Atomic Theory Powerpoint
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from the atoms of any other element. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from the atoms of any other element. ...
Emission Spectrum and Periodic Trends
... • Opposite charges attract and like charges repel – Increasing protons in the nucleus increases the attraction of electrons pulling them closer to the nucleus – Increasing electrons in the electron cloud, increase the repulsion between the electrons – The closer electrons are to the nucleus the stro ...
... • Opposite charges attract and like charges repel – Increasing protons in the nucleus increases the attraction of electrons pulling them closer to the nucleus – Increasing electrons in the electron cloud, increase the repulsion between the electrons – The closer electrons are to the nucleus the stro ...
Unit 1: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Since the # of electrons no longer equals the # of protons, these atoms must be charged. A charged atom is called an ion. Cations are positively charged ions – they have lost electrons (and now have more protons than electrons) Anions are negatively charged ions – they have gained electrons (and now ...
... Since the # of electrons no longer equals the # of protons, these atoms must be charged. A charged atom is called an ion. Cations are positively charged ions – they have lost electrons (and now have more protons than electrons) Anions are negatively charged ions – they have gained electrons (and now ...
Nothing exists except atoms and empty space
... a question, your answer must be a correctly numbered restatement of the question or statement followed by a series of complete sentences. No phrases, partial answers or isolated numbers will be given credit! Your answer must stand alone without the reader knowing the question asked or statement made ...
... a question, your answer must be a correctly numbered restatement of the question or statement followed by a series of complete sentences. No phrases, partial answers or isolated numbers will be given credit! Your answer must stand alone without the reader knowing the question asked or statement made ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
Groups of the Periodic Table
... All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same group are similar to each other and have similar chemical properties. This i ...
... All the different elements are arranged in a chart called the periodic table. Here are the main features of the table: the horizontal rows are called periods the vertical columns are called groups elements in the same group are similar to each other and have similar chemical properties. This i ...
Radiation
... Chemical Reactions • In some reactions, neither element is “strong” enough to take electrons from the other SO, the atoms share electrons. This is called a covalent bond. Covalent bonds most often form between similar types of elements (nonmetals with other non-metals, etc). This type of bond resul ...
... Chemical Reactions • In some reactions, neither element is “strong” enough to take electrons from the other SO, the atoms share electrons. This is called a covalent bond. Covalent bonds most often form between similar types of elements (nonmetals with other non-metals, etc). This type of bond resul ...
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... ether, which is perfect, eternal, and incorruptible. Even Democritus’ ideas were more correct, Aristotle’s idea of five basic elements was accepted for over 2000 years, until John Dalton proposed the modern theory of atoms in 1808. ...
... ether, which is perfect, eternal, and incorruptible. Even Democritus’ ideas were more correct, Aristotle’s idea of five basic elements was accepted for over 2000 years, until John Dalton proposed the modern theory of atoms in 1808. ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... 7. Illustration: In the boxes provided, draw and label a picture of the atomic model based on J.J. Thomson’s experiment, Ernest Rutherford’s experiment, Niels Bohr’s experiment and the Quantum model of the atom. Show protons, neutrons and electrons and their believed relationship to each other with ...
... 7. Illustration: In the boxes provided, draw and label a picture of the atomic model based on J.J. Thomson’s experiment, Ernest Rutherford’s experiment, Niels Bohr’s experiment and the Quantum model of the atom. Show protons, neutrons and electrons and their believed relationship to each other with ...
NS 4.1 Atoms and Ions
... During chemical reactions, atoms can lose or gain electrons. In fact they do so on a very regular basis. (Atoms only lose or gain protons and neutrons only during nuclear reactions.) Since electrons are negatively charged, when electron(s) are lost, an atom turns into an ion and ends up with a posit ...
... During chemical reactions, atoms can lose or gain electrons. In fact they do so on a very regular basis. (Atoms only lose or gain protons and neutrons only during nuclear reactions.) Since electrons are negatively charged, when electron(s) are lost, an atom turns into an ion and ends up with a posit ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... c. sulfur 3. Identify the elements having the following electron configurations: a. 1s22s22p63s23p3 b. [Ar]4s1 c. contains four electrons in its third and outer main energy level d. contains one set of paired and three unpaired electrons in its fourth and outer main energy level 4. Distinguish betwe ...
... c. sulfur 3. Identify the elements having the following electron configurations: a. 1s22s22p63s23p3 b. [Ar]4s1 c. contains four electrons in its third and outer main energy level d. contains one set of paired and three unpaired electrons in its fourth and outer main energy level 4. Distinguish betwe ...
1 - Bal Bharati Public School
... Q.22. The atom of an element 'A' has three electrons in the outermost shell. It loses one of hese to the atom of another element 'B'. What will be the nature and value of charge on the ion which results from 'A' ? Q.23.The atomic numbers of atoms of two elements are 18 and 20 respectively and their ...
... Q.22. The atom of an element 'A' has three electrons in the outermost shell. It loses one of hese to the atom of another element 'B'. What will be the nature and value of charge on the ion which results from 'A' ? Q.23.The atomic numbers of atoms of two elements are 18 and 20 respectively and their ...
4 1 introduction to atoms 65-68
... nucleus of an atom was ________________________. 7. In the atomic model proposed by ________________________ , electrons move in specific orbits, similar to how planets orbit the sun. 8. What particle did Chadwick discover in 1932 that was hard to detect because it had no electrical charge? ________ ...
... nucleus of an atom was ________________________. 7. In the atomic model proposed by ________________________ , electrons move in specific orbits, similar to how planets orbit the sun. 8. What particle did Chadwick discover in 1932 that was hard to detect because it had no electrical charge? ________ ...
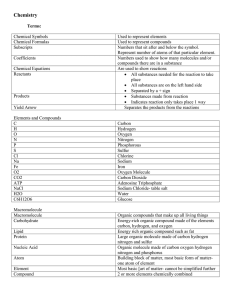
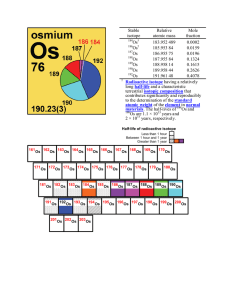
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
Structure of the Atom - Saint Mary Catholic School
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Document
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Electron cloud model
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... Electrons circle around the nucleus of an atom. Protons are a main part of the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons also hang out in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Week 9 CCA Test Review
... Why do elements with similar valence level of electrons have similar chemical properties? They will react the same way, because they ...
... Why do elements with similar valence level of electrons have similar chemical properties? They will react the same way, because they ...