Periodic Table Study Guide
... Use a periodic table to answer the following questions: 17) Where are the metals located on the periodic table? 18) Where are the nonmetals located on the periodic table? 19) What classification of elements are between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table? 20) What is the standard state f ...
... Use a periodic table to answer the following questions: 17) Where are the metals located on the periodic table? 18) Where are the nonmetals located on the periodic table? 19) What classification of elements are between the metals and nonmetals on the periodic table? 20) What is the standard state f ...
Periodic_Table
... Covalent Atomic Radius One half the distance betweeen nuclei of atoms in a diatomic molecule ...
... Covalent Atomic Radius One half the distance betweeen nuclei of atoms in a diatomic molecule ...
Bohr Model Activity
... e. Use a different colour to highlight the electrons in the outermost shell. ...
... e. Use a different colour to highlight the electrons in the outermost shell. ...
File
... data is available. Some elements, for example, may not form a compound with hydrogen. 3. Working together, discuss the possibilities for arrangement of the element cards with all members of the group, and look for a logical arrangement of the cards. Consider the similarities and differences among th ...
... data is available. Some elements, for example, may not form a compound with hydrogen. 3. Working together, discuss the possibilities for arrangement of the element cards with all members of the group, and look for a logical arrangement of the cards. Consider the similarities and differences among th ...
Test review
... _____22. tendency of an element to gain electrons when combining b. electron affinity with another element c. ionization energy _____23. energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom d. all of the above (a, b and c) _____24. increases across a period due to nuclear charge e. atomic size __ ...
... _____22. tendency of an element to gain electrons when combining b. electron affinity with another element c. ionization energy _____23. energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom d. all of the above (a, b and c) _____24. increases across a period due to nuclear charge e. atomic size __ ...
Chapter 5 - The Periodic Law
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
CBSE Class 10 Physics Periodic classification of elements Notes
... a. The law was applicable to elements upto calcium (Ca) only b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two element ...
... a. The law was applicable to elements upto calcium (Ca) only b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two element ...
Chemistry - OnMyCalendar
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclear radiation as they decay. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclear radiation as they decay. ...
Document
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclear radiation as they decay. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element, but have different masses. Isotopes with an unstable nucleus will tend to breakdown or decay; these atoms are called radioactive and will release energy in the form of nuclear radiation as they decay. ...
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... The properties of an element can be ________________ from its ________________ on the periodic table. ...
... The properties of an element can be ________________ from its ________________ on the periodic table. ...
e - WordPress.com
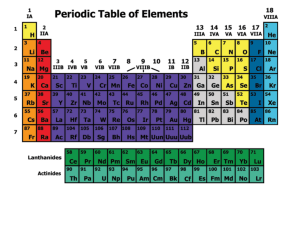
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group. ...
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group. ...
Atoms and Ions Practice Problems
... B) They are shiny. C) They are good conductors of electricity. D) They react vigorously with water. E) Most of them are liquids at room temperature. ...
... B) They are shiny. C) They are good conductors of electricity. D) They react vigorously with water. E) Most of them are liquids at room temperature. ...
Ri Christmas Lectures 2012: The Modern Alchemist
... of Protons in the nucleus determines which Element the atom is, and it is the number of Protons which gives an element its 'Atomic Number'. Neutrons carry no charge, and have a relative mass of 1. Neutrons make up the rest of the mass of the Nucleus (along with Protons). The number of neutrons that ...
... of Protons in the nucleus determines which Element the atom is, and it is the number of Protons which gives an element its 'Atomic Number'. Neutrons carry no charge, and have a relative mass of 1. Neutrons make up the rest of the mass of the Nucleus (along with Protons). The number of neutrons that ...
Ch. 11.4 Notes (Periodicity) teacher 2012
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
Relationships in The PeriodicTable
... energy, the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and an electron. Electron affinity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to gain an electron. ...
... energy, the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and an electron. Electron affinity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to gain an electron. ...
The Periodic Table
... are very reactive and have a low melting point. Shade the alkali metals blue. 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located ...
... are very reactive and have a low melting point. Shade the alkali metals blue. 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located ...
Periodic classificatiion of elements
... A. The tendency to lose electrons decreases on moving from left to right in a period because the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a gr ...
... A. The tendency to lose electrons decreases on moving from left to right in a period because the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a gr ...
ד"סב Chemistry Chapter 4 What is John Newland`s law of octaves
... Group 1, besides hydrogen. ● Metals ● Usually solid at room temperature ● Conductors of heat and electricity ● Metallic luster ● Very reactive with water and oxygen ○ Stored in oil and many layers of protective covering to prevent these reactions ● 1 valence electron ● Very reactive because they're ...
... Group 1, besides hydrogen. ● Metals ● Usually solid at room temperature ● Conductors of heat and electricity ● Metallic luster ● Very reactive with water and oxygen ○ Stored in oil and many layers of protective covering to prevent these reactions ● 1 valence electron ● Very reactive because they're ...
Groups
... Elements that exist in more than one form are called allotropes. An example is carbon in forms of ...
... Elements that exist in more than one form are called allotropes. An example is carbon in forms of ...
6.6 – Periodic Table
... similar chemical properties. Period – Horizontal row on the periodic table. These elements have the same number of occupied energy levels. Valence Electrons – Electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons determine the atom’s chemical properties. ...
... similar chemical properties. Period – Horizontal row on the periodic table. These elements have the same number of occupied energy levels. Valence Electrons – Electrons found in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons determine the atom’s chemical properties. ...
Periodic trends
... VERY reactive because one valence e• Found as compounds in nature • Not including H! ...
... VERY reactive because one valence e• Found as compounds in nature • Not including H! ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.