The Atom - Exam #2 Review
... 17. How can you determine if the atom is the most common isotope? Most common isotope = atomic mass from the Periodic Table rounded to a whole number 18. What is the difference between mass number and average atomic mass? Mass # = mass of each specific isotope (protons + neutrons) Average atomic mas ...
... 17. How can you determine if the atom is the most common isotope? Most common isotope = atomic mass from the Periodic Table rounded to a whole number 18. What is the difference between mass number and average atomic mass? Mass # = mass of each specific isotope (protons + neutrons) Average atomic mas ...
1s 2s 2p - Solon City Schools
... – When two elements form more than one compound, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with one gram of the first can be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
... – When two elements form more than one compound, the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with one gram of the first can be reduced to small whole numbers. ...
Everything around us is made up of atoms. Atoms are one of the
... elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is an atom. Each chemical element consists of only one type of atom. For ex ...
... elements. Familiar elements include hydrogen, helium, sodium, chlorine, iron, lead, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen. The smallest unit into which an element may be divided while keeping all of the characteristics of that element is an atom. Each chemical element consists of only one type of atom. For ex ...
Lesson 1: Alchemy and Atomic Models
... any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. However atoms of one element are not changed into a ...
... any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. However atoms of one element are not changed into a ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life ppt.
... pure water and have a pH below 7. • Bases: contain lower [ ] of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above 7. ...
... pure water and have a pH below 7. • Bases: contain lower [ ] of H+ ions than pure water and have pH values above 7. ...
Atomic Structure Unit Test 2016
... ____ 26. Oxygen can combine with carbon to form two compounds, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The ratio of the masses of oxygen that combine with a given mass of carbon is 1:2. This is an example of a. the law of conservation of mass. c. the law of conservation of energy. b. Dalton's atomic the ...
... ____ 26. Oxygen can combine with carbon to form two compounds, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The ratio of the masses of oxygen that combine with a given mass of carbon is 1:2. This is an example of a. the law of conservation of mass. c. the law of conservation of energy. b. Dalton's atomic the ...
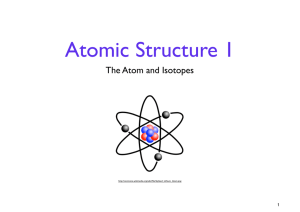
Isotopes
... • The nucleus contains protons & neutrons • Electrons orbit in the space around the nucleus. • “Planets around the sun” ...
... • The nucleus contains protons & neutrons • Electrons orbit in the space around the nucleus. • “Planets around the sun” ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... Electrons have a much greater mass than protons. All sodium cations (Na+) have 11 protons. If an atom loses electrons it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. The argon atom has 18 electrons. Different isotopes of the same element contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
... Electrons have a much greater mass than protons. All sodium cations (Na+) have 11 protons. If an atom loses electrons it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. The argon atom has 18 electrons. Different isotopes of the same element contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... separated into a series of specific frequencies(and therefore specific wavelengths, λ = c/f) of visible light. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom's electrons making a transition from a hi ...
... separated into a series of specific frequencies(and therefore specific wavelengths, λ = c/f) of visible light. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom's electrons making a transition from a hi ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
Chapter 20 notes
... Believed there were particles inside atoms (that atoms are divisible) Used cathode ray tube experiments to show that a positively charged plate attracted a beam of electrical energy. Concluded that the negatively charged particles were present in atoms. Termed these particles electrons. Suggested ...
... Believed there were particles inside atoms (that atoms are divisible) Used cathode ray tube experiments to show that a positively charged plate attracted a beam of electrical energy. Concluded that the negatively charged particles were present in atoms. Termed these particles electrons. Suggested ...
Atom
... • Atoms of an element don’t always have the same # of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. ...
... • Atoms of an element don’t always have the same # of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. ...
Atomic Structure
... more non-radioactive iodine available, then more of it will be used to make thyroxin. ...
... more non-radioactive iodine available, then more of it will be used to make thyroxin. ...
atomic number = of
... • Discovered by accident and was a result of spontaneous emission by uranium • Bequerel (1896) found that a piece of mineral containing uranium could produce an image on a photographic plate in the absence of light. • Three types of radiation were known: – alpha- helium nucleus (+2 charge, 7300 time ...
... • Discovered by accident and was a result of spontaneous emission by uranium • Bequerel (1896) found that a piece of mineral containing uranium could produce an image on a photographic plate in the absence of light. • Three types of radiation were known: – alpha- helium nucleus (+2 charge, 7300 time ...
CHEM 1411 CHAPTER 2
... Atomic number is taken as the basis for the arrangement of the elements, because when the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers, elements with similar properties repeat after a regular interval. This is called Periodic law The horizontal rows are called periods and th ...
... Atomic number is taken as the basis for the arrangement of the elements, because when the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers, elements with similar properties repeat after a regular interval. This is called Periodic law The horizontal rows are called periods and th ...
Chemistry
... found in different energy levels and can only move from a lower energy level (closer to nucleus) to a higher energy level (farther from nucleus) by absorbing energy in discrete packets. The energy content of the packets is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. These electron trans ...
... found in different energy levels and can only move from a lower energy level (closer to nucleus) to a higher energy level (farther from nucleus) by absorbing energy in discrete packets. The energy content of the packets is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. These electron trans ...
Multiple Choice W - Parkway C-2
... 14. Which statement about electrons and atomic orbitals is NOT true? a. An electron has the same amount of energy in all orbitals. b. An orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons. c. An electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. d. An atom’s lowest energy level has only one orbital. ...
... 14. Which statement about electrons and atomic orbitals is NOT true? a. An electron has the same amount of energy in all orbitals. b. An orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons. c. An electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. d. An atom’s lowest energy level has only one orbital. ...
atom
... compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combi ...
... compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound • Law of multiple proportions: if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combi ...
ppt Sc10 Review Notes
... charges on the ions are the result of taking or giving eto go from formula to name: name of first ion, then brackets for charge if multivalent, then name for second ion i.e. first element ( ) second element-ide eg) AlCl3 = aluminum chloride ...
... charges on the ions are the result of taking or giving eto go from formula to name: name of first ion, then brackets for charge if multivalent, then name for second ion i.e. first element ( ) second element-ide eg) AlCl3 = aluminum chloride ...
Atoms- Basic Units of Matter
... – Electron cloud: region surrounding an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found; electrons can be anywhere ...
... – Electron cloud: region surrounding an atomic nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found; electrons can be anywhere ...
Atoms - FTHS Wiki
... and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) • The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume • His model was called a “nuclear model” ...
... and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) • The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume • His model was called a “nuclear model” ...
Unit 3 Atomic Structure
... determines the element of an atom. atomic mass number = mass of the atom in amu, it includes the number of protons and neutrons. (electrons are not counted) Isotopes = atoms of the same element, with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes of each element have the same atomic number, ...
... determines the element of an atom. atomic mass number = mass of the atom in amu, it includes the number of protons and neutrons. (electrons are not counted) Isotopes = atoms of the same element, with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes of each element have the same atomic number, ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...