Atomic Structure
... • Atomic Number – how many protons and electrons there are in an atom • Mass Number – total number of protons and neutrons. • Atomic Mass Units – atomic mass does appear on the periodic table and is measured in u. – Not measured on a balance, it is how they are relative to each other – A proton is a ...
... • Atomic Number – how many protons and electrons there are in an atom • Mass Number – total number of protons and neutrons. • Atomic Mass Units – atomic mass does appear on the periodic table and is measured in u. – Not measured on a balance, it is how they are relative to each other – A proton is a ...
Objective - davis.k12.ut.us
... shared certain patterns and trends. He observed that the elements shared some chemical and physical properties. Dmitri believed the properties that the elements shared were important. Therefore, he wrote down all the properties he knew about elements on cards. He used the properties of melting point ...
... shared certain patterns and trends. He observed that the elements shared some chemical and physical properties. Dmitri believed the properties that the elements shared were important. Therefore, he wrote down all the properties he knew about elements on cards. He used the properties of melting point ...
The Periodic Table Notes
... observed that the elements shared some chemical and physical properties. Dmitri believed the properties that the elements shared were important. Therefore, he wrote down all the properties he knew about elements on cards. He used the properties of melting point, density, color, atomic mass and bondi ...
... observed that the elements shared some chemical and physical properties. Dmitri believed the properties that the elements shared were important. Therefore, he wrote down all the properties he knew about elements on cards. He used the properties of melting point, density, color, atomic mass and bondi ...
NAME - Cobb Learning
... In 1870, Dmitri Mendeleev first proposed a new way of studying and organizing the then known 63 elements. The modern form of the table has been modified and improved many times since Mendeleev’s tables. Pioneers like Moseley (1913) and Seaborg (1941) have made the properties of the elements much sim ...
... In 1870, Dmitri Mendeleev first proposed a new way of studying and organizing the then known 63 elements. The modern form of the table has been modified and improved many times since Mendeleev’s tables. Pioneers like Moseley (1913) and Seaborg (1941) have made the properties of the elements much sim ...
Reactivity of Atoms Based on Their Placement in The Periodic Table
... Elements are also classified based on whether the occur naturally or not Elements that do not occur naturally have an atomic number greater than 92 Check them out.... ...
... Elements are also classified based on whether the occur naturally or not Elements that do not occur naturally have an atomic number greater than 92 Check them out.... ...
Pre-Test Atomic Structure
... 5. An atom is usually neutrally charged. This means the number of protons must equal the number of ______________. 6. The atomic number of an atom equals the number of ____________ 7. All atoms of the same element will have the same number of ________________ 8. The periodic table is arranged in ord ...
... 5. An atom is usually neutrally charged. This means the number of protons must equal the number of ______________. 6. The atomic number of an atom equals the number of ____________ 7. All atoms of the same element will have the same number of ________________ 8. The periodic table is arranged in ord ...
The Periodic Table
... Hydrogen is a diatomic, reactive gas. Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of ...
... Hydrogen is a diatomic, reactive gas. Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of ...
R The Periodic Table
... •not able to conduct electricity or heat very well •exist in two of the three states of matter at room temperature: gases (such as oxygen) and solids (such as carbon). •very brittle, and cannot be rolled into wires or pounded into sheets •have no metallic luster, and do not reflect light. ...
... •not able to conduct electricity or heat very well •exist in two of the three states of matter at room temperature: gases (such as oxygen) and solids (such as carbon). •very brittle, and cannot be rolled into wires or pounded into sheets •have no metallic luster, and do not reflect light. ...
Periodic Table Notes
... The modern periodic table was created by the Russian chemist, ____________ ____________. ______________ are represented on the Periodic Table with _____________ _______________. The elements are arranged from left to right based on their ___________ _______________. The atomic number comes from the ...
... The modern periodic table was created by the Russian chemist, ____________ ____________. ______________ are represented on the Periodic Table with _____________ _______________. The elements are arranged from left to right based on their ___________ _______________. The atomic number comes from the ...
The Periodic Law
... a. Identify the element just below samarium in the periodic table. b. The atomic numbers of these two elements differ by how many units? 9. A certain isotope contains 53 protons, 78 neutrons, and 54 electrons. a. What is its atomic number? b. What is the mass of this atom in amus (to the nearest who ...
... a. Identify the element just below samarium in the periodic table. b. The atomic numbers of these two elements differ by how many units? 9. A certain isotope contains 53 protons, 78 neutrons, and 54 electrons. a. What is its atomic number? b. What is the mass of this atom in amus (to the nearest who ...
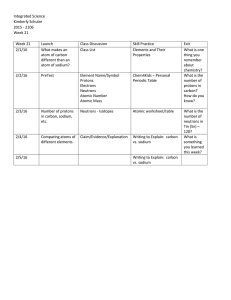
Week 21 Lessons - Highline Public Schools
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
Periodic Table PP revised 2014
... some are quite reactive, others are nonreactive. • Some can be found in pure form in nature (Cu, Ag, Au) ...
... some are quite reactive, others are nonreactive. • Some can be found in pure form in nature (Cu, Ag, Au) ...
Physical Science Chapter 18 Notes
... o Where is most of the mass of an atom located? The volume? o The mass of a proton is This is o The mass of an electron is o Atomic mass unit (amu): This is It is o What determines the identity of an element? ...
... o Where is most of the mass of an atom located? The volume? o The mass of a proton is This is o The mass of an electron is o Atomic mass unit (amu): This is It is o What determines the identity of an element? ...
3 Periodic Trends
... Match each of the four trends listed to its description by writing the correct letter of the description next to the trend’s name. Trends _____ Ionic Radius _____ Ionization Energy ...
... Match each of the four trends listed to its description by writing the correct letter of the description next to the trend’s name. Trends _____ Ionic Radius _____ Ionization Energy ...
Chapter 5 Section 1 - Ms. Halbohm`s Classroom
... 3. What is the relationship between the electron configuration of an element and the period in which that element appears in the periodic table? 4. What information is provided by the specific block location of an element? Identify, by number, the groups located within each of the four block areas. ...
... 3. What is the relationship between the electron configuration of an element and the period in which that element appears in the periodic table? 4. What information is provided by the specific block location of an element? Identify, by number, the groups located within each of the four block areas. ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... – an element that does not conduct electricity or heat and is usually a gas at room temperature. Nonmetals are brittle, have high ionization energies and high electronegativity values. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form anions. Nonmetals are found on the right side of the boron staircase. ...
... – an element that does not conduct electricity or heat and is usually a gas at room temperature. Nonmetals are brittle, have high ionization energies and high electronegativity values. Nonmetals tend to gain electrons to form anions. Nonmetals are found on the right side of the boron staircase. ...
12.3 The Periodic Table
... The periodic table’s vertical columns are called groups. Groups of elements have similar properties. Use the periodic table and the information found in Chapter 15 of your text to answer the following questions: 15. The first group of the periodic table is known by what name? 16. Name two characteri ...
... The periodic table’s vertical columns are called groups. Groups of elements have similar properties. Use the periodic table and the information found in Chapter 15 of your text to answer the following questions: 15. The first group of the periodic table is known by what name? 16. Name two characteri ...
Study Guide Atoms and Periodic Table TEST Nov 21st
... Power Points to study include: Historic Atomic Structures and Parts of an Atom Introduction to The Periodic table, Metals, Nonmetals and metalloids, Periodic table families You need to know: 1. The scientists responsible for developing and arranging the periodic table and how they arranged it. 2. Di ...
... Power Points to study include: Historic Atomic Structures and Parts of an Atom Introduction to The Periodic table, Metals, Nonmetals and metalloids, Periodic table families You need to know: 1. The scientists responsible for developing and arranging the periodic table and how they arranged it. 2. Di ...
How to Read the Periodic Table
... The vertical columns of the periodic table (there are 18) are called groups or families. Elements in the same group or family have similar but not identical characteristics. You will learn more about the 18 groups in a later section. You can know properties of a certain element by knowing which grou ...
... The vertical columns of the periodic table (there are 18) are called groups or families. Elements in the same group or family have similar but not identical characteristics. You will learn more about the 18 groups in a later section. You can know properties of a certain element by knowing which grou ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Riverton High School
... found that the families had similar chemical properties. Blank spaces were left open to add the new elements he predicted would occur. ...
... found that the families had similar chemical properties. Blank spaces were left open to add the new elements he predicted would occur. ...
Post-Lab Questions
... occurring. Of these 92 elements, the eight most abundant elements together account for more than 98 percent of the mass of the Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. Two of the eight most abundant elements on Earth are calcium and magnesium, which are present in mountains and minerals, seawater and ...
... occurring. Of these 92 elements, the eight most abundant elements together account for more than 98 percent of the mass of the Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. Two of the eight most abundant elements on Earth are calcium and magnesium, which are present in mountains and minerals, seawater and ...
The Periodic Table
... • Label X axis with Atomic #1-20 • Label y axis with 1st IE (KJ/mol atoms) • AFTER you plot the points – Label data points with element symbols ...
... • Label X axis with Atomic #1-20 • Label y axis with 1st IE (KJ/mol atoms) • AFTER you plot the points – Label data points with element symbols ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.