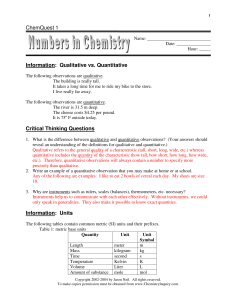
ChemQuest 1 Information: Qualitative vs. Quantitative Critical
... 5. How are compounds different from mixtures? Compounds are formed by a chemical change (i.e. two hydrogen and one oxygen atom bonding to form a water molecule), but mixtures are formed by a physical change (i.e. stirring salt and water together. 6. How are pure substances different from mixtures? P ...
... 5. How are compounds different from mixtures? Compounds are formed by a chemical change (i.e. two hydrogen and one oxygen atom bonding to form a water molecule), but mixtures are formed by a physical change (i.e. stirring salt and water together. 6. How are pure substances different from mixtures? P ...
2016-2018 Syllabus - Cambridge International Examinations
... final result.’ Page 39: Section C5.3.4 Suggesting improvements, paragraph after list, 6th line, now reads ‘may relate to sources of error or uncertainty identified by the candidate or to other sources of error or uncertainty.’ The changes below were introduced for version 1 of this syllabus. Part of ...
... final result.’ Page 39: Section C5.3.4 Suggesting improvements, paragraph after list, 6th line, now reads ‘may relate to sources of error or uncertainty identified by the candidate or to other sources of error or uncertainty.’ The changes below were introduced for version 1 of this syllabus. Part of ...
Quantum Tunnelling to the Origin and Evolution of Life
... where Zie is the positive nuclear charge of each nucleus i [23,25]. Since the values of Ecb are in the regime of MeV [27], the average kinetic energies available by the solar core temperature are more than a factor of 1000 below the necessary energy to overcome the Coulomb barrier. This difference i ...
... where Zie is the positive nuclear charge of each nucleus i [23,25]. Since the values of Ecb are in the regime of MeV [27], the average kinetic energies available by the solar core temperature are more than a factor of 1000 below the necessary energy to overcome the Coulomb barrier. This difference i ...
Chapter 14
... Based on low temperature experiments, it appears that the entropy of every pure substance approaches the same value as T 0. K. Third law of thermodynamics: The absolute entropy (S) of a perfect crystal of any pure substance at absolute zero is 0.0 J/mol.K. Because there are standard ways of find ...
... Based on low temperature experiments, it appears that the entropy of every pure substance approaches the same value as T 0. K. Third law of thermodynamics: The absolute entropy (S) of a perfect crystal of any pure substance at absolute zero is 0.0 J/mol.K. Because there are standard ways of find ...
Chapter 2
... • Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
... • Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. ...
(1125) Catalytic Dehydration Reactions for Green Synthesis of
... rhenium(VI) oxide (ReO3) and rhenium(IV) oxide (ReO2) were very low (entries 4–6). The other metal oxides such as molybdenum(VI) oxide (MoO3), tungsten(VI) oxide (WO3) and vanadium(V) oxide (V2O5) were almost inert (entries 7–9). Under the reaction conditions described above, rhenium(VII) oxo comoun ...
... rhenium(VI) oxide (ReO3) and rhenium(IV) oxide (ReO2) were very low (entries 4–6). The other metal oxides such as molybdenum(VI) oxide (MoO3), tungsten(VI) oxide (WO3) and vanadium(V) oxide (V2O5) were almost inert (entries 7–9). Under the reaction conditions described above, rhenium(VII) oxo comoun ...
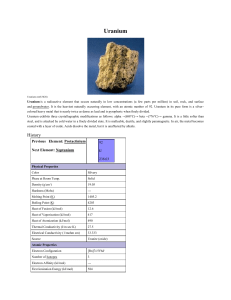
Uranium
... which means that atoms of uranium are unstable and decay by emitting particles and energy. Uranium decays very slowly by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioac ...
... which means that atoms of uranium are unstable and decay by emitting particles and energy. Uranium decays very slowly by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioac ...
Answer
... ΔG is the maximum amount of non-PV work obtainable from a system. The energy released by the oxidation of NADH in mitochondria is used to do non-PV work, viz. the pumping of H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane. By storing this energy in the form of an H+ gradient, the amount of energy wa ...
... ΔG is the maximum amount of non-PV work obtainable from a system. The energy released by the oxidation of NADH in mitochondria is used to do non-PV work, viz. the pumping of H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane. By storing this energy in the form of an H+ gradient, the amount of energy wa ...
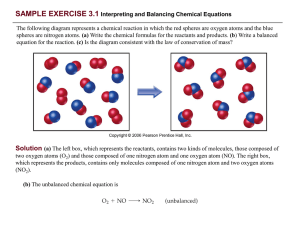
PRACTICE EXERCISE - Needham.K12.ma.us
... SAMPLE EXERCISE 3.4 Writing Balanced Equations for Combustion Reactions Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH3OH(l), is burned in air. ...
... SAMPLE EXERCISE 3.4 Writing Balanced Equations for Combustion Reactions Write the balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when methanol, CH3OH(l), is burned in air. ...
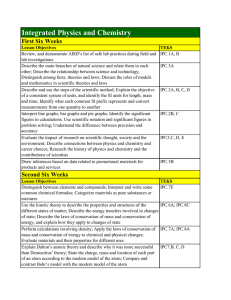
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent c ...
... between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predict the charge of a transition metal cation in an ionic compound; Write chemical formulas for simple ionic compounds; Distinguish a covalent c ...
Earth Science Chapter 4: Minerals Chapter Overview Section 1
... Each mineral has a specific and unique chemical composition. However, there can be some variation in the amounts of atoms of each element in the compound, but the ratio of the atoms remains the same. • Definite crystalline structure – the atoms in minerals are arranged in regular geometric pattern ...
... Each mineral has a specific and unique chemical composition. However, there can be some variation in the amounts of atoms of each element in the compound, but the ratio of the atoms remains the same. • Definite crystalline structure – the atoms in minerals are arranged in regular geometric pattern ...
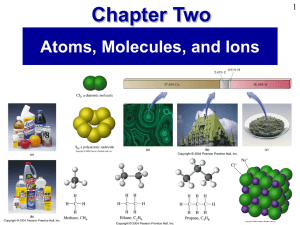
Prentice Hall Ch 02 Atoms Molecules Ions
... Example 2.1 A Conceptual Example Jan Baptista van Helmont (1579–1644) first measured the mass of a young willow tree and, separately, the mass of a bucket of soil and then planted the tree in the bucket. After five years, he found that the tree had gained 75 kg in mass even though the soil had lost ...
... Example 2.1 A Conceptual Example Jan Baptista van Helmont (1579–1644) first measured the mass of a young willow tree and, separately, the mass of a bucket of soil and then planted the tree in the bucket. After five years, he found that the tree had gained 75 kg in mass even though the soil had lost ...
EOCT Physical Science Study Guide August 2008
... chair, and take a few deep breaths. Then, sit up straight, pick up your pencil, and begin to concentrate on the test again. Remember that each test section is only 60 minutes. Use positive self-talk. If you find yourself saying negative things to yourself, such as “I can’t pass this test,” it is imp ...
... chair, and take a few deep breaths. Then, sit up straight, pick up your pencil, and begin to concentrate on the test again. Remember that each test section is only 60 minutes. Use positive self-talk. If you find yourself saying negative things to yourself, such as “I can’t pass this test,” it is imp ...
KEY
... number of moles of products. Increasing the pressure of the above system will result in the reaction proceeding to reduce that pressure increase. The system will shift to the right (the side that has fewer moles of gas), so the pressure will be reduced; thus more ammonia will be produced. ...
... number of moles of products. Increasing the pressure of the above system will result in the reaction proceeding to reduce that pressure increase. The system will shift to the right (the side that has fewer moles of gas), so the pressure will be reduced; thus more ammonia will be produced. ...
Line 4: Equation
... 7. Calculate the mole ratio. In order to get a ratio, you have to divide two numbers that have the same unit. We were given moles, so we can divide line 2 by line 6. If we were given grams, we would divide the given number on line 3 by line 7. Write this number next to mole ratio. 2.5 mol/ 1 mol = 2 ...
... 7. Calculate the mole ratio. In order to get a ratio, you have to divide two numbers that have the same unit. We were given moles, so we can divide line 2 by line 6. If we were given grams, we would divide the given number on line 3 by line 7. Write this number next to mole ratio. 2.5 mol/ 1 mol = 2 ...
An Efficient Oxidation of Benzoins to Benzils by Manganese (II
... An oxygen molecule from decomposition of H2 O2 reacts with Mn(II) to form an oxomanganese complex A [35, 36], which undergoes oxidative addition to benzoin and gives an intermediate � which �nally undergoes reductive elimination to give the desired product [37] and Mn(II) is regenerated back. As sho ...
... An oxygen molecule from decomposition of H2 O2 reacts with Mn(II) to form an oxomanganese complex A [35, 36], which undergoes oxidative addition to benzoin and gives an intermediate � which �nally undergoes reductive elimination to give the desired product [37] and Mn(II) is regenerated back. As sho ...
Exam Edge Digital
... Answer (a) (i) 18 electrons (3); (ii) 20 neutrons (3) (d) The principle of mass spectrometry is that charged particles moving in a magnetic field (3) are separated according to the masses (3) of the particles. (i) Mendeleev’s table was arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass (ato ...
... Answer (a) (i) 18 electrons (3); (ii) 20 neutrons (3) (d) The principle of mass spectrometry is that charged particles moving in a magnetic field (3) are separated according to the masses (3) of the particles. (i) Mendeleev’s table was arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass (ato ...
chapter 3 Questions
... copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O). When this compound is heated in air above 100° C, it loses the water molecules and also its blue color: CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O If 9.60 g of CuSO4 are left after heating 15.01 g of the blue compound, calculate the number of moles of H2O originally pres ...
... copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O). When this compound is heated in air above 100° C, it loses the water molecules and also its blue color: CuSO4.5H2O CuSO4 + 5H2O If 9.60 g of CuSO4 are left after heating 15.01 g of the blue compound, calculate the number of moles of H2O originally pres ...