Key - Sardis Secondary
... would mean that it would require a large amount of energy to remove any electrons from the atom, therefore resulting in a high ionization energy ...
... would mean that it would require a large amount of energy to remove any electrons from the atom, therefore resulting in a high ionization energy ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
Atomic structure and History Notes Democritus
... ________________ charged particles (e-) Located outside of the nucleus in ________________ or levels called atomic clouds Their mass is so small that it is usually considered________________ . It takes more than 1,800 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. However electrons occupy most of an ato ...
... ________________ charged particles (e-) Located outside of the nucleus in ________________ or levels called atomic clouds Their mass is so small that it is usually considered________________ . It takes more than 1,800 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. However electrons occupy most of an ato ...
Chapter 2: Matter is Made up of Atoms
... Atoms are arranged in energy levels (e.l.’s), at different distances from nucleus Close to nucleus = low energy Far from nucleus = high energy e-s in highest occupied level are “valence e-s” Only so many e-’s can fit in energy levels e-s fill lower e.l.’s before being located in higher e. ...
... Atoms are arranged in energy levels (e.l.’s), at different distances from nucleus Close to nucleus = low energy Far from nucleus = high energy e-s in highest occupied level are “valence e-s” Only so many e-’s can fit in energy levels e-s fill lower e.l.’s before being located in higher e. ...
Regents Chemistry
... Robert Boyle (1627 – 1691) – the first scientist to recognize the importance of careful measurements. Defined the term element in terms of experimentation; a substance was an element unless it could be broken down into two or more simpler substances ...
... Robert Boyle (1627 – 1691) – the first scientist to recognize the importance of careful measurements. Defined the term element in terms of experimentation; a substance was an element unless it could be broken down into two or more simpler substances ...
Periodic Trends - Sardis Secondary
... would mean that it would require a large amount of energy to remove any electrons from the atom, therefore resulting in a high ionization energy ...
... would mean that it would require a large amount of energy to remove any electrons from the atom, therefore resulting in a high ionization energy ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Atomic Theory of Matter The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter reemerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...
... Atomic Theory of Matter The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter reemerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...
Atoms, Electrons and Periodicity test - A
... Complete the electronic configuration of a bromine atom. 1s22s22p63s23p6 ................................................................................................ ...
... Complete the electronic configuration of a bromine atom. 1s22s22p63s23p6 ................................................................................................ ...
Periodic Table Trends
... These particles have different properties Electrons are tiny, very light and have a negative charge ...
... These particles have different properties Electrons are tiny, very light and have a negative charge ...
SUMMARY: Introduction and History of Atomism
... Performed famous “________ ________ Experiment” The experimental evidence that led to the Rutherford model was the results of bombarding a thin metal foil with an ________ particle (helium nuclei) beam. The beam was mostly____________, as expected; however, a small but significant number of alph ...
... Performed famous “________ ________ Experiment” The experimental evidence that led to the Rutherford model was the results of bombarding a thin metal foil with an ________ particle (helium nuclei) beam. The beam was mostly____________, as expected; however, a small but significant number of alph ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2.6 Ions and Ionic Compounds • If an electron is added or removed from an atom, then the atom now has a charge, or has become an ion. • Cation = positively charged = loss of electron • Anion = negatively charged = gain of electron • Polyatomic ion – ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecul ...
... 2.6 Ions and Ionic Compounds • If an electron is added or removed from an atom, then the atom now has a charge, or has become an ion. • Cation = positively charged = loss of electron • Anion = negatively charged = gain of electron • Polyatomic ion – ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecul ...
electrons.
... J. Thomson discovered that electricity passing through a gas caused the gas to give off particles that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
... J. Thomson discovered that electricity passing through a gas caused the gas to give off particles that were too small to be atoms. These negative particles were eventually called “electrons.” ...
Atomic Structure
... Each ring of the Bohr Model is an energy level As you go further out from the nucleus the energy of ...
... Each ring of the Bohr Model is an energy level As you go further out from the nucleus the energy of ...
1st Semester Exam in High School Chemistry
... about things that have been measured. B. Yes, because scientists cannot create new theories from nothing. C. No, because natural phenomena can be observed, but not always measured. D. No, because scientific theories change as ...
... about things that have been measured. B. Yes, because scientists cannot create new theories from nothing. C. No, because natural phenomena can be observed, but not always measured. D. No, because scientific theories change as ...
Review 2 - Solutions - Mayfield City Schools
... combine into compounds, they just change places. Dalton Who proposed the model of that atom that was like bread with raisins (electrons) stuck in it? - Thompson Who used light to figure out that atoms have distinct orbits? - Bohr ...
... combine into compounds, they just change places. Dalton Who proposed the model of that atom that was like bread with raisins (electrons) stuck in it? - Thompson Who used light to figure out that atoms have distinct orbits? - Bohr ...
What are atoms like???
... When a metal conducts electricity the electrons inside the metal move. Copper, silver and gold conduct electricity very well but don’t become superconductors. At very low temperatures, metals become superconductors which are used to make very fast circuits and to levitate magnets. Superconductors co ...
... When a metal conducts electricity the electrons inside the metal move. Copper, silver and gold conduct electricity very well but don’t become superconductors. At very low temperatures, metals become superconductors which are used to make very fast circuits and to levitate magnets. Superconductors co ...
Earth Materials
... -Diamond and graphite are both made of carbon (C), but why is one the hardest substance on Earth and the other very soft ? ...
... -Diamond and graphite are both made of carbon (C), but why is one the hardest substance on Earth and the other very soft ? ...
CHEM 1411 CHAPTER 2
... *Other examples of Carbon, Chlorine and Nitrogen. Periodic Table of Elements The periodic Table is a systematic arrangement of elements in the order of increasing atomic numbers. Atomic number is taken as the basis for the arrangement of the elements, because when the elements are arranged in the in ...
... *Other examples of Carbon, Chlorine and Nitrogen. Periodic Table of Elements The periodic Table is a systematic arrangement of elements in the order of increasing atomic numbers. Atomic number is taken as the basis for the arrangement of the elements, because when the elements are arranged in the in ...
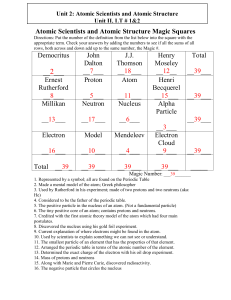
Atomic Scientists and Atomic Structure Magic Squares
... 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9. Current explanation of where electrons might be found in the atom. 10. Used by ...
... 6. The tiny positive core of an atom; contains protons and neutrons. 7. Credited with the first atomic theory model of the atom which had four main postulates. 8. Discovered the nucleus using his gold foil experiment. 9. Current explanation of where electrons might be found in the atom. 10. Used by ...
Atomic Theorists
... Thomson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel SO he proposed that a cathode ray is a stream of tiny negativelycharged particles moving at high speed ...
... Thomson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel SO he proposed that a cathode ray is a stream of tiny negativelycharged particles moving at high speed ...
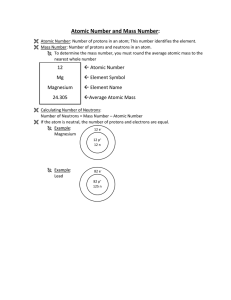
Chapter 4 Notes
... 17. The number of protons in an atom is the ___________________ number. All atoms of the same element have the _____________________ number of protons. Atoms of ________________________ elements have ______________________ numbers of protons. 18. The ___________________ ________________________ of a ...
... 17. The number of protons in an atom is the ___________________ number. All atoms of the same element have the _____________________ number of protons. Atoms of ________________________ elements have ______________________ numbers of protons. 18. The ___________________ ________________________ of a ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher 2010
... Balancing Equations: “Helpful Hints” a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound ________. last ...
... Balancing Equations: “Helpful Hints” a) Balance elements that appear in more than one compound ________. last ...