Introduction to Plant Virology • History • Definitions • Classification
... A. Acellular, don’t synthesize a cell membrane (+/- envelope= stolen host cell membrane) B. Genome = RNA or DNA C. Protein coat = capsid D. No ribosomes. Lack ability to synthesize organic molecules E. No metabolism. Can’t generate own energy therefore are “metabolic parasites” F. Obligate intracell ...
... A. Acellular, don’t synthesize a cell membrane (+/- envelope= stolen host cell membrane) B. Genome = RNA or DNA C. Protein coat = capsid D. No ribosomes. Lack ability to synthesize organic molecules E. No metabolism. Can’t generate own energy therefore are “metabolic parasites” F. Obligate intracell ...
Respiratory syndrom
... Serology - a retrospective diagnosis may be made by serology. CFT most widely used. HAI and EIA may be used to give a type-specific diagnosis ...
... Serology - a retrospective diagnosis may be made by serology. CFT most widely used. HAI and EIA may be used to give a type-specific diagnosis ...
Report for week ending January 30, 2016
... Wadsworth Center, the NYSDOH public health laboratory, tests specimens from sources including, outpatient healthcare providers (ILINet) and hospitals (FluSurv-NET). There are 2 common subtypes of influenza A viruses – H1 and H3. Each subtype has a slightly different genetic makeup. Wadsworth also id ...
... Wadsworth Center, the NYSDOH public health laboratory, tests specimens from sources including, outpatient healthcare providers (ILINet) and hospitals (FluSurv-NET). There are 2 common subtypes of influenza A viruses – H1 and H3. Each subtype has a slightly different genetic makeup. Wadsworth also id ...
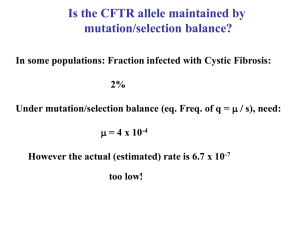
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Neutralist view: allele substitution and polymorphism are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
... Neutralist view: allele substitution and polymorphism are determined by the same evolutionary process. ...
DO NOT USE MY WORDING in your answers!!!
... Explain why violating EACH of the above could cause a population to be out of equilibrium. 12. Why is mutation the least likely to cause a state of non-equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg) within a large, sexually reproducing population? Most mutations are not beneficial, and even when they are beneficial c ...
... Explain why violating EACH of the above could cause a population to be out of equilibrium. 12. Why is mutation the least likely to cause a state of non-equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg) within a large, sexually reproducing population? Most mutations are not beneficial, and even when they are beneficial c ...
Heart Failure:
... fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches) to eye infections, pneumonia, severe respiratory diseases (such as acute respiratory distress), and other severe and life-threatening complications. The symptoms of avian influenza may depend on which virus caused the infection. Because these viruses do n ...
... fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches) to eye infections, pneumonia, severe respiratory diseases (such as acute respiratory distress), and other severe and life-threatening complications. The symptoms of avian influenza may depend on which virus caused the infection. Because these viruses do n ...
What can affect the effective population size? Genetic bottlenecks
... d) The specialization of a molecule affects how it may be impacted by mutations e) Evolution due to neutral mutations & genetic drift 5) What is an example of segregational load? a) Cheetahs having low genetic diversity b) Male elephant seals have a harem & therefore the effective population size is ...
... d) The specialization of a molecule affects how it may be impacted by mutations e) Evolution due to neutral mutations & genetic drift 5) What is an example of segregational load? a) Cheetahs having low genetic diversity b) Male elephant seals have a harem & therefore the effective population size is ...
Свиной Грипп - University of Pittsburgh
... Tamiflu: Allow for Tamiflu to be used to treat and prevent influenza in children under 1 year of age, and to provide alternate dosing recommendations for children older than 1 year. Tamiflu is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment and prevention of influenza in patients 1 year and older. ...
... Tamiflu: Allow for Tamiflu to be used to treat and prevent influenza in children under 1 year of age, and to provide alternate dosing recommendations for children older than 1 year. Tamiflu is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment and prevention of influenza in patients 1 year and older. ...
Свиной Грипп
... Tamiflu: Allow for Tamiflu to be used to treat and prevent influenza in children under 1 year of age, and to provide alternate dosing recommendations for children older than 1 year. Tamiflu is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment and prevention of influenza in patients 1 year and older. ...
... Tamiflu: Allow for Tamiflu to be used to treat and prevent influenza in children under 1 year of age, and to provide alternate dosing recommendations for children older than 1 year. Tamiflu is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment and prevention of influenza in patients 1 year and older. ...
Influenza Vaccination
... Shedding, transmission, and stability of vaccine viruses: Data indicate that both children and adults vaccinated with LAIV can shed vaccine viruses after vaccination, although in lower amounts than occur typically with shedding of wild-type influenza viruses. Rarely, shed vaccine viruses can be tran ...
... Shedding, transmission, and stability of vaccine viruses: Data indicate that both children and adults vaccinated with LAIV can shed vaccine viruses after vaccination, although in lower amounts than occur typically with shedding of wild-type influenza viruses. Rarely, shed vaccine viruses can be tran ...
Clinical Virology: Part Two The Viruses
... • Reoviridae family – Colorado tick fever • Flaviviridae family – Most common cause of arboviral encephalitis in the world, including St. Louis encephalitis (SLE) – West Nile – Dengue fever (Classic and hemorrhagic) – Yellow fever ...
... • Reoviridae family – Colorado tick fever • Flaviviridae family – Most common cause of arboviral encephalitis in the world, including St. Louis encephalitis (SLE) – West Nile – Dengue fever (Classic and hemorrhagic) – Yellow fever ...
Cells Alive
... 2. Why are some, but not all, human cells infected by HIV? What kind of cells does HIV infect? ...
... 2. Why are some, but not all, human cells infected by HIV? What kind of cells does HIV infect? ...
What is viral gastroenteritis
... How does food get contaminated by gastroenteritis viruses? Food may be contaminated by food preparers or handlers who have viral gastroenteritis, especially if they do not wash their hands regularly after using the bathroom. Drinking water can also be contaminated by sewage and be a source of spread ...
... How does food get contaminated by gastroenteritis viruses? Food may be contaminated by food preparers or handlers who have viral gastroenteritis, especially if they do not wash their hands regularly after using the bathroom. Drinking water can also be contaminated by sewage and be a source of spread ...
Bacteria Wanted Poster Research Project
... 4. Most common victims it preys upon. 5. Where it is most likely to be found. 6. Most common injury done to the victim. 7. Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. 8. Number of victims. 9. Most effective weapons against the germ. Can it be prevented or treated? 10. Any ...
... 4. Most common victims it preys upon. 5. Where it is most likely to be found. 6. Most common injury done to the victim. 7. Is it considered armed and dangerous? Rate the degree of damage caused. 8. Number of victims. 9. Most effective weapons against the germ. Can it be prevented or treated? 10. Any ...
ppt
... B. The Paint Box & exchangable distributions on Partitions. C. All coalescents are restrictions of “The Coalescent” – a process with entrance boundary infinity. D. Robustness of “The Coalescent”: If offspring distribution is exchangeable and Var(n1) --> s2 & E(n1m) < Mm for all m, then genealogies f ...
... B. The Paint Box & exchangable distributions on Partitions. C. All coalescents are restrictions of “The Coalescent” – a process with entrance boundary infinity. D. Robustness of “The Coalescent”: If offspring distribution is exchangeable and Var(n1) --> s2 & E(n1m) < Mm for all m, then genealogies f ...
Gram-negative bacteria
... – The mutation of existing viruses, which is especially high in RNA viruses – Dissemination of a viral disease from a small, isolated human population, allowing the disease to go unnoticed before it begins to spread – Spread of existing viruses from animal populations; about three-quarters of new hu ...
... – The mutation of existing viruses, which is especially high in RNA viruses – Dissemination of a viral disease from a small, isolated human population, allowing the disease to go unnoticed before it begins to spread – Spread of existing viruses from animal populations; about three-quarters of new hu ...
Antiviral_2011_Part2
... interfering with viral replication, effectively slowing the replication rate of the virus, and providing a greater opportunity for the immune response to intervene. • All drugs in this class depend on the activity of the viral thymidine kinase to convert the drug to a monophosphate form and subseque ...
... interfering with viral replication, effectively slowing the replication rate of the virus, and providing a greater opportunity for the immune response to intervene. • All drugs in this class depend on the activity of the viral thymidine kinase to convert the drug to a monophosphate form and subseque ...
Natural selection and phylogenetic analysis
... but by the consequences of those forces for changing the rates and patterns of substitution within and between lineages over time. A review of various kinds of forces suggests that natural selection need not be a problem for phylogenetic analysis. For example, stabilizing selection, probably the mos ...
... but by the consequences of those forces for changing the rates and patterns of substitution within and between lineages over time. A review of various kinds of forces suggests that natural selection need not be a problem for phylogenetic analysis. For example, stabilizing selection, probably the mos ...
Answer Sheet for Quiz1
... desirable? Give a reason for your answer! [2] This is desirable. Because there is no prescribed or known size for good solutions of a genetic programming problem, it is advantageous for the EC system to search through many different solution sizes. c) GP faces the problem of bloating (survival of th ...
... desirable? Give a reason for your answer! [2] This is desirable. Because there is no prescribed or known size for good solutions of a genetic programming problem, it is advantageous for the EC system to search through many different solution sizes. c) GP faces the problem of bloating (survival of th ...
Ne - reproseed
... developed - to assess diversity and perform parentage assignment in aquacultured mollusks species but their use is still relatively limited for effective management of inbreeding, domestication and selection of marine mollusks. • The ‘next step’ will be the use of QTLs / genomewide approaches in sel ...
... developed - to assess diversity and perform parentage assignment in aquacultured mollusks species but their use is still relatively limited for effective management of inbreeding, domestication and selection of marine mollusks. • The ‘next step’ will be the use of QTLs / genomewide approaches in sel ...
Control of Viral Infections and Diseases
... tissues), most virucides have no demonstrated therapeutic value. Antiviral agents inhibit viral replication at the cellular level, interrupting one or more steps in the life cycle of the virus. These agents have a limited spectrum of activity and, because most of them also interrupt host cell functi ...
... tissues), most virucides have no demonstrated therapeutic value. Antiviral agents inhibit viral replication at the cellular level, interrupting one or more steps in the life cycle of the virus. These agents have a limited spectrum of activity and, because most of them also interrupt host cell functi ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to viruses
... Influenza A virus Faecal-oral transmission Enterovirus Blood-borne transmission Hepatitis B virus Sexual Transmission HIV Animal or insect vectors Rabies virus ...
... Influenza A virus Faecal-oral transmission Enterovirus Blood-borne transmission Hepatitis B virus Sexual Transmission HIV Animal or insect vectors Rabies virus ...
Viral phylodynamics
Viral phylodynamics is defined as the study of how epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes act and potentially interact to shape viral phylogenies.Since the coining of the term in 2004, research on viral phylodynamics has focused on transmission dynamics in an effort to shed light on how these dynamics impact viral genetic variation. Transmission dynamics can be considered at the level of cells within an infected host, individual hosts within a population, or entire populations of hosts.Many viruses, especially RNA viruses, rapidly accumulate genetic variation because of short generation times and high mutation rates.Patterns of viral genetic variation are therefore heavily influenced by how quickly transmission occurs and by which entities transmit to one another.Patterns of viral genetic variation will also be affected by selection acting on viral phenotypes.Although viruses can differ with respect to many phenotypes, phylodynamic studies have to date tended to focus on a limited number of viral phenotypes.These include virulence phenotypes, phenotypes associated with viral transmissibility, cell or tissue tropism phenotypes, and antigenic phenotypes that can facilitate escape from host immunity.Due to the impact that transmission dynamics and selection can have on viral genetic variation, viral phylogenies can therefore be used to investigate important epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes, such as epidemic spread, spatio-temporal dynamics including metapopulation dynamics, zoonotic transmission, tissue tropism, and antigenic drift.The quantitative investigation of these processes through the consideration of viral phylogenies is the central aim of viral phylodynamics.