Unit 1, Lecture 1
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
c2 atomic structure f pmh
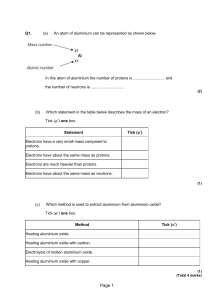
... Electrons have a very small mass compared to protons. Electrons have about the same mass as protons. Electrons are much heavier than protons. Electrons have about the same mass as neutrons. ...
... Electrons have a very small mass compared to protons. Electrons have about the same mass as protons. Electrons are much heavier than protons. Electrons have about the same mass as neutrons. ...
Article 2: Key Concepts and Vocabulary
... Fe, for example, is 45 days; after 45 days, half of it has become 59Co, a stable (non-radioactive) isotope of cobalt, and half is still 59Fe. After 90 days (two halflives) three quarters has become 59Co. The half-lives of 55Fe, 59Fe, and 60Fe are 2.7 years, 45 days, and 2.6 million years, respective ...
... Fe, for example, is 45 days; after 45 days, half of it has become 59Co, a stable (non-radioactive) isotope of cobalt, and half is still 59Fe. After 90 days (two halflives) three quarters has become 59Co. The half-lives of 55Fe, 59Fe, and 60Fe are 2.7 years, 45 days, and 2.6 million years, respective ...
Atoms
... National Science Education Standards NSES B1a. Matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. These components have measurable properties, such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively char ...
... National Science Education Standards NSES B1a. Matter is made of minute particles called atoms, and atoms are composed of even smaller components. These components have measurable properties, such as mass and electrical charge. Each atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively char ...
specific vocabulary of the unit
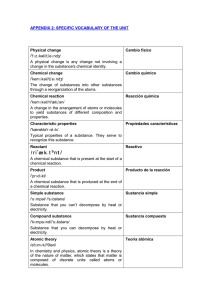
... and can be formed into sheets and other specific properties. Non-metal No metal /nɒn//'metḷ/ A non-metal is a substance that conducts heat and electricity poorly, is brittle, waxy or gaseous, and cannot be hammered into sheets or drawn into wire. Non-metals gain electrons easily to form anions. Abou ...
... and can be formed into sheets and other specific properties. Non-metal No metal /nɒn//'metḷ/ A non-metal is a substance that conducts heat and electricity poorly, is brittle, waxy or gaseous, and cannot be hammered into sheets or drawn into wire. Non-metals gain electrons easily to form anions. Abou ...
build your own atom - brittany
... 2. To be very simple today, we are making a neutrally charged atom, so we will be using equal amounts of protons, neutrons and electrons. Previous art projects have depleted our pom-pom supply, so the two examples we show will have very small atomic numbers. 3. The wire represents the electron path. ...
... 2. To be very simple today, we are making a neutrally charged atom, so we will be using equal amounts of protons, neutrons and electrons. Previous art projects have depleted our pom-pom supply, so the two examples we show will have very small atomic numbers. 3. The wire represents the electron path. ...
Atom questions
... 17. Carbon-14 and Carbon-12, two isotopes of Carbon, differ in the number of isotopes and …… E. Atomic Number F. Atomic Mass G. Number of electrons 18. Heptabromide is an element that has how many atoms? Please, answer on another sheet of paper. 19. Which atomic particle is mostly responsible for an ...
... 17. Carbon-14 and Carbon-12, two isotopes of Carbon, differ in the number of isotopes and …… E. Atomic Number F. Atomic Mass G. Number of electrons 18. Heptabromide is an element that has how many atoms? Please, answer on another sheet of paper. 19. Which atomic particle is mostly responsible for an ...
atoms = building blocks
... • Matter- the stuff that makes up everything in the universe • Element- A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means ...
... • Matter- the stuff that makes up everything in the universe • Element- A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means ...
NOTES – 14.1 – Structure of the Atom (FPS3)
... Atoms are normally neutral, but the things that make them up are charged. ...
... Atoms are normally neutral, but the things that make them up are charged. ...
Drawing Atomic Structure
... Protons and Neutrons can both be broken down even farther into quarks. More info on pg. 508 ...
... Protons and Neutrons can both be broken down even farther into quarks. More info on pg. 508 ...
The periodic table and the atom part 2
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element in atomic mass units . Though individual atoms always have an integer number of atomic mass units, the atomic mass on the periodic table is stated as a decimal number because it is an average of the various isotopes of an element. The average number ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element in atomic mass units . Though individual atoms always have an integer number of atomic mass units, the atomic mass on the periodic table is stated as a decimal number because it is an average of the various isotopes of an element. The average number ...
Chapter 3 Chemistry I notes
... • Atomic Theory of Matter – Each element is made of small particles called atoms – All atoms of same element are identical. – Atoms are neither created or destroyed – A given compound has the same number and kind of atoms ...
... • Atomic Theory of Matter – Each element is made of small particles called atoms – All atoms of same element are identical. – Atoms are neither created or destroyed – A given compound has the same number and kind of atoms ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions (2)
... given chemical compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of atoms—changes in the way they are bound together. The atoms themselves remain ...
... given chemical compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of atoms—changes in the way they are bound together. The atoms themselves remain ...
ChemCh4and6of2011
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reaction? 88. What does a ca ...
... 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reaction? 88. What does a ca ...
Unit 2 Notes Atomic
... ____________ available energy levels (the configuration on the periodic table) ! Excited state: electrons no longer occupy the lowest energy levels. One or more electrons ________ to a higher energy level (different than electron configuration ...
... ____________ available energy levels (the configuration on the periodic table) ! Excited state: electrons no longer occupy the lowest energy levels. One or more electrons ________ to a higher energy level (different than electron configuration ...
What are atoms like???
... For example, the resistance of mercury suddenly drops at 268.8°C. This is called superconductivity. The temprature where it drops is called the critical temperature. There are two types of superconductor: Type 1: which are metals Type 2: which are alloys ...
... For example, the resistance of mercury suddenly drops at 268.8°C. This is called superconductivity. The temprature where it drops is called the critical temperature. There are two types of superconductor: Type 1: which are metals Type 2: which are alloys ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
... hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is an atom. Each chemical element consists of only one type of atom. For example, pure 24K gold is composed of ...
... hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is an atom. Each chemical element consists of only one type of atom. For example, pure 24K gold is composed of ...
Monday, September 29
... • Max Born: Working with Heisenberg in 1927, Born modified Schrodinger's equation of quantum mechanics. His idea helped scientists develop the model of an atom with a nucleus surrounded by electrons at different locations when they are in different energy states. ...
... • Max Born: Working with Heisenberg in 1927, Born modified Schrodinger's equation of quantum mechanics. His idea helped scientists develop the model of an atom with a nucleus surrounded by electrons at different locations when they are in different energy states. ...
Notes for Unit 2
... From 1898-1907 Ernest Rutherford was doing some work and he shot some positively charged particles through gold foil. Rutherford proposed that atoms were mostly space. At the core was a tiny positive charged center. He called this core the nucleus. The nucleus is only about 1/10,000th the size of an ...
... From 1898-1907 Ernest Rutherford was doing some work and he shot some positively charged particles through gold foil. Rutherford proposed that atoms were mostly space. At the core was a tiny positive charged center. He called this core the nucleus. The nucleus is only about 1/10,000th the size of an ...