atomic number - iGCSE Science Courses
... stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
... stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
Atoms 1 ppt
... An “s” orbital is shaped like a sphere and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d ...
... An “s” orbital is shaped like a sphere and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d ...
Section 2: “The Structure of Atoms”
... An “s” orbital is shaped like a sphere and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d ...
... An “s” orbital is shaped like a sphere and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Each “p” orbital is shaped like a bar bell. There are 3 different types that can each hold 2 electrons. The “p” orbital, therefore, can hold up to 6 electrons. “d” and “f” orbitals are more complex. There are 5 types of “d ...
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE
... 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds containing the major organic functional groups. 46. explain the concept of thermal equilibrium and the chemistry of fire. 47. assign oxidation numbe ...
... 42. name alkenes and alkynes and draw their structures. 43. identify and name isomers. 44. name and describe cyclic compounds.. 45. recognize compounds containing the major organic functional groups. 46. explain the concept of thermal equilibrium and the chemistry of fire. 47. assign oxidation numbe ...
Mr. Cherry`s Chapter 5 Notes
... accurately determine where an electron is. Unlike Bohr model, makes no attempt to determine orbit of electron. States electrons are in noncircular orbitals. Orbitals are based on probability of location of electron. ...
... accurately determine where an electron is. Unlike Bohr model, makes no attempt to determine orbit of electron. States electrons are in noncircular orbitals. Orbitals are based on probability of location of electron. ...
Chemistry of Living cells PPT
... atom. The Greek word atomos, which means “unable to cut”. This word was first used nearly 2500 years ago by Greek philosopher Democritus. Democritus asked a simple question “If you take an object like chalk and break it in half are both pieces still chalk?” Yes, suppose you break the chalk down agai ...
... atom. The Greek word atomos, which means “unable to cut”. This word was first used nearly 2500 years ago by Greek philosopher Democritus. Democritus asked a simple question “If you take an object like chalk and break it in half are both pieces still chalk?” Yes, suppose you break the chalk down agai ...
ion
... Models are often used for things that are too small or too large to be observed or that are too difficult to be understood easily ...
... Models are often used for things that are too small or too large to be observed or that are too difficult to be understood easily ...
Slide 1 - James Goodwin
... chemical and physical. We will define “physical change” to refer to a change in the state of an atomic or molecular substance that is not associated with a change in the molecular species that compose that substance. This could be a change between solid, liquid and gas phases or it could involve cha ...
... chemical and physical. We will define “physical change” to refer to a change in the state of an atomic or molecular substance that is not associated with a change in the molecular species that compose that substance. This could be a change between solid, liquid and gas phases or it could involve cha ...
Chapter 30 Notes - Valdosta State University
... when energy is added to them by heating, electric current, etc. In the case of a solid, a continuous spectrum is produced because of the interactions among the atoms and molecules that make up the solid. If atoms of an element can be separated from other atoms and each other, they can be made to emi ...
... when energy is added to them by heating, electric current, etc. In the case of a solid, a continuous spectrum is produced because of the interactions among the atoms and molecules that make up the solid. If atoms of an element can be separated from other atoms and each other, they can be made to emi ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemical and PHYSICAL properties *b. elements can NOT be BROKEN down into other substances by any CHEMICAL means c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] ...
... 5. ELEMENT matter that is composed of one kind of ATOM (e.g. sulfur [S]; carbon [C]) a. each ELEMENT has its own CHARACTERISTIC chemical and PHYSICAL properties *b. elements can NOT be BROKEN down into other substances by any CHEMICAL means c. some MATTER exists in elemental form [(e.g.) gold [Au] ...
Atoms - Issaquah Connect
... so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
... so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
AP Chemistry Summer Work
... 4.11 Using the solubility guidelines , predict whether each of the following compounds is a soluble or insoluble in water: a)NiCl2 ; b) Ag2 S c) Cs3PO4 d)SrCO3 e) (NH4)2 SO4 4.13 Will Precipitation occur when the following solutions are mixed? If so write the balanced chemical equation for the react ...
... 4.11 Using the solubility guidelines , predict whether each of the following compounds is a soluble or insoluble in water: a)NiCl2 ; b) Ag2 S c) Cs3PO4 d)SrCO3 e) (NH4)2 SO4 4.13 Will Precipitation occur when the following solutions are mixed? If so write the balanced chemical equation for the react ...
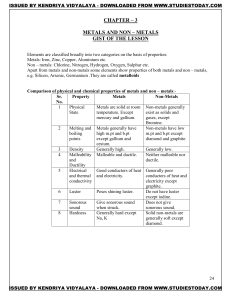
METALS AND NON – METALS Concepts
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
... Metals: Iron, Zinc, Copper, Aluminium etc. Non – metals: Chlorine, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulphur etc. Apart from metals and non-metals some elements show properties of both metals and non – metals, e.g. Silicon, Arsenic, Germanium .They are called metalloids Comparison of physical and chemical ...
Week 6 Review 2014-15
... substances that are not chemically combined. Zn + Cu • substances held together by physical forces, not chemical • No chemical change takes place • Each item retains its properties in the mixture • They can be separated physically ...
... substances that are not chemically combined. Zn + Cu • substances held together by physical forces, not chemical • No chemical change takes place • Each item retains its properties in the mixture • They can be separated physically ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... 70. When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron _____. a) always doubles its energy b) absorbs a continuously variable amount of energy c) absorbs a quantum of energy d) moves closer to the nucleus ...
... 70. When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron _____. a) always doubles its energy b) absorbs a continuously variable amount of energy c) absorbs a quantum of energy d) moves closer to the nucleus ...
,ALgor (JoWr z:
... -. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons 'in an atom of a chemical element The mass number (A) is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus in an atom of a chemical element. ~ A nuclide is an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons. Nuclides are described by the notation ...
... -. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons 'in an atom of a chemical element The mass number (A) is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus in an atom of a chemical element. ~ A nuclide is an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons. Nuclides are described by the notation ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... In Topic 1 we met relative isotopic mass and relative atomic mass. Remember that relative means compared with 12C The relative mass of a simple covalent substance, like H2O or O2, is called its relative molecular mass The relative mass of a giant ionic or giant covalent substance, like NaCl or SiO2, ...
... In Topic 1 we met relative isotopic mass and relative atomic mass. Remember that relative means compared with 12C The relative mass of a simple covalent substance, like H2O or O2, is called its relative molecular mass The relative mass of a giant ionic or giant covalent substance, like NaCl or SiO2, ...
atomic mass - Bruder Chemistry
... All elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of anyone element are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine w/ one another in simple ...
... All elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of anyone element are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine w/ one another in simple ...
PSCH4PP
... Thomason had the nucleus (positively charged area) and the electrons (negatively charged particles) in one spherical mass. The model had several nicknames: The Plum Pudding Model, The Watermelon Model, and The Raisin Cookie Model. ...
... Thomason had the nucleus (positively charged area) and the electrons (negatively charged particles) in one spherical mass. The model had several nicknames: The Plum Pudding Model, The Watermelon Model, and The Raisin Cookie Model. ...
drawing bohr models
... Bohr’s Atomic Theory Ex.3) Draw a Bohr model of Lithium-3. Step-1 Draw a circle to represent the nucleus. Step-2 Determine the number of protons and neutrons and place them in the nucleus. Step-3 Draw circles around the nucleus to represent the electron shells. Step-4 Place the electrons in the she ...
... Bohr’s Atomic Theory Ex.3) Draw a Bohr model of Lithium-3. Step-1 Draw a circle to represent the nucleus. Step-2 Determine the number of protons and neutrons and place them in the nucleus. Step-3 Draw circles around the nucleus to represent the electron shells. Step-4 Place the electrons in the she ...
Reactions and Balancing
... Some helpful hints for balancing equations: Take one element at a time, working left to right except for H and O. Metals, then nonmetals are a good way, too. Save H for next to last, and O until last. IF everything balances except for O, and there is no way to balance O with a whole number, doub ...
... Some helpful hints for balancing equations: Take one element at a time, working left to right except for H and O. Metals, then nonmetals are a good way, too. Save H for next to last, and O until last. IF everything balances except for O, and there is no way to balance O with a whole number, doub ...
AP Chemistry Notes
... – For more complicated ligands, the prefixes bis (twice), tris (thrice), tetrakis (four times), pentakis (five times), and hexakis (six times) are used. – NOTE: Prefixes do not affect the alphabetical order ...
... – For more complicated ligands, the prefixes bis (twice), tris (thrice), tetrakis (four times), pentakis (five times), and hexakis (six times) are used. – NOTE: Prefixes do not affect the alphabetical order ...
Atomic Electron Configurations and Chapter 8 Chemical Periodicity
... the outermost electron ¾ IE: The energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. ¾ Successive ionization ...
... the outermost electron ¾ IE: The energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. ¾ Successive ionization ...