C1 - Powerpoint - tonyconnett.com
... 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom would most strongly attract an electron to the ‘gap’ in the outer shell? 5. Whi ...
... 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom would most strongly attract an electron to the ‘gap’ in the outer shell? 5. Whi ...
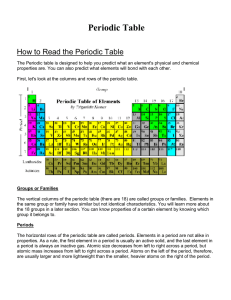
How to Read the Periodic Table
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
Topics 3 and 13 Outline
... • The group numbering scheme from group 1 to group 18, as recommended by IUPAC, should be used. 3.2 Periodic trends Essential idea: Elements show trends in their physical and chemical properties across periods and down groups. Nature of science: Looking for patterns—the position of an element in the ...
... • The group numbering scheme from group 1 to group 18, as recommended by IUPAC, should be used. 3.2 Periodic trends Essential idea: Elements show trends in their physical and chemical properties across periods and down groups. Nature of science: Looking for patterns—the position of an element in the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Atoms, the Periodic Table & more review!
... 7 valence electrons F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
... 7 valence electrons F, Cl, Br, I, At very reactive They are very reactive because have 7 valence electrons, this means they are ALMOST full and can combine with many elements. • Nonmetals • Halogen elements combine with metals to form compounds called salts. ...
The Periodic Table of the Elements
... • A valence electron for a transition metal is defined as an electron that resides outside a noble-gas core, which can be in an inner or outer shell. • The energies of electrons in the d sublevels are comparable to the s sublevel of the next highest main level (3d and 4s, 4d and 5s), so an element’s ...
... • A valence electron for a transition metal is defined as an electron that resides outside a noble-gas core, which can be in an inner or outer shell. • The energies of electrons in the d sublevels are comparable to the s sublevel of the next highest main level (3d and 4s, 4d and 5s), so an element’s ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Explanation: The formula of the compound MCl2 indicates that M must have 2+ charges on it and it must be an alkaline-earth metal. Element reactivity and atomic radius typically increase down the group, which means that the element could be Ca or Sr. Since Sr is the only option that fits the answer i ...
... Explanation: The formula of the compound MCl2 indicates that M must have 2+ charges on it and it must be an alkaline-earth metal. Element reactivity and atomic radius typically increase down the group, which means that the element could be Ca or Sr. Since Sr is the only option that fits the answer i ...
Chapter 6 Review “The Periodic Table”
... Chapter 6 Review To what category of elements does an element belong if it is a poor conductor of electricity? What is the charge of a cation? Which of these elements has the lowest electronegativity value: a) cesium, or b) calcium? Which of the following is correct: a) In, 49 protons, 49 ele ...
... Chapter 6 Review To what category of elements does an element belong if it is a poor conductor of electricity? What is the charge of a cation? Which of these elements has the lowest electronegativity value: a) cesium, or b) calcium? Which of the following is correct: a) In, 49 protons, 49 ele ...
MATTER AND PERIODIC TABLE
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
Microsoft Word - HONORS CHEMISTRY MID
... a. melting gold b. running an electric current through copper c. corroding iron d. breaking an ice cube Multiple Choice: Ch. 4 Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of al ...
... a. melting gold b. running an electric current through copper c. corroding iron d. breaking an ice cube Multiple Choice: Ch. 4 Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of al ...
Periodic Trends Notes
... “There is in the atom a fundamental quantity which increases by regular steps as we pass from each element to the next. This quantity can only be the charge on the central positive nucleus.” Moseley’s research was halted when the British government sent him to serve as a foot soldier in WWI. He was ...
... “There is in the atom a fundamental quantity which increases by regular steps as we pass from each element to the next. This quantity can only be the charge on the central positive nucleus.” Moseley’s research was halted when the British government sent him to serve as a foot soldier in WWI. He was ...
module-21 (worksheet-1)
... On the basis of the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9. (a) Name the most electropositive element among them_____________________________. (b) Name the most electronegative element_______________________________________. (c) Name th ...
... On the basis of the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9. (a) Name the most electropositive element among them_____________________________. (b) Name the most electronegative element_______________________________________. (c) Name th ...
Cations (positive ions) are smaller than their respective atoms.
... Is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase. Each atom can have a series of ionization energies, since more than one electron can always be removed ...
... Is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase. Each atom can have a series of ionization energies, since more than one electron can always be removed ...
Periodicity
... atoms of the elements. Moseley arranged the elements in a table by order of atomic number. The Periodic Table - Horizontal rows are called periods. - Vertical columns are called groups or families - The Periodic Law states, “When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a ...
... atoms of the elements. Moseley arranged the elements in a table by order of atomic number. The Periodic Table - Horizontal rows are called periods. - Vertical columns are called groups or families - The Periodic Law states, “When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a ...
Periodicity
... Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself. . The electronegativity increases from bottom to top and from left to right. . Fluorine is the most electronegative element. . Cesium and Francium are the least electronegative elements. ...
... Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons to itself. . The electronegativity increases from bottom to top and from left to right. . Fluorine is the most electronegative element. . Cesium and Francium are the least electronegative elements. ...
vocab - SALAZAR!!
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
Enriched Chemistry Chapter 5 * The Periodic Law
... The p-Block elements: groups 13-18 • The p-block elements together with the s-block elements are called the main-group elements • props of p-block elements vary greatly • includes all of the nonmetals except H and He, and the six metalloids • The families are known by the first element in each fami ...
... The p-Block elements: groups 13-18 • The p-block elements together with the s-block elements are called the main-group elements • props of p-block elements vary greatly • includes all of the nonmetals except H and He, and the six metalloids • The families are known by the first element in each fami ...
Regions of the Periodic Table
... ions are not soluble in water transition metals: elements in the center section of the periodic table. have a partially-filled d sub-level form colored ions when dissolved in water officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons into and out of s and d sub-levels. Often form mor ...
... ions are not soluble in water transition metals: elements in the center section of the periodic table. have a partially-filled d sub-level form colored ions when dissolved in water officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons into and out of s and d sub-levels. Often form mor ...
File
... All the elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons Group number (1A-8A) = number of valence e- **this only works for the Representative Elements (s & p block)** Elements with the same number of valence e- have similar properties ...
... All the elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons Group number (1A-8A) = number of valence e- **this only works for the Representative Elements (s & p block)** Elements with the same number of valence e- have similar properties ...
day4-periodictrends
... Work silently. Raise hand to ask Ms. Hughes anything. 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
... Work silently. Raise hand to ask Ms. Hughes anything. 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
Labeling a Blank Periodic Table
... the tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element ...
... the tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element ...
File - the prayas tutorial
... discovered later but the properties were similar to eka-boron, eka-aluminium and ekasilicon. Noble gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon have been mentioned in his context though they are highly inert and low concentration in our atmosphere. When these gases were discovered they placed a new group with ...
... discovered later but the properties were similar to eka-boron, eka-aluminium and ekasilicon. Noble gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon have been mentioned in his context though they are highly inert and low concentration in our atmosphere. When these gases were discovered they placed a new group with ...
the Alkali Metals
... – Harder and denser then s-block alkaline-earth metals – Softer and less dense than d-block metals – Stable in the presence of air ...
... – Harder and denser then s-block alkaline-earth metals – Softer and less dense than d-block metals – Stable in the presence of air ...
The perfect K-12 presentation ever (replace this with your title)
... Red Giants Main Sequence Stars, such as Red Giants, derive their energy from hydrogen fusion. ...
... Red Giants Main Sequence Stars, such as Red Giants, derive their energy from hydrogen fusion. ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.