
C1 - Powerpoint - tonyconnett.com
... Isotopes… • Isotopes are identical in their chemical reactions. • This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. • The uncharged neutrons make no difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and density. ...
... Isotopes… • Isotopes are identical in their chemical reactions. • This is because they have the same number of protons and the same number of electrons. • The uncharged neutrons make no difference to chemical properties but do affect physical properties such as melting point and density. ...
The Atom - Pleasantville High School
... • Mercury (Hg) - the only liquid metal at room temperature • Bromine (Br) - the only liquid nonmetal at room temperature ...
... • Mercury (Hg) - the only liquid metal at room temperature • Bromine (Br) - the only liquid nonmetal at room temperature ...
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
- Williamsburg High School for
... As atomic number increases within Group 15 on the Periodic Table, atomic radius ...
... As atomic number increases within Group 15 on the Periodic Table, atomic radius ...
Slide 1
... They are the most reactive nonmetal group. They typically react with metals to form salts. The normal states of these elements include two solids, one liquid, and two gases. ...
... They are the most reactive nonmetal group. They typically react with metals to form salts. The normal states of these elements include two solids, one liquid, and two gases. ...
The Periodic Table
... and helicopters) which stay aloft by moving an airfoil through the air in order to produce lift, aerostatic craft such as airships (and balloons) stay aloft primarily by means of a cavity (usually quite large) filled with a gas of lesser density than the surrounding atmosphere. ...
... and helicopters) which stay aloft by moving an airfoil through the air in order to produce lift, aerostatic craft such as airships (and balloons) stay aloft primarily by means of a cavity (usually quite large) filled with a gas of lesser density than the surrounding atmosphere. ...
How the Periodic Table Works
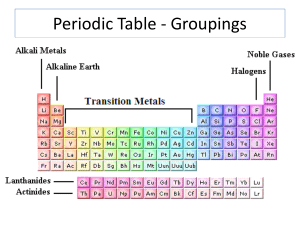
... (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, nonmetals, noble gases and so on). Within the table, the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, as you'll recall. The elements stretch across seven rows. Each row is called a period and indicates the energy levels or shells occupied by the electron ...
... (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, nonmetals, noble gases and so on). Within the table, the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, as you'll recall. The elements stretch across seven rows. Each row is called a period and indicates the energy levels or shells occupied by the electron ...
History of the Periodic Table
... The familiar periodic table that adorns many science classrooms is based on a number of early efforts to identify and classify the elements. In the 1790’s, one of the first lists of elements and their compounds was compiled by French chemist Antioine-Laurent Lavioser. It was Lavoisier who divided th ...
... The familiar periodic table that adorns many science classrooms is based on a number of early efforts to identify and classify the elements. In the 1790’s, one of the first lists of elements and their compounds was compiled by French chemist Antioine-Laurent Lavioser. It was Lavoisier who divided th ...
lecture
... • It is the charged pole in the compounds due to difference in electron negativity and the asymmetry of the compound's structure Water is a polar ...
... • It is the charged pole in the compounds due to difference in electron negativity and the asymmetry of the compound's structure Water is a polar ...
Develo ment of the Atomic Theo John Dalton - (English 1766
... Group 8/Group 0 - Noble Gases/Inert gases - non reactive elements, these elements react only under special conditions, traces of all of these elements are found in the earth’s atmosphere Group 7A - Halogens - most reactive non-metals, not found flee in nature but in compounds Horizontal Rows - Peri ...
... Group 8/Group 0 - Noble Gases/Inert gases - non reactive elements, these elements react only under special conditions, traces of all of these elements are found in the earth’s atmosphere Group 7A - Halogens - most reactive non-metals, not found flee in nature but in compounds Horizontal Rows - Peri ...
Topic 5 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... Figure 2.37 Carbon occurs naturally in different forms, such as graphite and diamonds. In which ways are the physical properties of graphite and diamonds different? ...
... Figure 2.37 Carbon occurs naturally in different forms, such as graphite and diamonds. In which ways are the physical properties of graphite and diamonds different? ...
File
... Figure 2.37 Carbon occurs naturally in different forms, such as graphite and diamonds. In which ways are the physical properties of graphite and diamonds different? ...
... Figure 2.37 Carbon occurs naturally in different forms, such as graphite and diamonds. In which ways are the physical properties of graphite and diamonds different? ...
Chemistry Unit 4: The Periodic Table – Reading
... 10. Where are the lanthanides and actinides located on the table, and why? Section 5.2; pp 138-149 11. Vertical columns are known as ______. What do those elements share in common? 12. Horizontal rows are known as ______. What do those elements share in common? 13. List the name and properties of th ...
... 10. Where are the lanthanides and actinides located on the table, and why? Section 5.2; pp 138-149 11. Vertical columns are known as ______. What do those elements share in common? 12. Horizontal rows are known as ______. What do those elements share in common? 13. List the name and properties of th ...
Next > Mendeleev and Meyer
... Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. ...
... Many transition metals combine chemically with oxygen to form compounds called oxides. ...
In modern periodic table, elements in the same column have similar
... Most reactive nonmetals react with metals to form salts end in s2p5 gain 1 e- to form -1 ions ...
... Most reactive nonmetals react with metals to form salts end in s2p5 gain 1 e- to form -1 ions ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... • Nonmetals• Are mostly gases while others are solid or liquid at room temperature • Are brittle when they are solid • Most are dull in solid form • Are poor conductors of electricity and heat • Tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions ...
... • Nonmetals• Are mostly gases while others are solid or liquid at room temperature • Are brittle when they are solid • Most are dull in solid form • Are poor conductors of electricity and heat • Tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions ...
(FOR STUDENTS 2015)
... valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase across periods, and decrease or remain about the same ...
... valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. • Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. • Electronegativities tend to increase across periods, and decrease or remain about the same ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... Based on their electron configurations. The noble gases all have a full outer shell so they rarely take part in a reaction ...
... Based on their electron configurations. The noble gases all have a full outer shell so they rarely take part in a reaction ...
10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Key Points Notes The
... 10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Notes ...
... 10.2 – District 2: Periodic Table and Trends Notes ...
Periodic Table
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
... Atoms of this family have 6 valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
Adv Chem Multiple Choice Practice: The Periodic Table
... 1-9: Match each item with the correct statement below (not all choices will not be used) a. electronegativity f. periodic law b. ionization energy g. cation c. atomic radius h. period d. metal i. group e. transition metal j. Electrons k. anion ____ ...
... 1-9: Match each item with the correct statement below (not all choices will not be used) a. electronegativity f. periodic law b. ionization energy g. cation c. atomic radius h. period d. metal i. group e. transition metal j. Electrons k. anion ____ ...
5-2%20Using%20the%20Periodic%20Table[1]
... element to attract electrons when an element is in a compound. In general, Electronegativity values decrease from top to bottom within a group. For representative elements ( s- and p- block elements), the values tend to increase from left o right across a period. ...
... element to attract electrons when an element is in a compound. In general, Electronegativity values decrease from top to bottom within a group. For representative elements ( s- and p- block elements), the values tend to increase from left o right across a period. ...
Topic 3-Periodicity
... Essential idea: The arrangement of elements in the periodic table helps to predict their electron configuration. 3.1 Periodic table Nature of science: Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; ...
... Essential idea: The arrangement of elements in the periodic table helps to predict their electron configuration. 3.1 Periodic table Nature of science: Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.



















![5-2%20Using%20the%20Periodic%20Table[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004413504_1-36f532b333702bb3fb3bd75d47d5f6a8-300x300.png)
