The placement of an element on the periodic table gives clues about
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids The elements in the periodic table can be subdivided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Elements have greater metallic character moving from right to left and from top to bottom within the periodic table. The stairstep line that begins between boron, B, and alu ...
... Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids The elements in the periodic table can be subdivided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Elements have greater metallic character moving from right to left and from top to bottom within the periodic table. The stairstep line that begins between boron, B, and alu ...
The Periodic Table
... oxygen to the element when it oxidized. Periodic law states that properties of the elements repeat periodically when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers. The Modern Periodic Table The first ionization energy is the energy needed to remove one electron from an atom in the gaseo ...
... oxygen to the element when it oxidized. Periodic law states that properties of the elements repeat periodically when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers. The Modern Periodic Table The first ionization energy is the energy needed to remove one electron from an atom in the gaseo ...
Daily Inquiry: 10-31-2011
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. • By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. • By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
nucleic acids - Cloudfront.net
... Isotopes are the various forms of an atom that differ based on the number of neutrons in the nucleus such as C 14. The isotopes that differ from the most common form are often radioactive or unstable. ...
... Isotopes are the various forms of an atom that differ based on the number of neutrons in the nucleus such as C 14. The isotopes that differ from the most common form are often radioactive or unstable. ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements Classification of Matter Matter Matter
... are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction. Subatomic Particles Atoms contains subatomic particles, electrons have a negative (‐) charge. like charges repel and unlike charges attract. ...
... are rearranged to form new combinations in a chemical reaction. Subatomic Particles Atoms contains subatomic particles, electrons have a negative (‐) charge. like charges repel and unlike charges attract. ...
day4-periodictrends
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
Ch 5 Notes
... • Nonmetals: Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Selenium • Metalloids: Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic Antimony, and Terellium ...
... • Nonmetals: Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Selenium • Metalloids: Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic Antimony, and Terellium ...
CBSE Class 10 Physics Periodic classification of elements Notes
... b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two elements in the same slot and also put some unlike elements under sa ...
... b. It contained only 56 elements. Further it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. c. In order to fit elements into the table. Newlands’ adjusted two elements in the same slot and also put some unlike elements under sa ...
The Periodic Law
... table), and then determine the name of the element (with the periodic table) ...
... table), and then determine the name of the element (with the periodic table) ...
Atomic Structure Test – Study Guide
... 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom What subatomic particles are in the nucleus of the atom and what is the charge of the nucleus? Answer: Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is p ...
... 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom What subatomic particles are in the nucleus of the atom and what is the charge of the nucleus? Answer: Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is p ...
First Term Science Al-Karma Language School Prep 2 Question (1
... weight, while Moseley arranged them ascending according to atomic number. 10)-Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) elements are examples of alkaline earth metals. 11)-The valency energy level of halogen contains seven electrons, while that of alkaline earth metal has two electrons. 12)-Sodium and potassi ...
... weight, while Moseley arranged them ascending according to atomic number. 10)-Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) elements are examples of alkaline earth metals. 11)-The valency energy level of halogen contains seven electrons, while that of alkaline earth metal has two electrons. 12)-Sodium and potassi ...
Periodicity
... • is divided into metals (left side), nonmetals (right side), and metalliods. • is arranged in rows (across) in order of increasing energy levels of valence electrons (called periods). The period number represents the energy level for that row. • is arranged in columns (down) in order of similar orb ...
... • is divided into metals (left side), nonmetals (right side), and metalliods. • is arranged in rows (across) in order of increasing energy levels of valence electrons (called periods). The period number represents the energy level for that row. • is arranged in columns (down) in order of similar orb ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
Chapter 5.1 History of PT - Effingham County Schools
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group ...
... The Periodic Table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column, or group ...
File
... in Group 13. What is element Q? What is its atomic number? _____________________ 6. This metal element has an atomic number that some people think is unlucky. What is the element? What did you guess as its atomic number? ...
... in Group 13. What is element Q? What is its atomic number? _____________________ 6. This metal element has an atomic number that some people think is unlucky. What is the element? What did you guess as its atomic number? ...
1 - contentextra
... electronegativities increase as the nuclear charge increases and electrons are added to the same outer shell. The attraction between the outer electrons and nucleus increases. ...
... electronegativities increase as the nuclear charge increases and electrons are added to the same outer shell. The attraction between the outer electrons and nucleus increases. ...
MENDELEEV AND THE ATOMIC TABLE Dmitri Ivanovich
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...
... All versions of the periodic table only include chemical elements, not mixtures, compounds, or subatomic particles, and isotopes of a given element are represented in the same cell. Isotopes are atoms that have an excess or deficiency of Neutrons in the atomic nucleus, giving them in-between atomic ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... This ordering, however, seemed to place some elements out of sequence. A better arrangement, based on atomic number, became possible in 1913, when Henry G. J. Moseley found that the atomic numbers of elements could be determined experimentally from their characteristic x-ray frequencies. Today the ...
... This ordering, however, seemed to place some elements out of sequence. A better arrangement, based on atomic number, became possible in 1913, when Henry G. J. Moseley found that the atomic numbers of elements could be determined experimentally from their characteristic x-ray frequencies. Today the ...
MATTER AND PERIODIC TABLE
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
The Periodic Table: Chapter Problems Periodic Table Class Work
... higher principal quantum number than so the electrons in the outer energy level are farther away from the nucleus. c. Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorous. Although it has the same number of valence electrons as phosphorus, it has a smaller atomic radius. According to Coulomb’s Law, ele ...
... higher principal quantum number than so the electrons in the outer energy level are farther away from the nucleus. c. Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorous. Although it has the same number of valence electrons as phosphorus, it has a smaller atomic radius. According to Coulomb’s Law, ele ...
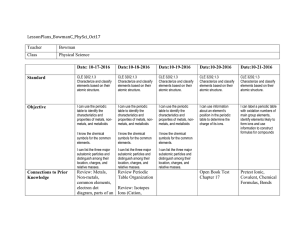
Oct 17-Oct 21
... identify elements likely to form ions and use information to construct formulas for compounds ...
... identify elements likely to form ions and use information to construct formulas for compounds ...
Powerpoint for Periodicity and Density
... the British government sent him to serve as a foot soldier in WWI. He was killed in the fighting in Gallipoli by a sniper’s bullet, at the age of 28. Because of this loss, the ...
... the British government sent him to serve as a foot soldier in WWI. He was killed in the fighting in Gallipoli by a sniper’s bullet, at the age of 28. Because of this loss, the ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.