South Pasadena · Chemistry
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
Atomic Structure
... more non-radioactive iodine available, then more of it will be used to make thyroxin. ...
... more non-radioactive iodine available, then more of it will be used to make thyroxin. ...
Atomic Concepts
... 4. Can it be seen by the human eye? Answer: No, it is in the infrared range. ...
... 4. Can it be seen by the human eye? Answer: No, it is in the infrared range. ...
Second Semester Notes 09-10
... Ionic bonding- Occurs when electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. Held together by electrostatic force. This is the strongest type of bond. Occurs between metals & nonmetals ...
... Ionic bonding- Occurs when electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. Held together by electrostatic force. This is the strongest type of bond. Occurs between metals & nonmetals ...
The Egyptian American International School
... 1. The orbitals are different from the Bohr orbits. 2. Probability maps indicate the likelihood of finding the electron at a given point in space. 3. The size of an atom can be described by a surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. 11.4 Electron Configurations and Atomic Propert ...
... 1. The orbitals are different from the Bohr orbits. 2. Probability maps indicate the likelihood of finding the electron at a given point in space. 3. The size of an atom can be described by a surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability. 11.4 Electron Configurations and Atomic Propert ...
Study List
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
Chapter 4 Review Worksheet
... atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element equals the number of neutrons plus the number of protons in an atom 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom the number of protons in the nucleus of ...
... atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of an element equals the number of neutrons plus the number of protons in an atom 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom the number of protons in the nucleus of ...
Gr. 11 Review
... a broken pencil point and divided it in half, then divided that piece in half and again half of that piece. This process could be continued as long as possible. If matter was continuous, the process could be continued indefinitely without ever "running out" of graphite. If matter was discontinuous, ...
... a broken pencil point and divided it in half, then divided that piece in half and again half of that piece. This process could be continued as long as possible. If matter was continuous, the process could be continued indefinitely without ever "running out" of graphite. If matter was discontinuous, ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... Essential Content and Skills: How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
... Essential Content and Skills: How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
eastern illinois university
... 38. Put the following elements in order from smallest to largest atomic radius: Br, Fe, N, Ba a. N, Br, Ba, Fe b. Ba, Fe, Br, N c. Br, N, Fe, Ba d. N, Br, Fe, Ba e. Fe, Br, N, Ba 39. The ground state electron configuration for copper is an exception to the usual rules of filling orbitals from lower ...
... 38. Put the following elements in order from smallest to largest atomic radius: Br, Fe, N, Ba a. N, Br, Ba, Fe b. Ba, Fe, Br, N c. Br, N, Fe, Ba d. N, Br, Fe, Ba e. Fe, Br, N, Ba 39. The ground state electron configuration for copper is an exception to the usual rules of filling orbitals from lower ...
Greek philosophers (300 BC)
... Atoms are arranged in energy levels (e.l.’s), at different distances from nucleus Close to nucleus = low energy Far from nucleus = high energy e-s in highest occupied level are “valence e-s” Only so many e-’s can fit in energy levels e-s fill lower e.l.’s before being located in higher e. ...
... Atoms are arranged in energy levels (e.l.’s), at different distances from nucleus Close to nucleus = low energy Far from nucleus = high energy e-s in highest occupied level are “valence e-s” Only so many e-’s can fit in energy levels e-s fill lower e.l.’s before being located in higher e. ...
atomic number - Net Start Class
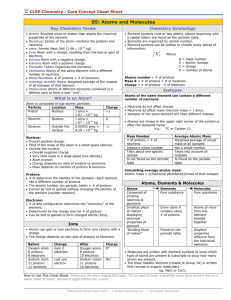
... • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
... • An atom with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons are called isotopes. • Isotopes are chemically alike, because it is the protons which are responsible for the chemical behavior. ...
Trends of period 3
... Members of group 7 lower down the group are solids, while those such as Bromine near the middle are liquid and Fluorine & Chlorine near the top are gases at room temperature. Explain this graded change of state from solid to gas? ...
... Members of group 7 lower down the group are solids, while those such as Bromine near the middle are liquid and Fluorine & Chlorine near the top are gases at room temperature. Explain this graded change of state from solid to gas? ...
Intro to Chapter 5 Development of the Periodic Table
... observations followed by organization of data into trends resulted in a consistent hypothesis which could explain known facts and makes correct predictions of the elements. B. Mendeleev s organized chemical information by: 1) listing elements by atomic weight 2) grouping them together according to c ...
... observations followed by organization of data into trends resulted in a consistent hypothesis which could explain known facts and makes correct predictions of the elements. B. Mendeleev s organized chemical information by: 1) listing elements by atomic weight 2) grouping them together according to c ...
Structure of the atom
... students start by counting the number of protons (red) and the number of neutrons (blue). They can then confirm their count using the 'explore' buttons. The main properties of each sub-atomic particle are given. Emphasise that the electrons are much smaller than the protons and neutrons. ...
... students start by counting the number of protons (red) and the number of neutrons (blue). They can then confirm their count using the 'explore' buttons. The main properties of each sub-atomic particle are given. Emphasise that the electrons are much smaller than the protons and neutrons. ...
Chemistry
... of electrons in chemical bonds • Bonds hold together the atoms in molecules • An atom with a full outer electron shell is stable and unlikely to form a bond with another atom Name at least one atom that is non-reactive for this reason. ...
... of electrons in chemical bonds • Bonds hold together the atoms in molecules • An atom with a full outer electron shell is stable and unlikely to form a bond with another atom Name at least one atom that is non-reactive for this reason. ...
Atomic Structure - OCPS TeacherPress
... The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
... The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
Lecture-1: Atomic Structure
... nucleus. These orbits are stable and called "stationary" orbits. 2) Each orbit has an energy associated with it. For example the orbit closest to the nucleus has an energy E1, the next closest E2 and so on. ...
... nucleus. These orbits are stable and called "stationary" orbits. 2) Each orbit has an energy associated with it. For example the orbit closest to the nucleus has an energy E1, the next closest E2 and so on. ...
File
... 6. The effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Na is different than the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Ne. This difference best accounts for which of the following? A. Na has a greater density at standard conditions than Ne. B. Na has a lo ...
... 6. The effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Na is different than the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electron of Ne. This difference best accounts for which of the following? A. Na has a greater density at standard conditions than Ne. B. Na has a lo ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...
... Elements with more than one positive oxidation number (Transition Metals) (This is called the Stock System) When the oxidation number varies we us a Roman numeral in parentheses to indicate the charge. Roman number is used for the positive element only!!! ...