helium
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Unit 1 Topics to Review
... There are 7 energy levels, they are shown as periods on the Periodic Table of Elements. The history of the Periodic Table. Know that there are Groups 1-18 on the Periodic Table, and be able to find them. There is a staircase that separates metals and nonmetals Number of protons determines the elemen ...
... There are 7 energy levels, they are shown as periods on the Periodic Table of Elements. The history of the Periodic Table. Know that there are Groups 1-18 on the Periodic Table, and be able to find them. There is a staircase that separates metals and nonmetals Number of protons determines the elemen ...
Chemistry test Review
... 5. Write your own definition for element and pure substance (do not use the book definition!!!!) ...
... 5. Write your own definition for element and pure substance (do not use the book definition!!!!) ...
Post-Lab Questions
... metals. Elements that share similar properties are arranged together in the periodic table within vertical columns called groups or families. The alkaline earth metals—beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium—are a reactive group of metals. Because they combine easily with many o ...
... metals. Elements that share similar properties are arranged together in the periodic table within vertical columns called groups or families. The alkaline earth metals—beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium—are a reactive group of metals. Because they combine easily with many o ...
The Periodic Table
... *As you move across the period, the number of electrons in the outermost orbital increases by one. *In a group, the outermost orbital has the same number of electrons. *Because electrons are the outermost particles in an atom, they are the ones that give an atom it’s properties, so elements with sim ...
... *As you move across the period, the number of electrons in the outermost orbital increases by one. *In a group, the outermost orbital has the same number of electrons. *Because electrons are the outermost particles in an atom, they are the ones that give an atom it’s properties, so elements with sim ...
Nomenclature Notes
... Step 1: Use the periodic table to identify the symbols of the elements (note that the second elements’ ending is –ide meaning, for example, that bromide is actually bromine). Step 2: Determine what number the prefix stands for and write this number as a subscript after the symbol. The number one (1) ...
... Step 1: Use the periodic table to identify the symbols of the elements (note that the second elements’ ending is –ide meaning, for example, that bromide is actually bromine). Step 2: Determine what number the prefix stands for and write this number as a subscript after the symbol. The number one (1) ...
Next > Mendeleev and Meyer
... about an element can be gathered from its position in the period table. For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react with chemically. Understanding the organiza ...
... about an element can be gathered from its position in the period table. For example, you can predict with reasonably good accuracy the physical and chemical properties of the element. You can also predict what other elements a particular element will react with chemically. Understanding the organiza ...
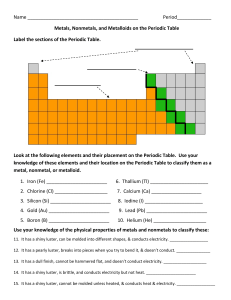
Name Period_____________ Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids on
... 13. It has a dull finish, cannot be hammered flat, and doesn’t conduct electricity. ___________________ 14. It has a shiny luster, is brittle, and conducts electricity but not heat. ______________________ 15. It has a shiny luster, cannot be molded unless heated, & conducts heat & electricity. _____ ...
... 13. It has a dull finish, cannot be hammered flat, and doesn’t conduct electricity. ___________________ 14. It has a shiny luster, is brittle, and conducts electricity but not heat. ______________________ 15. It has a shiny luster, cannot be molded unless heated, & conducts heat & electricity. _____ ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE Introduction • Dmitri Mendeleev is the father
... • Some metalloids such as silicon, germanium (Ge), and arsenic (As) are semiconductors. • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. 3. Atomic Radius • Atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron. It affects the ...
... • Some metalloids such as silicon, germanium (Ge), and arsenic (As) are semiconductors. • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. 3. Atomic Radius • Atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron. It affects the ...
Full Chapter - CPO Science
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Periodic Table - Marian High School
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Do-now
... How does ionization energy increase? What will produce larger ions, Oxygen or Nitrogen? What has a larger atomic radius, Cesium or Potassium? Which is more likely to attract more electrons, Silicon or ...
... How does ionization energy increase? What will produce larger ions, Oxygen or Nitrogen? What has a larger atomic radius, Cesium or Potassium? Which is more likely to attract more electrons, Silicon or ...
File
... • Cu, Ag, Au are three of the oldest known elements. • By the year 1700, only 13 elements had been identified and isolated. • From 1765-1775, five new elements including H, N, and O had been isolated. • As soon as elements were (are) identified, scientists begin to look for similarities and ...
... • Cu, Ag, Au are three of the oldest known elements. • By the year 1700, only 13 elements had been identified and isolated. • From 1765-1775, five new elements including H, N, and O had been isolated. • As soon as elements were (are) identified, scientists begin to look for similarities and ...
studyguideperiodictrends
... _____ and chemical properties___. Bonus: What scientist is given the most credit because he published his info first? Mendeleev ...
... _____ and chemical properties___. Bonus: What scientist is given the most credit because he published his info first? Mendeleev ...
Name
... 12. Each clue refers to a property of an element or a relationship an element has to other elements in the periodic table. 13. Along with logic and knowledge of properties, you will use periodic trends to solve the puzzle. 14. When you are done, each element will be in its unique place on the table. ...
... 12. Each clue refers to a property of an element or a relationship an element has to other elements in the periodic table. 13. Along with logic and knowledge of properties, you will use periodic trends to solve the puzzle. 14. When you are done, each element will be in its unique place on the table. ...
... and its placement on the periodic table. viii. Which element will have the smallest atomic radius in this period? Why? Answers will vary for each period. Electrons added to the same energy level experience increasing attraction to the nucleus due to successive addition of protons. ix. Which element ...
File - Ricci Math and Science
... ___ 9. Group of metals that have two (2) valence electrons. ___ 10. Very reactive nonmetals that include iodine. ...
... ___ 9. Group of metals that have two (2) valence electrons. ___ 10. Very reactive nonmetals that include iodine. ...
The Periodic Table
... Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of alkali metals Hydrogen was involved in ...
... Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of alkali metals Hydrogen was involved in ...
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law
... He insisted that elements with similar characteristics be listed in the same groups (vertical columns)…for this reason, he had to leave several blank spaces in his periodic table ...
... He insisted that elements with similar characteristics be listed in the same groups (vertical columns)…for this reason, he had to leave several blank spaces in his periodic table ...
Periodic Table Notes
... The periodic table as we have it today has not always existed; it developed much in the same way as atomic theory did. In the early 1800’s scientists began looking for ways to classify the elements that had been discovered. ...
... The periodic table as we have it today has not always existed; it developed much in the same way as atomic theory did. In the early 1800’s scientists began looking for ways to classify the elements that had been discovered. ...
Chapter 10
... (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium) 8. Alkaline-earth metal-one of the elements of Group 2 of the periodic table (beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium) 9. Halogen-one of the elements of Group 17 of the periodic table (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodi ...
... (lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium) 8. Alkaline-earth metal-one of the elements of Group 2 of the periodic table (beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium) 9. Halogen-one of the elements of Group 17 of the periodic table (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodi ...
Port Said International Schools
... 11.All the following elements don’t react with dilute HCL except (Cu- Zn- S- C) 12.Elements which have atomic number( 2,8,16- 2,10,18- 3,11,19- 4,12,20) are called alkali metals. 13.Alkali metals have the following properties except (they have low density- they conduct electricity- they conduct heat ...
... 11.All the following elements don’t react with dilute HCL except (Cu- Zn- S- C) 12.Elements which have atomic number( 2,8,16- 2,10,18- 3,11,19- 4,12,20) are called alkali metals. 13.Alkali metals have the following properties except (they have low density- they conduct electricity- they conduct heat ...
Chemistry 4.2
... The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. A weighted average mass reflects both the mass and the relative abundance of the isotopes as they occur in nature. ...
... The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average mass of the atoms in a naturally occurring sample of the element. A weighted average mass reflects both the mass and the relative abundance of the isotopes as they occur in nature. ...
Periodic Table2011
... Alkaline Earth Metals • They are never found uncombined in nature. • They have two valence electrons. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... Alkaline Earth Metals • They are never found uncombined in nature. • They have two valence electrons. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Periodic Table - MunterChemistry
... shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron affinity of nitrogen. ...
... shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron affinity of nitrogen. ...