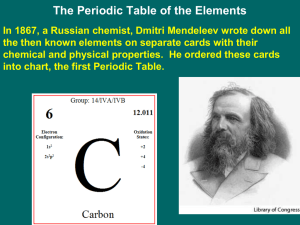
4.3 Exploring the Modern Periodic Table
... bonds with the following elements: (hint: compare the column # below with the example above) (silicon is in column # ...
... bonds with the following elements: (hint: compare the column # below with the example above) (silicon is in column # ...
Y10 Chem SLOs 2016 File
... 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number and identify an elements position on the periodic table 7. I know what an ion is and how ...
... 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number and identify an elements position on the periodic table 7. I know what an ion is and how ...
Atomic/Periodic Table Review
... table and show the atomic number and mass number for each example: 8. How do isotopes vary from the elements found on the periodic table? b. Give 3 examples of isotopes of carbon, oxygen, and uranium make sure to include the new mass number and explain why it changed 9. If the relative abundance of ...
... table and show the atomic number and mass number for each example: 8. How do isotopes vary from the elements found on the periodic table? b. Give 3 examples of isotopes of carbon, oxygen, and uranium make sure to include the new mass number and explain why it changed 9. If the relative abundance of ...
2.2 Periodic Chart
... distinctive colours (Ne is reddish) when electricity is passed through them. Their ion charges of zero indicate that they do not form charged ions. ...
... distinctive colours (Ne is reddish) when electricity is passed through them. Their ion charges of zero indicate that they do not form charged ions. ...
Periodic Trends - The Green Isle
... the nucleus and the attraction of the nucleus. Why do you think the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus determines the amount of energy required to remove electrons from the atom? ...
... the nucleus and the attraction of the nucleus. Why do you think the distance between the valence electrons and the nucleus determines the amount of energy required to remove electrons from the atom? ...
assignment-07-a3
... 20- Which of the following has the highest ionization energy? Na, Na+, K+, Mg2+? a) Na+ b) Mg2+ c) K+ d) Na (This magnesium ion has the largest positive charge of the list of atoms and ions, and has an inertgas-like electron configuration.) 21- Which of the following are metalloids? a) O, S, Se b) A ...
... 20- Which of the following has the highest ionization energy? Na, Na+, K+, Mg2+? a) Na+ b) Mg2+ c) K+ d) Na (This magnesium ion has the largest positive charge of the list of atoms and ions, and has an inertgas-like electron configuration.) 21- Which of the following are metalloids? a) O, S, Se b) A ...
Date Period - Swift Classroom
... He put the elements in order by _______________________ He found that other properties such as _________________________, _______________________, and the ability to ______________________ with other elements seemed to ____________________ over and over. This repeating pattern is called ______ ...
... He put the elements in order by _______________________ He found that other properties such as _________________________, _______________________, and the ability to ______________________ with other elements seemed to ____________________ over and over. This repeating pattern is called ______ ...
Alchemy Unit Concepts Review
... f. Metals vs. nonmetals (where does H belong?) Metals are the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals and H are the right side periodic table. 11. Using your periodic table, what are the trends for … a. atomic number (both across a period and down a group) Atomic number increases as you move left ...
... f. Metals vs. nonmetals (where does H belong?) Metals are the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals and H are the right side periodic table. 11. Using your periodic table, what are the trends for … a. atomic number (both across a period and down a group) Atomic number increases as you move left ...
Periodic Table Notes Page
... The smallest piece of an element that still has the properties of that element is called an ___________________. An element is a _______________substance, containing only one kind of _________. The ____________________________________ is a list of all the elements that have been discovered and named ...
... The smallest piece of an element that still has the properties of that element is called an ___________________. An element is a _______________substance, containing only one kind of _________. The ____________________________________ is a list of all the elements that have been discovered and named ...
The Periodic Table
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. ...
... Transition elements have properties similar to one another and to other metals, but their properties do not fit in with those of any other family. Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. ...
(periods) to
... sometimes shown as having a coordinate bond between sulfur and oxygen or they are show as having double between the sulfur and the oxygen. Both are acceptable. ...
... sometimes shown as having a coordinate bond between sulfur and oxygen or they are show as having double between the sulfur and the oxygen. Both are acceptable. ...
Periodic Table Patterns -text 133
... a.They all have the same atomic mass. b.They all have similar characteristics. c.They all have similar atomic numbers. d.They all have the same chemical symbol. 14.The atomic number for the element calcium (Ca) is 20. How many protons and electrons does each calcium atom have? ______________________ ...
... a.They all have the same atomic mass. b.They all have similar characteristics. c.They all have similar atomic numbers. d.They all have the same chemical symbol. 14.The atomic number for the element calcium (Ca) is 20. How many protons and electrons does each calcium atom have? ______________________ ...
PeriodicTableNotes
... the square. (typically has a decimal point with numbers after it) o The _____________ ____________ is the number given to element that represents its place on the periodic table. This number is generally the smaller of the two numbers and is normally at the top of the square. It is also the number o ...
... the square. (typically has a decimal point with numbers after it) o The _____________ ____________ is the number given to element that represents its place on the periodic table. This number is generally the smaller of the two numbers and is normally at the top of the square. It is also the number o ...
Science Review Sheet: Periodic Table Test Name: __________
... 12. What are the columns on the periodic table called? What do the elements in each column of the periodic table have in common with each other? ...
... 12. What are the columns on the periodic table called? What do the elements in each column of the periodic table have in common with each other? ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... gases or liquids in their pure form. Fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), and bromine (Br) form salts when the bond with alkali metals. ...
... gases or liquids in their pure form. Fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), and bromine (Br) form salts when the bond with alkali metals. ...
Mr. Trachtenberg`s Big Chemistry Test Review Part I of III 20pts
... 11.) Elements in the upper right-‐hand corner of the Periodic Table have the highest electronegativies and ionization energies. 12.) Moving down a group atoms get larger 13.) Moving from l ...
... 11.) Elements in the upper right-‐hand corner of the Periodic Table have the highest electronegativies and ionization energies. 12.) Moving down a group atoms get larger 13.) Moving from l ...
- sartep.com
... 7. From left to right across a period, what change is occurring within the atomic nuclei? a. A proton is gained. _ b. An electron is gained. c. A neutron is lost. d. The electron cloud size is decreasing. 8. The chart to the right shows the relationship between the first ionization potential and the ...
... 7. From left to right across a period, what change is occurring within the atomic nuclei? a. A proton is gained. _ b. An electron is gained. c. A neutron is lost. d. The electron cloud size is decreasing. 8. The chart to the right shows the relationship between the first ionization potential and the ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Worksheet
... 22. Most of the elements in the periodic table are non-metals. ___________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Electrons are found in the nucleus and have a positive charge. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 22. Most of the elements in the periodic table are non-metals. ___________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Electrons are found in the nucleus and have a positive charge. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Periodic Table Cloze - Science
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. atom gold nonmetals ...
... Fill in the blanks with words from the box. atom gold nonmetals ...
The Periodic Table Worksheet
... 4. a) What is the link between the group to which an element belongs in the periodic table and the number of electrons in an atom of the element’s outer shell? ...
... 4. a) What is the link between the group to which an element belongs in the periodic table and the number of electrons in an atom of the element’s outer shell? ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.