Periodic Trends - CK
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
Ch. 14 notes (teacher)3
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. ...
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. ...
Periodic Table PowerPoint
... – can be stretched into a wire 5. malleable – can be hammered or rolled into sheets ...
... – can be stretched into a wire 5. malleable – can be hammered or rolled into sheets ...
Nov 9 Agenda
... 2) Atoms with a larger period number have lower ionization energies because it’s easier to remove an electron that far away from the nucleus. ...
... 2) Atoms with a larger period number have lower ionization energies because it’s easier to remove an electron that far away from the nucleus. ...
400 Chem periodic table
... • Electron Affinity is effectively the opposite of ionization energy. • It is the energy released by an atom when it gains an electron (exothermic). • The halogens have the greatest electron affinity because gaining one electron gets them to noble gas configuration. • Electron Affinity generally inc ...
... • Electron Affinity is effectively the opposite of ionization energy. • It is the energy released by an atom when it gains an electron (exothermic). • The halogens have the greatest electron affinity because gaining one electron gets them to noble gas configuration. • Electron Affinity generally inc ...
Protons, Valence Electrons, and the Periodic Table
... • Atoms are the simplest form of an element that cannot be broken down chemically. • They maintain the element’s properties. • Each element is an atom that has the same number of protons – – i.e. the same atomic number on the periodic table of elements. ...
... • Atoms are the simplest form of an element that cannot be broken down chemically. • They maintain the element’s properties. • Each element is an atom that has the same number of protons – – i.e. the same atomic number on the periodic table of elements. ...
Periodic Law
... electron is acquired by a neutral atom When an atom gains an electron easily, a large amount of energy is released (indicated by a high negative number). These elements will have a high electron affinity. ...
... electron is acquired by a neutral atom When an atom gains an electron easily, a large amount of energy is released (indicated by a high negative number). These elements will have a high electron affinity. ...
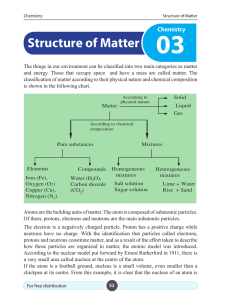
Compounds have different properties from the elements that make
... substances are compounds. A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more different elements. Just as the 26 letters in the alphabet can form thousands of words, the elements in the periodic table can form millions of compounds. The atoms of different elements are held together in compounds b ...
... substances are compounds. A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more different elements. Just as the 26 letters in the alphabet can form thousands of words, the elements in the periodic table can form millions of compounds. The atoms of different elements are held together in compounds b ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
Questions on Chapter 7
... B) They all readily form ions with a +1 charge. C) They all have 2 electrons in their valence shells. D) They are very reactive elements. E) They have the lowest first ionization energies of the elements. 71) Consider the following properties of an element: (i) It is solid at room temperature. (ii) ...
... B) They all readily form ions with a +1 charge. C) They all have 2 electrons in their valence shells. D) They are very reactive elements. E) They have the lowest first ionization energies of the elements. 71) Consider the following properties of an element: (i) It is solid at room temperature. (ii) ...
Powerpoint for Periodicity and Density
... transition metals (rare earth elements) Electrons are added to the f – orbitals. Ex: Ce Lu Th Lr ...
... transition metals (rare earth elements) Electrons are added to the f – orbitals. Ex: Ce Lu Th Lr ...
Periodicity PPt
... transition metals (rare earth elements) Electrons are added to the f – orbitals. Ex: Ce Lu Th Lr ...
... transition metals (rare earth elements) Electrons are added to the f – orbitals. Ex: Ce Lu Th Lr ...
The periodic table shows all the elements and their
... The periodic table is structured as an 18 X 7 grid, positioned above a smaller double row of elements. The periodic table only lists chemical elements, and includes each isotope of each element within one cell. In the typical periodic table, each element is listed by its element symbol and atomic nu ...
... The periodic table is structured as an 18 X 7 grid, positioned above a smaller double row of elements. The periodic table only lists chemical elements, and includes each isotope of each element within one cell. In the typical periodic table, each element is listed by its element symbol and atomic nu ...
Unit 6 Review Packet - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... 24. Outershell electrons are also called ________________________ ______________________. 26. The most active Alkali Metal is ____________________. 28. Ce (cerium) is a member of the _______________________ series. 23. Nonmetals have _____________________ ionization energies and electron affiniti ...
... 24. Outershell electrons are also called ________________________ ______________________. 26. The most active Alkali Metal is ____________________. 28. Ce (cerium) is a member of the _______________________ series. 23. Nonmetals have _____________________ ionization energies and electron affiniti ...
315`01-01
... 40. A negative ion is ( smaller / larger ) than its parent atom. Why? (more electrons than protons) 41. A positive ion is ( smaller / larger ) than its parent atom. Why? (more protons than electrons) 42. Use the periodic table to write the symbol, the most likely oxidation number (ionic charge) and ...
... 40. A negative ion is ( smaller / larger ) than its parent atom. Why? (more electrons than protons) 41. A positive ion is ( smaller / larger ) than its parent atom. Why? (more protons than electrons) 42. Use the periodic table to write the symbol, the most likely oxidation number (ionic charge) and ...
Study Guide Chapter 6
... 2. Define: (a) group (b) period (c) octet (d) octet rule (e) duet rule (f) semiconductor (a) group: one of the 18 columns of elements in the periodic table. (b) period: one of the 7 rows of elements in the periodic table. (c) octet: 8 electrons in the outer level of an atom. (d) octet rule: 8 electr ...
... 2. Define: (a) group (b) period (c) octet (d) octet rule (e) duet rule (f) semiconductor (a) group: one of the 18 columns of elements in the periodic table. (b) period: one of the 7 rows of elements in the periodic table. (c) octet: 8 electrons in the outer level of an atom. (d) octet rule: 8 electr ...
Structure of Matter - e
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
d. Group 1
... a. Metals have low IE and nonmetals have high IE b. Nonmetals have low IE and metals have high IE c. Relative IE varies for metals and ...
... a. Metals have low IE and nonmetals have high IE b. Nonmetals have low IE and metals have high IE c. Relative IE varies for metals and ...
Chapter Twelve: Atoms and the Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE
... • Describe the historical development of the periodic table. • Describe the organization of the modern periodic table according to the periodic law. A. Patterns in Element Properties 1. The elements vary widely in their properties, but in an orderly way. 2. English chemist, John Newlands was the fir ...
... • Describe the historical development of the periodic table. • Describe the organization of the modern periodic table according to the periodic law. A. Patterns in Element Properties 1. The elements vary widely in their properties, but in an orderly way. 2. English chemist, John Newlands was the fir ...
The Periodic Table
... Throw it off the highest building, and I'll not break. But put me in the ocean, and I will. What am I? What can run but never walks, has a mouth but never talks, has a head but never weeps, has a bed but ...
... Throw it off the highest building, and I'll not break. But put me in the ocean, and I will. What am I? What can run but never walks, has a mouth but never talks, has a head but never weeps, has a bed but ...
Chemistry 1 Notes #10 Chapter 6 Modern Periodic Table
... • lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium • In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
... • lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium • In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.