File
... A metal, M, was obtained from a compound in a rock sample. Experiments have determined that the element is a member of Group 2 on the Periodic Table of the Elements. What is the phase of element M at STP? 89. In the 19th century, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of a then unknown element X w ...
... A metal, M, was obtained from a compound in a rock sample. Experiments have determined that the element is a member of Group 2 on the Periodic Table of the Elements. What is the phase of element M at STP? 89. In the 19th century, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted the existence of a then unknown element X w ...
CHAPTER 1 -Chemistry -Matter -Elements -Atoms
... A.speed. B. shape of the orbital it's in. C. Energy. D. Momentum. E. principle quantum number. 5. Wavelength and frequency are A. Directly related. B. proportional. C. Inversely related. D second cousins. E.the same 1. An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 656nm. How much energy is there in a ...
... A.speed. B. shape of the orbital it's in. C. Energy. D. Momentum. E. principle quantum number. 5. Wavelength and frequency are A. Directly related. B. proportional. C. Inversely related. D second cousins. E.the same 1. An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 656nm. How much energy is there in a ...
Quantum Theory of the Atom The Wave Nature of
... in position and the uncertainty in the momentum of a particle can be no smaller than Planck's constant divided by 4π. (∆x) (∆px) ≥ h / 4 π ...
... in position and the uncertainty in the momentum of a particle can be no smaller than Planck's constant divided by 4π. (∆x) (∆px) ≥ h / 4 π ...
Elements and Compounds Chapter 3
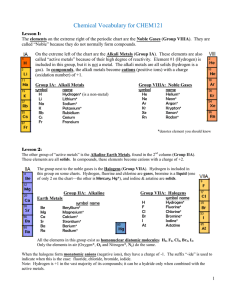
... H really belongs to its own group, which is why it’s shown by itself in my periodic table! It has 1 electron in outer shell, like the 1A elements, but it’s not a metal, and reacts more like group 7A. ...
... H really belongs to its own group, which is why it’s shown by itself in my periodic table! It has 1 electron in outer shell, like the 1A elements, but it’s not a metal, and reacts more like group 7A. ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, ...
... atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, ...
What is an atom?
... models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
... models to represent the atoms nucleus and their electron arrangement because the atoms are too small to see. These models are easy to draw – if you follow the steps! ...
atomic number Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
... Avg. (mass # )(# of atoms) (mass # )(# of atoms) Atomic total # of atoms Mass ...
... Avg. (mass # )(# of atoms) (mass # )(# of atoms) Atomic total # of atoms Mass ...
Bohr Models 1
... Write the number of P and N in the nucleus and draw the correct number of electrons on each energy level. The energy levels are: (2, 8, 18, 32, 50, 72). Many times an energy level will be satisfied with eight electrons. Place a happy or sad face next to each atoms to show its status as an atom. ...
... Write the number of P and N in the nucleus and draw the correct number of electrons on each energy level. The energy levels are: (2, 8, 18, 32, 50, 72). Many times an energy level will be satisfied with eight electrons. Place a happy or sad face next to each atoms to show its status as an atom. ...
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Compounds may be divided into 2 general types: 1. Molecular (covalent) compounds are combinations of non-metals 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecul ...
... Compounds may be divided into 2 general types: 1. Molecular (covalent) compounds are combinations of non-metals 2. Ionic (contains ions) includes: Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecul ...
chemistry final - Madison Public Schools
... raisin into his ginger ale. Both he and Ronika notice that the raisin falls to the bottom of the glass. Soon, the raisin rises to the surface of the ginger ale and then sinks. Within a couple ...
... raisin into his ginger ale. Both he and Ronika notice that the raisin falls to the bottom of the glass. Soon, the raisin rises to the surface of the ginger ale and then sinks. Within a couple ...
The Periodic Table, Atomic Structure, Isotopes, Ions and Nomenclature
... known as the nuclear force counteracts this repulsion. • As the number of protons increases, more neutrons are required to stabilize the atom. Stable nuclei up to atomic number 20 have equal numbers of protons and neutrons. • For nuclei with atomic number above 20, the number of neutrons exceeds the ...
... known as the nuclear force counteracts this repulsion. • As the number of protons increases, more neutrons are required to stabilize the atom. Stable nuclei up to atomic number 20 have equal numbers of protons and neutrons. • For nuclei with atomic number above 20, the number of neutrons exceeds the ...
Chapter 2 - Ector County ISD.
... combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
... combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
Atomic Models & Scientists
... combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
... combine. Each compound has a specific number and kinds of atom. 4) Chemical reactions are rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed. ...
Ch 2 Notes
... Discovered the nucleus: center has a positive charge and most of the atoms mass Electron move around the nucleus at a distance that is large relative to the nuclear radius ...
... Discovered the nucleus: center has a positive charge and most of the atoms mass Electron move around the nucleus at a distance that is large relative to the nuclear radius ...
SCH 3U - othsmath
... the group we go, the less strongly the valence electrons are held and the less likely the atom will pull electrons toward itself in a bond, so the lower the electronegativity value. 1) Across a period, nuclear charge increases by increments of one while each new valence electron is added. This means ...
... the group we go, the less strongly the valence electrons are held and the less likely the atom will pull electrons toward itself in a bond, so the lower the electronegativity value. 1) Across a period, nuclear charge increases by increments of one while each new valence electron is added. This means ...
Chemistry - Beck-Shop
... Atomic structure (AS) By the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1 recognise and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses; 2 describe the distribution of mass and charge within an atom; 3 describe the contribution of protons and neutrons ...
... Atomic structure (AS) By the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1 recognise and describe protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and relative masses; 2 describe the distribution of mass and charge within an atom; 3 describe the contribution of protons and neutrons ...
- MrKowalik.com
... recent model, in class we will be using the Bohr model since it shows important information about the electrons. ...
... recent model, in class we will be using the Bohr model since it shows important information about the electrons. ...
Key Concepts
... 10. Cations are positive (+) ions and form when a neutral atom loses electrons. They are smaller than their parent atom. 11. Anions are negative ions and form when a neutral atom gains electrons. They are larger than their parent atom. 12. Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment showed that an atom ...
... 10. Cations are positive (+) ions and form when a neutral atom loses electrons. They are smaller than their parent atom. 11. Anions are negative ions and form when a neutral atom gains electrons. They are larger than their parent atom. 12. Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment showed that an atom ...
3.2-3.3 Honors Notes - teacherstroh
... ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
... ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
What is hydrogen peroxide?
... Democritus theorized that atomos were specific to the material that they made up, meaning that the atomos of stone were unique to stone and different from the atomos of other materials, such as fur. This was a remarkable theory that attempted to explain the whole physical world in terms of a small n ...
... Democritus theorized that atomos were specific to the material that they made up, meaning that the atomos of stone were unique to stone and different from the atomos of other materials, such as fur. This was a remarkable theory that attempted to explain the whole physical world in terms of a small n ...
electrons
... 1913 In Niels Bohr's model, the electrons move in spherical orbits at fixed distances from the nucleus. ...
... 1913 In Niels Bohr's model, the electrons move in spherical orbits at fixed distances from the nucleus. ...
“Plum Pudding” model
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
... – Fixed electrons do not emit radiation – Angular momentum is quantized – Can’ Can’t explain how electrons move from one energy state to the next ...
1. Atoms that have eight valence electrons would tend to A) be very
... 13. Using the laws governing moving particles and the forces of electrical attraction, Bohr reasoned that electrons could A) move in orbits whose radii depended on their velocity. B) move, as the planets, in orbits at any distance from the nucleus. C) move in orbits whose radii matched the distances ...
... 13. Using the laws governing moving particles and the forces of electrical attraction, Bohr reasoned that electrons could A) move in orbits whose radii depended on their velocity. B) move, as the planets, in orbits at any distance from the nucleus. C) move in orbits whose radii matched the distances ...