Ex. 41 Answer
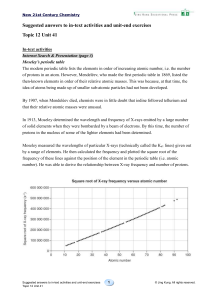
... 19 a) Going across Period 3, there is a regular increase in the number of moles of oxygen atoms that combines with one mole of atoms of each element. This number reaches a maximum ...
... 19 a) Going across Period 3, there is a regular increase in the number of moles of oxygen atoms that combines with one mole of atoms of each element. This number reaches a maximum ...
The Periodic Table
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
... Atoms of the same element always have the same number of protons. This identifies them as the element that they are. But all atoms of an element don’t have to have the same number of neutrons. For example, all boron atoms have 5 protons. However, four-fifths of them have 6 neutrons and one-fifth of ...
Chapter 2 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 percent abundant on earth. • For boron atomic weight ...
... • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. • Average mass = ATOMIC WEIGHT • Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 percent abundant on earth. • For boron atomic weight ...
Atoms & Elements
... • are good insulators. Metalloids • are better conductors than nonmetals, but not as good as metals. • are used as semiconductors and insulators. ...
... • are good insulators. Metalloids • are better conductors than nonmetals, but not as good as metals. • are used as semiconductors and insulators. ...
Chapter 2 Elements are made up of small particles called atoms. All
... A is the Mass number is the total number of neutrons and protons ...
... A is the Mass number is the total number of neutrons and protons ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Spring Packet
... 2. My atomic mass is 35.453. 5. I have 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second shell, and 6 in the third shell. 6. I am the head of the carbon family known as the “basis of life”. 9. My atomic number is 79. 11. I am a transition metal with 25 electrons. 13. I make up 78% of the air and am fo ...
... 2. My atomic mass is 35.453. 5. I have 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second shell, and 6 in the third shell. 6. I am the head of the carbon family known as the “basis of life”. 9. My atomic number is 79. 11. I am a transition metal with 25 electrons. 13. I make up 78% of the air and am fo ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy ____ 33. For Group 2 (2A) metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove? a. the first b. the second c. th ...
... ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy ____ 33. For Group 2 (2A) metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove? a. the first b. the second c. th ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
Chemistry 4.2
... o In general, nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electric current. • Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature. • A few nonmetals are solids, such as sulfur and phosphorus. • One nonmetal, bromine, is a dark-red liquid. ...
... o In general, nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and electric current. • Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature. • A few nonmetals are solids, such as sulfur and phosphorus. • One nonmetal, bromine, is a dark-red liquid. ...
The Periodical Table and chemical properties
... The transition metals, also called the d-block elements, are found in groups 3-12 of the periodic table. These elements make the transition between the representative metals in groups 1 and 2 and the metalloids, representative metals, and nonmetals in groups 13-18. Moreover, it is in this block of e ...
... The transition metals, also called the d-block elements, are found in groups 3-12 of the periodic table. These elements make the transition between the representative metals in groups 1 and 2 and the metalloids, representative metals, and nonmetals in groups 13-18. Moreover, it is in this block of e ...
Click Here
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
Focus On Physical Science
... • Metallic refers to the properties of common metals. • Luster, or shine, is one property of metals. ...
... • Metallic refers to the properties of common metals. • Luster, or shine, is one property of metals. ...
CHAPTER 5, THE PERIODIC LAW Section 1, History of the Periodic
... allow for electrons to be more easily acquired. ...
... allow for electrons to be more easily acquired. ...
Addrienne`s Element Lesson Plan
... Definition: A solid substance made by mixing a metal with another substance, usually another metal, to have specific properties that metals alone lack Context: The earliest metalworkers combined different elemental metals in search of the best alloys for weapons and tools. element Definition: A subs ...
... Definition: A solid substance made by mixing a metal with another substance, usually another metal, to have specific properties that metals alone lack Context: The earliest metalworkers combined different elemental metals in search of the best alloys for weapons and tools. element Definition: A subs ...
Section 4 Powerpoint review lecure
... substance interacts with other substances to produce different kinds of matter. Iron rusting ...
... substance interacts with other substances to produce different kinds of matter. Iron rusting ...
File
... ii. All the elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons and show similar chemical properties. iii. Elements present in a period contain the same number of shells. The number of elements in a period is fixed by the maximum number of electrons which can be accommodated in the various ...
... ii. All the elements in a group have the same number of valence electrons and show similar chemical properties. iii. Elements present in a period contain the same number of shells. The number of elements in a period is fixed by the maximum number of electrons which can be accommodated in the various ...
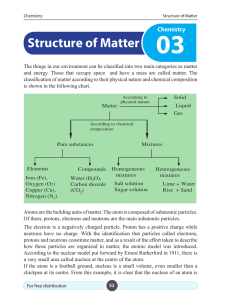
Structure of Matter - e
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
Chapter 4 – Atomic Structure (Sec 4.2 pages 108
... Al: does not react with water, but it does react with oxygen Si: least reactive element (except for argon) P and S: do not react with water, but they do react with oxygen Cl: highly reactive nonmetal Ar: hardly reacts at all ...
... Al: does not react with water, but it does react with oxygen Si: least reactive element (except for argon) P and S: do not react with water, but they do react with oxygen Cl: highly reactive nonmetal Ar: hardly reacts at all ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
... current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the Actinide series. ...
File
... Group 1 = alkali metals (highly reactive) Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (reactive) Groups 3-12 = transition metals Group 17 = the halogens (very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (unreactive) ...
... Group 1 = alkali metals (highly reactive) Group 2 = alkaline earth metals (reactive) Groups 3-12 = transition metals Group 17 = the halogens (very reactive) Group 18 = noble gases (unreactive) ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.