Sistem Keta - IGP355 – PATOFISIOLOGI PENYAKIT II
... not removed in the thymus or bone marrow during development. They can also occur if new self-antigens appear later in the life. The immune system can unfortunately see these new antigens as foreign. Also, sometimes, bacterial or viral antigens may resemble proteins normally on the cell surface (e.g. ...
... not removed in the thymus or bone marrow during development. They can also occur if new self-antigens appear later in the life. The immune system can unfortunately see these new antigens as foreign. Also, sometimes, bacterial or viral antigens may resemble proteins normally on the cell surface (e.g. ...
Mechanism
... Activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and CD4+ helper T cells response to the donor’s HLA antigens. Proliferation of B-cell – mediated antibody production and a delayedtype hypersensitivity reaction. The initial target of the recipient antibodies is graft vasculature. The antibodies can produce injur ...
... Activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and CD4+ helper T cells response to the donor’s HLA antigens. Proliferation of B-cell – mediated antibody production and a delayedtype hypersensitivity reaction. The initial target of the recipient antibodies is graft vasculature. The antibodies can produce injur ...
The Immune System
... against infection by catching harmful organisms in the lymph nodes located along the lymph system. ...
... against infection by catching harmful organisms in the lymph nodes located along the lymph system. ...
Beat The Flu with These Essential Vitamins
... least two pieces of fruit and three vegetables a day to get a complete complement of vitamins and minerals for immune health. In particular, mushrooms help in the production of white blood cells. Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, kale, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower are go ...
... least two pieces of fruit and three vegetables a day to get a complete complement of vitamins and minerals for immune health. In particular, mushrooms help in the production of white blood cells. Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, kale, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower are go ...
The Immune System
... This is based on memory cells which are produced during the primary immune response Memory cells are not active during the primary response but survive in the system for a long time This is acquired immunity ...
... This is based on memory cells which are produced during the primary immune response Memory cells are not active during the primary response but survive in the system for a long time This is acquired immunity ...
The Immune System
... • Biofilms – groups of bacteria bonded together on surfaces that function as a unit – Plaque on teeth ...
... • Biofilms – groups of bacteria bonded together on surfaces that function as a unit – Plaque on teeth ...
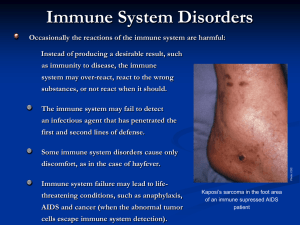
Immune System Disorders
... Rheumatoid arthritis Inflammation of joints leading to destruction of cartilage. ...
... Rheumatoid arthritis Inflammation of joints leading to destruction of cartilage. ...
Module 6 Immunology
... Part of secondary immune response This is the only antibody that can cross through the placenta Causes agglutination of pathogens Coats surface of foreign bodies for ingestion by phagocytes Activates complement system ...
... Part of secondary immune response This is the only antibody that can cross through the placenta Causes agglutination of pathogens Coats surface of foreign bodies for ingestion by phagocytes Activates complement system ...
Immune Disorders and Imbalances
... Auto immune diseases • The reason why the immune system looses the ability to recognize it’s self is dependent upon a variety of factors. – Lymphocyte programming is ineffective – New proteins appear that the immune system has not had a chance to become acquainted with. – Self antigens look very si ...
... Auto immune diseases • The reason why the immune system looses the ability to recognize it’s self is dependent upon a variety of factors. – Lymphocyte programming is ineffective – New proteins appear that the immune system has not had a chance to become acquainted with. – Self antigens look very si ...
Antigen-presenting cells
... the magnitude and duration of the immune response with repeated exposure to the same antigen is due to the proliferation of antigenspecific lymphocytes after each exposure. The numbers of responding cells will remain increased even after the immune response subsides. Therefore, whenever the organism ...
... the magnitude and duration of the immune response with repeated exposure to the same antigen is due to the proliferation of antigenspecific lymphocytes after each exposure. The numbers of responding cells will remain increased even after the immune response subsides. Therefore, whenever the organism ...
Lymphocytes - MBBS Students Club
... destroy the specific invading organism or toxin • Passive immunity--- produced by already made antibodies or activated T cells from horse or human serum • Active immunity--- a person itself produces an immune reaction in response to the entry of antigens into the body ...
... destroy the specific invading organism or toxin • Passive immunity--- produced by already made antibodies or activated T cells from horse or human serum • Active immunity--- a person itself produces an immune reaction in response to the entry of antigens into the body ...
Immunology Practice Exam - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... there are factors that enable the tumor to escape the immune system, as listed below. Which one of the following is INCORRECT? A. Tumors may be in privileged sites. B. Tumors may change their surface antigens (antigenic modulation). C. Tumor antigens may be recognized by T-cells in the absence of MH ...
... there are factors that enable the tumor to escape the immune system, as listed below. Which one of the following is INCORRECT? A. Tumors may be in privileged sites. B. Tumors may change their surface antigens (antigenic modulation). C. Tumor antigens may be recognized by T-cells in the absence of MH ...
Immunity - Yengage
... body. Done by administration of serum or gamma globulins from a person who is already immunized Passive natural– maternal antibodies Passive artificial– injecting antibodies from other sources ...
... body. Done by administration of serum or gamma globulins from a person who is already immunized Passive natural– maternal antibodies Passive artificial– injecting antibodies from other sources ...
chapter16
... Overview of Humoral (Type II) Immunity B cells are covered with thousands of copies of a membranebound immunoglobulin, termed B cell receptor (BCR) or surface Ig (sIg) The immunoglobulin is specific for a particular molecule from a particular species of pathogen If the pathogen enters the body, then ...
... Overview of Humoral (Type II) Immunity B cells are covered with thousands of copies of a membranebound immunoglobulin, termed B cell receptor (BCR) or surface Ig (sIg) The immunoglobulin is specific for a particular molecule from a particular species of pathogen If the pathogen enters the body, then ...
complement deficiency - ascls-nd
... Includes: >1 episode of invasive meningococcal infection or other Neisserial bacteria. Guidelines – if all antibody responses are normal and patient has recurrent meningococcal disease test for complement deficiency ...
... Includes: >1 episode of invasive meningococcal infection or other Neisserial bacteria. Guidelines – if all antibody responses are normal and patient has recurrent meningococcal disease test for complement deficiency ...
Document
... system response. Antigens are often naturally occurring molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in res ...
... system response. Antigens are often naturally occurring molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in res ...
antigenantibody
... foreign invader because of its ANTIGENS and will cause our B cells (types of lymphocytes, white blood cells) to begin to make proteins called ANTIBODIES. 3. ANTIBODIES have a special molecular form that allows them to match ANTIGENS like a puzzle piece. 4. Once attached, the invader can be destroyed ...
... foreign invader because of its ANTIGENS and will cause our B cells (types of lymphocytes, white blood cells) to begin to make proteins called ANTIBODIES. 3. ANTIBODIES have a special molecular form that allows them to match ANTIGENS like a puzzle piece. 4. Once attached, the invader can be destroyed ...
Complement system
The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. However, it can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 5% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.