“Plum Pudding” model
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
1. Atoms that have eight valence electrons would tend to A) be very
... 13. Using the laws governing moving particles and the forces of electrical attraction, Bohr reasoned that electrons could A) move in orbits whose radii depended on their velocity. B) move, as the planets, in orbits at any distance from the nucleus. C) move in orbits whose radii matched the distances ...
... 13. Using the laws governing moving particles and the forces of electrical attraction, Bohr reasoned that electrons could A) move in orbits whose radii depended on their velocity. B) move, as the planets, in orbits at any distance from the nucleus. C) move in orbits whose radii matched the distances ...
Which of the following statements correctly describes the
... If an atom has a mass number of 18, what can be said about the number of protons and neutrons it contains? A ...
... If an atom has a mass number of 18, what can be said about the number of protons and neutrons it contains? A ...
atomic number
... 2) What percentage of the mass of the atom is in the nucleus? 3) What effect does electrostatic force have on a proton and an electron interaction? 4) How can some elements have no charge when they are made up of charged particles? 5) What is strong nuclear force? slide 9 ...
... 2) What percentage of the mass of the atom is in the nucleus? 3) What effect does electrostatic force have on a proton and an electron interaction? 4) How can some elements have no charge when they are made up of charged particles? 5) What is strong nuclear force? slide 9 ...
atom
... • Are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons • These are what cause the atomic mass to be an average ...
... • Are atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons • These are what cause the atomic mass to be an average ...
An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be chemically
... Accuracy and Precision: Correct use: Accuracy: shows how close to the true value a given measurement is ...
... Accuracy and Precision: Correct use: Accuracy: shows how close to the true value a given measurement is ...
Avg. Atomic Mass - Greer Middle College
... like raisins in a pudding. (or chocolate chip cookie model) Thomson studied the passage of an electric current through a gas. As the current passed through the gas, it gave off rays of negatively charged particles. D. _____________ Gold Foil Experiment (Discovery of the _________) ...
... like raisins in a pudding. (or chocolate chip cookie model) Thomson studied the passage of an electric current through a gas. As the current passed through the gas, it gave off rays of negatively charged particles. D. _____________ Gold Foil Experiment (Discovery of the _________) ...
CHEMISTRY OLYMPICS 2nd 6 weeks What particles form the
... • A) Subtract the number of electrons from the number of protons • B) Add the number of electrons and protons ...
... • A) Subtract the number of electrons from the number of protons • B) Add the number of electrons and protons ...
WAHS—Chemistry Unit 4: Atomic Structure 1 Unit Assignment #1
... 11. How many protons are in the nuclei of the following atoms? a. Sulfur b. Hydrogen c. Phosphorus d. Cadmium e. Calcium 12. How do the three isotopes of hydrogen (H–1, H–2, H–3) compare in terms of the numbers of subatomic particles in each? 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Ide ...
... 11. How many protons are in the nuclei of the following atoms? a. Sulfur b. Hydrogen c. Phosphorus d. Cadmium e. Calcium 12. How do the three isotopes of hydrogen (H–1, H–2, H–3) compare in terms of the numbers of subatomic particles in each? 13. Write the nuclear symbol for deuterium (H-2): a. Ide ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint
... a physical model. However, not all models are physical. In fact, several theoretical models of the atom have been developed over the last few hundred years. You will learn about the currently accepted model of how electrons behave in atoms. ...
... a physical model. However, not all models are physical. In fact, several theoretical models of the atom have been developed over the last few hundred years. You will learn about the currently accepted model of how electrons behave in atoms. ...
Atoms and Molecules
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
... states the arrangement of electrons within the electron cloud; includes the energy level, orbital type and number of electrons. examples: H = 1s1 N = 1s2 2s2 2p3 Notes All families have the same valence electron configuration noble gas configuration ns2np6 halogen configuration ns2np5 chalcogen (O-f ...
Atomic Structure File
... isotopes: atoms of the same element (same atomic number = same # of protons), but that have different numbers of neutrons (and therefore different mass numbers) from each other. Isotopes are described by their mass numbers. For example, carbon-12 (12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, which gives it a ...
... isotopes: atoms of the same element (same atomic number = same # of protons), but that have different numbers of neutrons (and therefore different mass numbers) from each other. Isotopes are described by their mass numbers. For example, carbon-12 (12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, which gives it a ...
H - Shelton School District
... Oxygen has 6 electrons in it’s highest shell. It wants to have 8 Hydrogen has only one electron in it’s outer shell, it wants 2. ...
... Oxygen has 6 electrons in it’s highest shell. It wants to have 8 Hydrogen has only one electron in it’s outer shell, it wants 2. ...
Isotopes-Chemistry
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
... Same Element Different AtomIsotopes All atoms of a particular element are not exactly alike. Some elements have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
Honors Ch 4 Powerpoint
... The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. A weighted average mass reflects both the mass and the relative abundance of the isotopes as they occur in nature. ...
... The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. A weighted average mass reflects both the mass and the relative abundance of the isotopes as they occur in nature. ...
atom`s - Hauppauge School District
... around the nucleus, not in orbits like planets around the Sun • As per the Modern Atomic Model • Also known as the Wave Mechanical Model of the Atom ...
... around the nucleus, not in orbits like planets around the Sun • As per the Modern Atomic Model • Also known as the Wave Mechanical Model of the Atom ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... discussions. If you missed any notes, please get the information from a classmate, or from myself. ...
... discussions. If you missed any notes, please get the information from a classmate, or from myself. ...
topic 3: periodicity
... dip from N to O: oxygen fourth 2p electron goes into the first 2p orbital on which there is already an electron with opposite spin; the resulting repulsion between these two electrons - which is minimised because of their opposite spin - makes it easier to remove that electron. ...
... dip from N to O: oxygen fourth 2p electron goes into the first 2p orbital on which there is already an electron with opposite spin; the resulting repulsion between these two electrons - which is minimised because of their opposite spin - makes it easier to remove that electron. ...
File
... 59. The amount of energy required to remove the outermost electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state is known as A) first ionization energy B) activation energy C) conductivity D) electronegativity 60. In Period 2 of the Periodic Table, which Group contains the element with the highest first i ...
... 59. The amount of energy required to remove the outermost electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state is known as A) first ionization energy B) activation energy C) conductivity D) electronegativity 60. In Period 2 of the Periodic Table, which Group contains the element with the highest first i ...
Unit 3 Chap. 3 Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Electrons are held in the electron cloud by electrical attraction. ...
... Electrons are held in the electron cloud by electrical attraction. ...
Test - Chemical Bonding- Practice Test
... ____ 29. the force of attraction between a positive and negative charge ____ 30. the element oxygen will gain two electrons to form a(n) ___________ ____ 31. the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom in its ground state ____ 32. atom or group of atoms having a positive charge ____ 3 ...
... ____ 29. the force of attraction between a positive and negative charge ____ 30. the element oxygen will gain two electrons to form a(n) ___________ ____ 31. the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom in its ground state ____ 32. atom or group of atoms having a positive charge ____ 3 ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
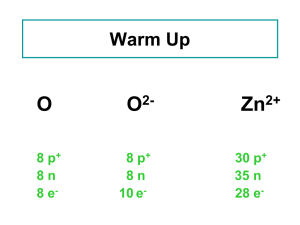
... Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Isotopes are atoms of the same element (X) with different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei ...
... Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Isotopes are atoms of the same element (X) with different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei ...
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with
... The Pauli exclusion principle requires that a. no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. b. the wavelength of a photon of light times its frequency is equal to the speed of light. c. an electron can have either particle character or wave character. d. the wavel ...
... The Pauli exclusion principle requires that a. no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. b. the wavelength of a photon of light times its frequency is equal to the speed of light. c. an electron can have either particle character or wave character. d. the wavel ...