I - Holland Public Schools
... 1) Law of Constant Composition – a given compound always contains the same proportion of elements by mass * example: water is always composed of 88.9% O & 11.1% H 2) Law of Conservation of Mass * 4 parts to his theory: 1) All matter is composed of indivisible, indestructible atoms. 2) All atoms of t ...
... 1) Law of Constant Composition – a given compound always contains the same proportion of elements by mass * example: water is always composed of 88.9% O & 11.1% H 2) Law of Conservation of Mass * 4 parts to his theory: 1) All matter is composed of indivisible, indestructible atoms. 2) All atoms of t ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... – Each object must have a different number of red blocks – Each object must have an equal number of red and blue blocks – Each object must have at least as many yellow blocks as red blocks but can have no more than 2 extra yellow blocks ...
... – Each object must have a different number of red blocks – Each object must have an equal number of red and blue blocks – Each object must have at least as many yellow blocks as red blocks but can have no more than 2 extra yellow blocks ...
Bonding. A. Ionic bonds form when anions and cations arise
... octet rules to be followed rigorously. Oxidation numbers offer a summary of the octet rule each atom followed in the bonding process. Follow these rules to determine the oxidation number of any atom: 1. The oxidation number of any element in its free (or uncombined) state is 0. 2. The oxidation numb ...
... octet rules to be followed rigorously. Oxidation numbers offer a summary of the octet rule each atom followed in the bonding process. Follow these rules to determine the oxidation number of any atom: 1. The oxidation number of any element in its free (or uncombined) state is 0. 2. The oxidation numb ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements
... 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible and retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the combination of atoms of unlike elements in sma ...
... 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible and retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the combination of atoms of unlike elements in sma ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
Unit III * Introduction to Atomic Theory
... The electrons orbit a large distance away from the nucleus. Proposes a “Solar System” or “Orbital” model of the atom Cute Summary of History ...
... The electrons orbit a large distance away from the nucleus. Proposes a “Solar System” or “Orbital” model of the atom Cute Summary of History ...
2 Atomic Theory Development of Theory Historical Atomic Models
... A defined region (shape) of space, where it is most probable to find an electron. Each orbital contains 0, 1, or 2 e’s. There are four classes of orbitals: s, p d, f. Each class of orbital can have certain types. For instance the p-orbital has 3 types: px, py, pz. Each orbital is hourglass shaped an ...
... A defined region (shape) of space, where it is most probable to find an electron. Each orbital contains 0, 1, or 2 e’s. There are four classes of orbitals: s, p d, f. Each class of orbital can have certain types. For instance the p-orbital has 3 types: px, py, pz. Each orbital is hourglass shaped an ...
Chemistry
... 2. Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the energy created by the interaction of matter 3. Matter: anything that has mass & volume 4. Mass: quantity of matter in an object often determined by weighing with a scale ...
... 2. Chemistry: the study of the composition of matter and the energy created by the interaction of matter 3. Matter: anything that has mass & volume 4. Mass: quantity of matter in an object often determined by weighing with a scale ...
Atoms - ChemConnections
... The understanding that matter is composed of different elements evolved over thousands of years. Substances such as gold and silver were known in ancient times, but they were not understood to be elements. The alchemists, who did not understand elements or atoms, tried to change substances into gold ...
... The understanding that matter is composed of different elements evolved over thousands of years. Substances such as gold and silver were known in ancient times, but they were not understood to be elements. The alchemists, who did not understand elements or atoms, tried to change substances into gold ...
Chapter 3: Atomic Structure
... and # no •“belt of stability” – as atomic number increases, you need more neutrons to keep the atom stable ...
... and # no •“belt of stability” – as atomic number increases, you need more neutrons to keep the atom stable ...
atom
... All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical change, only ...
... All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical change, only ...
Chapter 3 - Blair Community Schools
... Using atomic concepts & previous pg. Laws 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in their chemical and physical properties 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of differen ...
... Using atomic concepts & previous pg. Laws 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in their chemical and physical properties 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of differen ...
File
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
... 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical. 3. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? Alkali metals = group 1, alkaline earth metals = group 2, transition metals = middle of periodic table, halogens = group 7, and noble gas = group 8 3. On the periodic table, what are the trends for atomic mass, at ...
... 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? Alkali metals = group 1, alkaline earth metals = group 2, transition metals = middle of periodic table, halogens = group 7, and noble gas = group 8 3. On the periodic table, what are the trends for atomic mass, at ...
Atoms - McEachern High School
... – The first energy level (or ring around the nucleus) only can hold 2 electrons – Once the first ring is “full”, the next set of electrons will begin to fill in to a new energy level. – With the exception of the first energy level, All outer energy levels only wants to have 8 electrons. • This is ca ...
... – The first energy level (or ring around the nucleus) only can hold 2 electrons – Once the first ring is “full”, the next set of electrons will begin to fill in to a new energy level. – With the exception of the first energy level, All outer energy levels only wants to have 8 electrons. • This is ca ...
30.09.2013 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules Warning!! Chapter
... • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named using Roman numerals indicating ...
... • Cations with more than one charge (e.g., transition metals) are named using Roman numerals indicating ...
Lab Science 9 Pacing Guide
... same number of protons, and elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Those with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are el ...
... same number of protons, and elements with the same number of protons may or may not have the same mass. Those with different masses (different numbers of neutrons) are called isotopes. 2. Illustrate that atoms with the same number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons are el ...
Atomic Structure
... Each ring of the Bohr Model is an energy level As you go further out from the nucleus the energy of ...
... Each ring of the Bohr Model is an energy level As you go further out from the nucleus the energy of ...
The Periodic Table - River Dell Regional School District
... I. History of the Atomic Theory F. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties while atoms of different elements have different properties (isotopes) 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, ...
... I. History of the Atomic Theory F. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element have the same chemical properties while atoms of different elements have different properties (isotopes) 3. Not all atoms of an element have the same mass, ...
atomic theory of matter
... It is impossible to know the velocity and position of a particle at the same time We can not know the exact location of an electron. Any effort to do so, will change the position. We can only figure the probability of finding it in a certain region. ...
... It is impossible to know the velocity and position of a particle at the same time We can not know the exact location of an electron. Any effort to do so, will change the position. We can only figure the probability of finding it in a certain region. ...
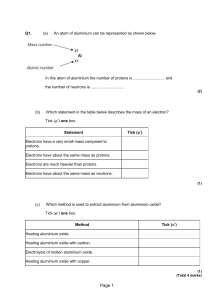
c2 atomic structure f pmh
... Electrons have a very small mass compared to protons. Electrons have about the same mass as protons. Electrons are much heavier than protons. Electrons have about the same mass as neutrons. ...
... Electrons have a very small mass compared to protons. Electrons have about the same mass as protons. Electrons are much heavier than protons. Electrons have about the same mass as neutrons. ...