Extraintestinal Crohn`s Disease Mimicking Autoimmune Inner Ear
... Autoimmune inner ear disease (AIED) is a rare cause of sensorineural hearing loss which first was described in 1979 [McCabe, 1979]. It is important to recognise this disease entity, because early diagnosis and proper management may prevent complete hearing loss. The problem is, that there are only l ...
... Autoimmune inner ear disease (AIED) is a rare cause of sensorineural hearing loss which first was described in 1979 [McCabe, 1979]. It is important to recognise this disease entity, because early diagnosis and proper management may prevent complete hearing loss. The problem is, that there are only l ...
Treatment
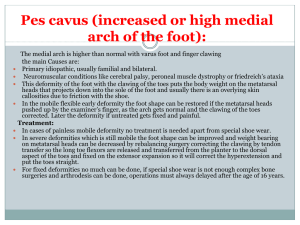
... because of rubbing with shoe wear on its medial side there will be the formation of thick bony exostosis and over it there is a protective synovial bursa (the bunion) that may get swollen, inflamed or infected. Both of the above changes can be a cause of pain. ...
... because of rubbing with shoe wear on its medial side there will be the formation of thick bony exostosis and over it there is a protective synovial bursa (the bunion) that may get swollen, inflamed or infected. Both of the above changes can be a cause of pain. ...
Periodontal Treatment
... Increased frequency of oral hygiene appointments: Tooth cleanings and scalings are usually performed once every 6 months. Patients with minimal periodontal disease can often control its progress by increasing the frequency of scalings and exams to once every two to four months. ...
... Increased frequency of oral hygiene appointments: Tooth cleanings and scalings are usually performed once every 6 months. Patients with minimal periodontal disease can often control its progress by increasing the frequency of scalings and exams to once every two to four months. ...
GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION Lecture1
... indigestible antigenic material in macrophages Antigen presentation on cell membrane to appropriate CD4+TH1 lymphocytes, causing them to become activated. The responding T cells produce cytokines, such as IL-2, and IFN-γ, IFN-γ is important in activating macrophages and transforming them into ep ...
... indigestible antigenic material in macrophages Antigen presentation on cell membrane to appropriate CD4+TH1 lymphocytes, causing them to become activated. The responding T cells produce cytokines, such as IL-2, and IFN-γ, IFN-γ is important in activating macrophages and transforming them into ep ...
Acute inflammation - immunology.unideb.hu
... Acute inflammation Acute inflammation is a protective response that is intended to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, as well as the necrotic cells and damaged tissues resulting from the original insult, and to initiate the process of repair. ...
... Acute inflammation Acute inflammation is a protective response that is intended to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, as well as the necrotic cells and damaged tissues resulting from the original insult, and to initiate the process of repair. ...
Inflammation
... Leakage - Leukocytes migrate out of the capillaries into the surrounding Tissues. In the earliest stages of inflammation, neutrophils are particularly prevalent, but later monocytes and lymphocytes also migrate towards the site of infection. Neutrophils line up within the capillary wall. Monocytes w ...
... Leakage - Leukocytes migrate out of the capillaries into the surrounding Tissues. In the earliest stages of inflammation, neutrophils are particularly prevalent, but later monocytes and lymphocytes also migrate towards the site of infection. Neutrophils line up within the capillary wall. Monocytes w ...
- Robert Fox, MD, Ph.D.
... We measure blood counts, sedimentation rates and autoantibodies. This gives an idea of the “activity” of the immune system based on lymphocyte hormones. However, these lab tests do not often correlate well with the patient’s symptoms. ...
... We measure blood counts, sedimentation rates and autoantibodies. This gives an idea of the “activity” of the immune system based on lymphocyte hormones. However, these lab tests do not often correlate well with the patient’s symptoms. ...
Schedule for Lectures of the Summer School “Molecular Interactions
... Poster Session with Coffee Break and Snack ...
... Poster Session with Coffee Break and Snack ...
Spring 2012 - Logan Memorial Hospital
... body type can influence your risk for developing colorectal cancer. Those with an “apple” shape and those carrying extra weight around the waist are at greatest risk. Take Your Vitamin D. The American Cancer Society suggests that Vitamin D can reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer by helpi ...
... body type can influence your risk for developing colorectal cancer. Those with an “apple” shape and those carrying extra weight around the waist are at greatest risk. Take Your Vitamin D. The American Cancer Society suggests that Vitamin D can reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer by helpi ...
common mycotic infection - ksu - Home
... granulomatous disease of childhood. Patients with this condition unable to form toxic oxygen radicals after phagocytosis. Progressive and disseminated disease can complicate neoplastic diseases, esp. ac. Leukemia, BM and organ transplantation. In immunosuppressed host: Invasive pulmonary infec ...
... granulomatous disease of childhood. Patients with this condition unable to form toxic oxygen radicals after phagocytosis. Progressive and disseminated disease can complicate neoplastic diseases, esp. ac. Leukemia, BM and organ transplantation. In immunosuppressed host: Invasive pulmonary infec ...
Nature_and_role_of_inflammation _
... responds by increasing the temperature of the body, which may result in fever, which aids in the defence of the body against infection. This increase in temperature decreases the rate in which bacteria can divide, thus slowing down the spread of infection. Fever also accelerates the speed at which t ...
... responds by increasing the temperature of the body, which may result in fever, which aids in the defence of the body against infection. This increase in temperature decreases the rate in which bacteria can divide, thus slowing down the spread of infection. Fever also accelerates the speed at which t ...
Do you want to know? - American University of Beirut
... Population at risk Hyperthyroidism may occur at any age, but is much more frequent in the following cases: • In women of reproductive age group (5 times more than men) • In the presence of an autoimmune disease (disease that results from the body’s immune function such as juvenile diabetes) • After ...
... Population at risk Hyperthyroidism may occur at any age, but is much more frequent in the following cases: • In women of reproductive age group (5 times more than men) • In the presence of an autoimmune disease (disease that results from the body’s immune function such as juvenile diabetes) • After ...
Ecosystems, Biodiversity and Human Health
... Primary production Soil formation Adapted from the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, 2005. ...
... Primary production Soil formation Adapted from the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, 2005. ...
IBD Slides - Annenberg Center for Health Sciences
... Other skin lesions: • Psoriasis ~10% in Crohn’s disease • Sweet’s syndrome • Metastatic Crohn’s disease ...
... Other skin lesions: • Psoriasis ~10% in Crohn’s disease • Sweet’s syndrome • Metastatic Crohn’s disease ...
Autoimmunity and autoimmune disease
... the autoantigen and the renal structures in this mechanism of kidney injury. Cell-mediated immunity in glomerular and tubulointerstitial injury Activated T cells, specific, for self-peptide–MHC complexes, can cause local inflammation by activating macrophages or by direct cell damage. Extensive infi ...
... the autoantigen and the renal structures in this mechanism of kidney injury. Cell-mediated immunity in glomerular and tubulointerstitial injury Activated T cells, specific, for self-peptide–MHC complexes, can cause local inflammation by activating macrophages or by direct cell damage. Extensive infi ...
Autoimmune Endocrinopathies
... mainly in the thymus (medullary epithelial cells) that controls the presentation of self antigens to the developing T lymphocytes • When the gene is mutated, tolerance to multiple self antigens is lost ...
... mainly in the thymus (medullary epithelial cells) that controls the presentation of self antigens to the developing T lymphocytes • When the gene is mutated, tolerance to multiple self antigens is lost ...
Efficacy of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL
... the efficacy of a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [1]. RA is a chronic and progressive autoimmune inflammatory disease that is associated with joint damage of the hands and feet. Although the etiology of RA is not fully ...
... the efficacy of a humanized anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [1]. RA is a chronic and progressive autoimmune inflammatory disease that is associated with joint damage of the hands and feet. Although the etiology of RA is not fully ...
Epidemiology
... smokers have much higher risk of lung cancers than non-smokers Example: People with high blood pressure have increased risk of heart disease ...
... smokers have much higher risk of lung cancers than non-smokers Example: People with high blood pressure have increased risk of heart disease ...
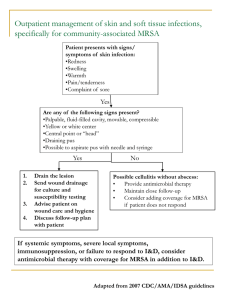
Outpatient management of skin and soft tissue infections specifically
... D-zone test should be performed to identify inducible clindamycin resistance in erythromycinresistant isolates ...
... D-zone test should be performed to identify inducible clindamycin resistance in erythromycinresistant isolates ...
- Dr. Robert Fox
... • All work by inhibiting synthesis of ribonucleotides that serve as an energy source (de novo synthesis pathway) required for G1-S transition of maturation. • This pathway links p52 and p21 driven apoptosis; p52 is the “sensor” for adequate ribonucleotide level. • Ribonucleotide synthesis as an ener ...
... • All work by inhibiting synthesis of ribonucleotides that serve as an energy source (de novo synthesis pathway) required for G1-S transition of maturation. • This pathway links p52 and p21 driven apoptosis; p52 is the “sensor” for adequate ribonucleotide level. • Ribonucleotide synthesis as an ener ...
Skeletal Disorders - Woodstown-Pilesgrove Regional School
... Bone bleeds and becomes inflamed Callus (bony framework) formed around injury which stabilizes the bone fragment ...
... Bone bleeds and becomes inflamed Callus (bony framework) formed around injury which stabilizes the bone fragment ...
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long lasting autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly the wrist and hands are involved with typically the same joints involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body. This may result in low red blood cells, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months.While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mostly on the basis of a person's signs and symptoms. X-rays and laboratory testing may support a diagnosis or exclude other diseases with similar symptoms. Other diseases that may present similarly include systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriatic arthritis, and fibromyalgia among others.The goal of treatment is to improve pain, decrease inflammation, and improve a person's overall functioning. This may be helped by balancing rest and exercise, the use of splints and braces, or the use of assistive devices. Pain medications, steroids, and NSAIDs are frequently used to help with symptoms. A group of medications called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be used to try to slow the progression of disease. They include the medications hydroxychloroquine and methotrexate. Biological DMARDs may be used when disease does not respond to other treatments. However, they may have a greater rate of adverse effects. Surgery to repair, replace, or fusion joints may help in certain situations. Most alternative medicine treatments are not supported by evidence.RA affects between 0.5 and 1% of adults in the developed world with between 5 and 50 per 100,000 people newly developing the condition each year. Onset is most frequent during middle age and women are affected 2.5 times as frequently as men. In 2013 it resulted in 38,000 deaths up from 28,000 deaths in 1990. The first recognized description of RA was made in 1800 by Dr. Augustin Jacob Landré-Beauvais (1772–1840) of Paris. The term rheumatoid arthritis is based on the Greek for watery and inflamed joints.