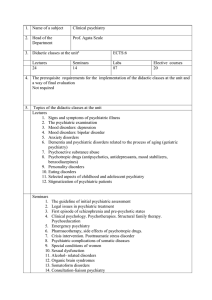
... Topics of the didactic classes at the unit Lectures 1. Signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness 2. The psychiatric examination 3. Mood disorders: depression 4. Mood disorders: bipolar disorder 5. Anxiety disorders 6. Dementia and psychiatric disorders related to the process of aging (geriatric psyc ...
... Topics of the didactic classes at the unit Lectures 1. Signs and symptoms of psychiatric illness 2. The psychiatric examination 3. Mood disorders: depression 4. Mood disorders: bipolar disorder 5. Anxiety disorders 6. Dementia and psychiatric disorders related to the process of aging (geriatric psyc ...
The DSM-V
... • Not all diagnoses meet Robins and Guze criteria for validity (such as Mathematics Disorder). • Not all criteria are based on scientific data. Some of them are based on subjective committee decisions. • High level of comorbidity = individuals with one diagnosis frequently have one or more additiona ...
... • Not all diagnoses meet Robins and Guze criteria for validity (such as Mathematics Disorder). • Not all criteria are based on scientific data. Some of them are based on subjective committee decisions. • High level of comorbidity = individuals with one diagnosis frequently have one or more additiona ...
XII. Psychological Disorders
... - Previously called multiple personality. - People have two or more distinct personalities that alternately control behavior. - Why is this disorder so controversial? ...
... - Previously called multiple personality. - People have two or more distinct personalities that alternately control behavior. - Why is this disorder so controversial? ...
Mood Disorders, Dissociation, Schizophrenia, and Personality
... some type of mild depression in their life often due to some external sad event. Major Depressive Disorder: differentiates itself from mild depression since a person has depressed mood, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished ...
... some type of mild depression in their life often due to some external sad event. Major Depressive Disorder: differentiates itself from mild depression since a person has depressed mood, feelings of worthlessness, and diminished ...
Co-occurring Disorders: Drug Abuse And Mental Health
... phobias, and general anxiety disorder, are high in treatment populations, ranging from 10 to 60 percent. Eating disorders. Most studies find that between 15 and 32 percent of women with alcohol/drug disorders meet diagnostic criteria for an eating disorder at some time in their lives. ...
... phobias, and general anxiety disorder, are high in treatment populations, ranging from 10 to 60 percent. Eating disorders. Most studies find that between 15 and 32 percent of women with alcohol/drug disorders meet diagnostic criteria for an eating disorder at some time in their lives. ...
Conscious symptom production and unconscious motivation
... – Significant appetite/weight change – Psychomotor agitation/retardation – Pervasive loss of energy/fatigue – Feeling worthless; excessive or inappropriate guilt – Recurrent thoughts of death/suicide Symptoms present for 2 weeks ...
... – Significant appetite/weight change – Psychomotor agitation/retardation – Pervasive loss of energy/fatigue – Feeling worthless; excessive or inappropriate guilt – Recurrent thoughts of death/suicide Symptoms present for 2 weeks ...
Anxiety Disorders
... •Women are more likely to be affected than men. •Rape is the most likely trigger of PTSD, 65% of men and 45.9% of women who are raped will develop ...
... •Women are more likely to be affected than men. •Rape is the most likely trigger of PTSD, 65% of men and 45.9% of women who are raped will develop ...
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder - Association for Academic Psychiatry
... Derealization Depersonalization Dissociative amnesia ...
... Derealization Depersonalization Dissociative amnesia ...
Downloadable PowerPoint Presentation
... of adult onset BAD Characterized by a mixed presentation versus discrete episode of depression & mania First episode more likely mixed or mania, with irritability & “affective storm” then euphoria Often predicts a chronic or rapid cycling course & poor or partial response ...
... of adult onset BAD Characterized by a mixed presentation versus discrete episode of depression & mania First episode more likely mixed or mania, with irritability & “affective storm” then euphoria Often predicts a chronic or rapid cycling course & poor or partial response ...
General classes of disorders
... Depression is a serious disorder that afflicts approximately 14 million adults in the United States each year. The lifetime prevalence rate of depression in the United States has been estimated to include 16 percent of adults (21 percent of women, 13 percent of men), or more than 32 million people ...
... Depression is a serious disorder that afflicts approximately 14 million adults in the United States each year. The lifetime prevalence rate of depression in the United States has been estimated to include 16 percent of adults (21 percent of women, 13 percent of men), or more than 32 million people ...
3 Mood Disorders
... To be classified as MDD, the DSM-5 says you need to have over two weeks of these symptoms: ...
... To be classified as MDD, the DSM-5 says you need to have over two weeks of these symptoms: ...
An Overview of Psychiatric Disorders Commonly Seen in
... evaluated by history, physical and labs ( CBC,CMP, thyroid studies, and vitamin D level) to rule out secondary medical causes , such as Thyroid Disease, Substance Abuse or Vitamin D Insuffiency. Distinguish Unipolar vs. Bipolar Depression – screen for ...
... evaluated by history, physical and labs ( CBC,CMP, thyroid studies, and vitamin D level) to rule out secondary medical causes , such as Thyroid Disease, Substance Abuse or Vitamin D Insuffiency. Distinguish Unipolar vs. Bipolar Depression – screen for ...
Mood Disorders, Dissociation, Schizophrenia, and Personality
... Stressful events usually precede depression Depression is striking more and earlier ...
... Stressful events usually precede depression Depression is striking more and earlier ...
Schizophrenia
... • the most debilitating mental illnesses • Greek terms - "splitting of the mind” • do not have more than one distinct personality • distortions in their perceptions, feelings, and relationships with the world around them. • 1% of the population suffer (in 12 m period) ...
... • the most debilitating mental illnesses • Greek terms - "splitting of the mind” • do not have more than one distinct personality • distortions in their perceptions, feelings, and relationships with the world around them. • 1% of the population suffer (in 12 m period) ...
(1) sex (men vs women), (2)
... treatment. In OCD there is an increase in activity in a neuronal circuit running from the frontal cortex to the cingulate gyrus, striatum, globus pallidus, thalamus and back to the frontal cortex. Surgical interruption of this loop by cingulotomy (destruction of 2–3 cm of white matter) at the anteri ...
... treatment. In OCD there is an increase in activity in a neuronal circuit running from the frontal cortex to the cingulate gyrus, striatum, globus pallidus, thalamus and back to the frontal cortex. Surgical interruption of this loop by cingulotomy (destruction of 2–3 cm of white matter) at the anteri ...
2017 Exam 1 Q`s and A`s - UCF College of Sciences
... A constellation of symptoms [2] that significantly impairs [1] an individual’s ability to function and is characterized by a particular symptom picture with a specifiable onset [1], course [1], duration [1], outcome [1], and response to treatment [1], and associated familial [1], psychosocial [1], a ...
... A constellation of symptoms [2] that significantly impairs [1] an individual’s ability to function and is characterized by a particular symptom picture with a specifiable onset [1], course [1], duration [1], outcome [1], and response to treatment [1], and associated familial [1], psychosocial [1], a ...
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY - Thomas Jefferson High School for …
... Single most effective treatment for psychotic depression Used as treatment of last resort Actual understanding of how it works is not complete--disrupts electrical impulses of brain Within two to four weeks many see profound mood elevation Side Effects include memory loss (usually short term) ...
... Single most effective treatment for psychotic depression Used as treatment of last resort Actual understanding of how it works is not complete--disrupts electrical impulses of brain Within two to four weeks many see profound mood elevation Side Effects include memory loss (usually short term) ...
DSM-5: CONCEPTS, CHANGES, AND CRITIQUE© by Joan Turkus
... realistically feasible today for practitioners is no longer sufficient for researchers…It is increasingly evident that mental illness will be best understood as disorders of brain structure and function…This is the focus of NIMH’s Research Domain Criteria (RDoc) project.” There is a middle ground. W ...
... realistically feasible today for practitioners is no longer sufficient for researchers…It is increasingly evident that mental illness will be best understood as disorders of brain structure and function…This is the focus of NIMH’s Research Domain Criteria (RDoc) project.” There is a middle ground. W ...
changes to diagnostic criteria for eating disorders from dsm-iv
... The chapter on Feeding and Eating Disorders in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) includes quite a few changes from the previous fourth edition (DSM-IV-TR) to better represent the symptoms and behaviours of patients dealing with these conditions (s ...
... The chapter on Feeding and Eating Disorders in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) includes quite a few changes from the previous fourth edition (DSM-IV-TR) to better represent the symptoms and behaviours of patients dealing with these conditions (s ...
Schizoaffective disorder

Schizoaffective disorder (abbreviated as SZA or SAD) is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and deregulated emotions. The diagnosis is made when the patient has features of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder—either bipolar disorder or depression—but does not strictly meet diagnostic criteria for either alone. The bipolar type is distinguished by symptoms of mania, hypomania, or mixed episode; the depressive type by symptoms of depression only. Common symptoms of the disorder include hallucinations, paranoid delusions, and disorganized speech and thinking. The onset of symptoms usually begins in young adulthood, currently with an uncertain lifetime prevalence because the disorder was redefined, but DSM-IV prevalence estimates were less than 1 percent of the population, in the range of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the patient's reported experiences.Genetics, neurobiology, early and current environment, behavioral, social, and experiential components appear to be important contributory factors; some recreational and prescription drugs may cause or worsen symptoms. No single isolated organic cause has been found, but extensive evidence exists for abnormalities in the metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), dopamine, and glutamic acid in people with schizophrenia, psychotic mood disorders, and schizoaffective disorder. People with schizoaffective disorder are likely to have co-occurring conditions, including anxiety disorders and substance use disorder. Social problems such as long-term unemployment, poverty and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is shorter than those without it, due to increased physical health problems from an absence of health promoting behaviors including a sedentary lifestyle, and a higher suicide rate.The mainstay of current treatment is antipsychotic medication combined with mood stabilizer medication or antidepressant medication, or both. There is growing concern by some researchers that antidepressants may increase psychosis, mania, and long-term mood episode cycling in the disorder. When there is risk to self or others, usually early in treatment, brief hospitalization may be necessary. Psychiatric rehabilitation, psychotherapy, and vocational rehabilitation are very important for recovery of higher psychosocial function. As a group, people with schizoaffective disorder diagnosed using DSM-IV and ICD-10 criteria have a better outcome than people with schizophrenia, but have variable individual psychosocial functional outcomes compared to people with mood disorders, from worse to the same. Outcomes for people with DSM-5 diagnosed schizoaffective disorder depend on data from prospective cohort studies, which haven't been completed yet.In DSM-5 and ICD-9 (which is being revised to ICD-10, to be published in 2015), schizoaffective disorder is in the same diagnostic class as schizophrenia, but not in the same class as mood disorders. The diagnosis was introduced in 1933, and its definition was slightly changed in the DSM-5, published in May 2013, because the DSM-IV schizoaffective disorder definition leads to excessive misdiagnosis. The changes made to the schizoaffective disorder definition were intended to make the DSM-5 diagnosis more consistent (or reliable), and to substantially reduce the use of the diagnosis. Additionally, the DSM-5 schizoaffective disorder diagnosis can no longer be used for first episode psychosis.