1 February 04, 2016
... - old labelling system: Roman numerals followed by the letter A or B - includes elements with similar chemical properties - the elements in a group have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell/orbit - the electrons in the outermost shell are called the valence numbers ...
... - old labelling system: Roman numerals followed by the letter A or B - includes elements with similar chemical properties - the elements in a group have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell/orbit - the electrons in the outermost shell are called the valence numbers ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table Notes
... The nitrogen family is named after the element that makes up _____ of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they ________. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arsenic, ...
... The nitrogen family is named after the element that makes up _____ of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they ________. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arsenic, ...
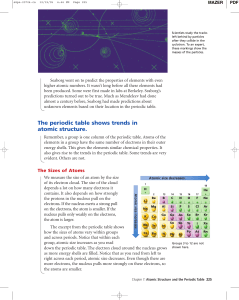
The periodic table shows trends in atomic structure.
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
Parts of the Periodic Table
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
CHEMISTRY
... Metals ___________ electrons and nonmetals ___________ electrons when they react together. 11.5 Patterns for Transition Elements and Ions Fourth period transition elements Why do unexpected configurations occur? Ion Formation Transition metals tend to form more than one ion. Why? ...
... Metals ___________ electrons and nonmetals ___________ electrons when they react together. 11.5 Patterns for Transition Elements and Ions Fourth period transition elements Why do unexpected configurations occur? Ion Formation Transition metals tend to form more than one ion. Why? ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet
... 19. A colored solution absorbs strongest at 680 nm, which is in the visible red region. Does this solution appear red to our eyes? Explain your answer. What is the difference between transmittance and absorbance? Be able to interpret a graph similar to that from Lab 6-1. 20. Which of the following a ...
... 19. A colored solution absorbs strongest at 680 nm, which is in the visible red region. Does this solution appear red to our eyes? Explain your answer. What is the difference between transmittance and absorbance? Be able to interpret a graph similar to that from Lab 6-1. 20. Which of the following a ...
File
... electrons increases. B) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of valence electrons decreases. C) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of orbits increases. D) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of o ...
... electrons increases. B) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of valence electrons decreases. C) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of orbits increases. D) Ionization rates increase as you go across a period because the number of o ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Understanding Main Ideas
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. _____________ An atom’s valence electrons are those electrons that have the highest energy. 2. _____________ Atoms tend to be stable and nonreactive if they have six va ...
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. _____________ An atom’s valence electrons are those electrons that have the highest energy. 2. _____________ Atoms tend to be stable and nonreactive if they have six va ...
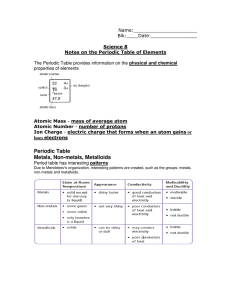
Periodic Table Metals, Non
... Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
... Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
Page 1
... Which group of elements has the highest ionization energies? Which group has the lowest? ...
... Which group of elements has the highest ionization energies? Which group has the lowest? ...
Periodic Trends Name: Part 1: Summary of the Periodic Trends
... Part 3: Applying Periodic Trends 1. Which group on the periodic table has the largest atomic radii? 2. Which group on the periodic table has the largest 1st ionization energy? 3. Which element on the periodic table has the highest and lowest electron affinity? 4. Which element on the periodic table ...
... Part 3: Applying Periodic Trends 1. Which group on the periodic table has the largest atomic radii? 2. Which group on the periodic table has the largest 1st ionization energy? 3. Which element on the periodic table has the highest and lowest electron affinity? 4. Which element on the periodic table ...
questions on periodic classification of elements
... of occupied shells are placed at the same period. (iii) The number of shells increases by one unit as we go down the group. (iv) The number of Valence shell electrons increase by one unit on moving from left to right in a period. Trends in the Modern Periodic Table: Valency: Elements present in a g ...
... of occupied shells are placed at the same period. (iii) The number of shells increases by one unit as we go down the group. (iv) The number of Valence shell electrons increase by one unit on moving from left to right in a period. Trends in the Modern Periodic Table: Valency: Elements present in a g ...
Labeling a Blank Periodic Table
... one of a class of elements that includes a large majority of the known elements; metals are characteristically lustrous, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and ...
... one of a class of elements that includes a large majority of the known elements; metals are characteristically lustrous, malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and ...
The Periodic Table PP
... • The most reactive group of the non metal elements • They have 8 valence electrons • React with most metals to produce salts – Sodium and Chlorine – Table Salt ...
... • The most reactive group of the non metal elements • They have 8 valence electrons • React with most metals to produce salts – Sodium and Chlorine – Table Salt ...
Document
... Periodic Trends Lab - Honors In this graphing lab, you’ll graph 3 different atomic properties to discover trends within a family and period on the periodic table. Procedure 1: 1. Graph on graph paper, the trend of first ionization energy (potential). The graph should have the atomic number on the x- ...
... Periodic Trends Lab - Honors In this graphing lab, you’ll graph 3 different atomic properties to discover trends within a family and period on the periodic table. Procedure 1: 1. Graph on graph paper, the trend of first ionization energy (potential). The graph should have the atomic number on the x- ...
Ch. 5.1 History of the periodic table ppt.
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
... • In order for similar elements to line up, Mendeleev left gaps in his chart. • Mendeleev stated these were undiscovered elements. He made predictions about these undiscovered elements based on the other elements in the same row. – By 1886, these elements (scandium, gallium, and germanium) were disc ...
HS standard 4 2017
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
Chemical Names and Formula
... • Any atom or group of atoms with a positive charge • Na ion is form by the loss of one electron from the Na atom • Sodium ion has 11 protons and 10 electrons it has a charge of 1+ • Atomic charges are written with the number followed by a sign – Na1+ or Na+ (always write ions this way) – If the num ...
... • Any atom or group of atoms with a positive charge • Na ion is form by the loss of one electron from the Na atom • Sodium ion has 11 protons and 10 electrons it has a charge of 1+ • Atomic charges are written with the number followed by a sign – Na1+ or Na+ (always write ions this way) – If the num ...
File
... The periodic table of elements presents three different ways to classify elements. o __________________________________________________ based on their states at room temperature Typically represented by different colors on the periodic table o Naturally occurring vs synthetic All but two element ...
... The periodic table of elements presents three different ways to classify elements. o __________________________________________________ based on their states at room temperature Typically represented by different colors on the periodic table o Naturally occurring vs synthetic All but two element ...
The Periodic Table
... Periods = Horizontal rows #’d 1-7 Each period contains more and more elements ...
... Periods = Horizontal rows #’d 1-7 Each period contains more and more elements ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of Elements - GCG-42
... solids and reactive non-metals. Each period ends with a non-reactive noble gas ...
... solids and reactive non-metals. Each period ends with a non-reactive noble gas ...
graphingtrendschemistry
... a.) Beryllium would have the highest electronegativity because it’s smaller than the other two, and therefore its nucleus is closer to the surface and can take electrons far more easily than the other two elements. b.) Fluorine would have the highest electronegativity in this set, and it’s actually ...
... a.) Beryllium would have the highest electronegativity because it’s smaller than the other two, and therefore its nucleus is closer to the surface and can take electrons far more easily than the other two elements. b.) Fluorine would have the highest electronegativity in this set, and it’s actually ...
10C The Periodic Table
... Symbol and atomic mass: For each of the following, write the element name that corresponds to the symbol. In addition, write the atomic mass for each element. 7. Fe ...
... Symbol and atomic mass: For each of the following, write the element name that corresponds to the symbol. In addition, write the atomic mass for each element. 7. Fe ...
Chapter 5 Reading Guide Please answer the following questions in
... How did the discovery of new elements such as gallium demonstrate the usefulness of Mendeleev’s table? ...
... How did the discovery of new elements such as gallium demonstrate the usefulness of Mendeleev’s table? ...
The Periodic Table
... • malleable – “bendable” (can be pounded into sheets) • ductile - can be pulled into wires ...
... • malleable – “bendable” (can be pounded into sheets) • ductile - can be pulled into wires ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.