Document
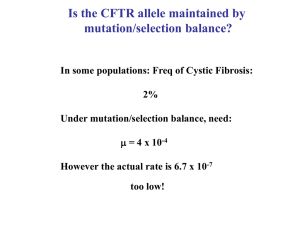
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
... Depends upon: (2Nu) number of mutations arising at locus per generation, and initial frequency of new allele (1/2N) ...
Chapter 2A: Viruses and Bacteria
... --Viruses vary in shape: round, rod-shaped, bricklike, robotlike, etc. --An example of a robotlike virus is the bacteriophage: virus that infects bacteria (“bacteria eater”) --Viruses vary in size, but all are smaller than cells, can ONLY be seen with powerful microscopes, and are measured in nanome ...
... --Viruses vary in shape: round, rod-shaped, bricklike, robotlike, etc. --An example of a robotlike virus is the bacteriophage: virus that infects bacteria (“bacteria eater”) --Viruses vary in size, but all are smaller than cells, can ONLY be seen with powerful microscopes, and are measured in nanome ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population KEY
... All the individuals of a species that live in the same area. ...
... All the individuals of a species that live in the same area. ...
Evolutionary Computation - A 2-page Overview for
... first expanded and then collapsed, mimicking the processes of breeding and struggling for survival. Some evolutionary algorithms do not store a collection of distinct individuals, and evolution is depicted through the variation of the statistical parameters that describe the population. Most of the ...
... first expanded and then collapsed, mimicking the processes of breeding and struggling for survival. Some evolutionary algorithms do not store a collection of distinct individuals, and evolution is depicted through the variation of the statistical parameters that describe the population. Most of the ...
Population Genetics – Modeling Natural Selection Purpose – To
... pea represents a gamete carrying a particular allele (colour). Removing two peas from the beaker, therefore, represents fertilization and “birth” of an individual. Note that because any two peas can be removed, “mating” in our models is at random. This is unlikely to occur in most real populations. ...
... pea represents a gamete carrying a particular allele (colour). Removing two peas from the beaker, therefore, represents fertilization and “birth” of an individual. Note that because any two peas can be removed, “mating” in our models is at random. This is unlikely to occur in most real populations. ...
(Traditional) estimators based on gene frequencies
... This is an introduction and overview of the currently used methods for the analysis of population subdivision and estimation of migration rates. We will discuss theoretical population models such as the group of single migration parameter models with two or n islands, stepping stone models, and mult ...
... This is an introduction and overview of the currently used methods for the analysis of population subdivision and estimation of migration rates. We will discuss theoretical population models such as the group of single migration parameter models with two or n islands, stepping stone models, and mult ...
Evolutionary forces in plant pathogen population: empirical
... genes in plant genome, management of alternative host, chemical applications and other cultural practices. In response, the relative efficiency of evolutionary forces and subsequent genetic structure of ...
... genes in plant genome, management of alternative host, chemical applications and other cultural practices. In response, the relative efficiency of evolutionary forces and subsequent genetic structure of ...
Time – the emerging dimension of plant virus studies
... samples collected serially. However, in practice, evolutionary rates are estimated most often from phylogenetic analysis of gene sequences obtained from natural populations after the removal of recombinant sequences. Recombination (and reassortment) between genomes confounds attempts to estimate evo ...
... samples collected serially. However, in practice, evolutionary rates are estimated most often from phylogenetic analysis of gene sequences obtained from natural populations after the removal of recombinant sequences. Recombination (and reassortment) between genomes confounds attempts to estimate evo ...
64th Western Poultry Disease Conference (March 23
... Poster Viewing & Break. **All poster presenters to be available for discussion** TOPIC: Coccidiosis/Raised Without Antibiotics Moderator: Susantha Gomis Invited Speaker: Managing coccidiosis in raised without antibiotic birds Assessment of changes in sensitivity of coccidia to nicarbazin White strip ...
... Poster Viewing & Break. **All poster presenters to be available for discussion** TOPIC: Coccidiosis/Raised Without Antibiotics Moderator: Susantha Gomis Invited Speaker: Managing coccidiosis in raised without antibiotic birds Assessment of changes in sensitivity of coccidia to nicarbazin White strip ...
INFLUENZA (The Flu) What Nurses Should Know
... • Household contracts and caregivers of children aged <5 years and adults aged >= 50 years, with particular emphasis on vaccinating contracts of children aged <6 months; and, • Households contracts and caregivers of persons with medical conditions that put them athigh risk for severe complication fr ...
... • Household contracts and caregivers of children aged <5 years and adults aged >= 50 years, with particular emphasis on vaccinating contracts of children aged <6 months; and, • Households contracts and caregivers of persons with medical conditions that put them athigh risk for severe complication fr ...
Diagnosis of viral infections
... Human embryo skin muscle cells were infected with human CMV & stained at selected times to demonstrate: (A) uninfected cells, (B) late CPE (nuclear inclusions, cell enlargement), (C) cell degeneration (D) a focus of cell lysis in a cell monolayer ( plaque). ...
... Human embryo skin muscle cells were infected with human CMV & stained at selected times to demonstrate: (A) uninfected cells, (B) late CPE (nuclear inclusions, cell enlargement), (C) cell degeneration (D) a focus of cell lysis in a cell monolayer ( plaque). ...
Effective population size
... Both focused on morphological or physiological characters with a clear role for selection. First data from allozyme electrophoresis (Lewontin and Hubby 1966) suggested that selection alone could not be responsible for maintaining the high observed levels of polymorphism. At around the same time in 1 ...
... Both focused on morphological or physiological characters with a clear role for selection. First data from allozyme electrophoresis (Lewontin and Hubby 1966) suggested that selection alone could not be responsible for maintaining the high observed levels of polymorphism. At around the same time in 1 ...
Document
... • A tree is a mathematical structure that has many uses: trees can be descriptive and used to show clusters of similar taxa (classification). • Trees are also used as evolutionary models for phylogenies. ...
... • A tree is a mathematical structure that has many uses: trees can be descriptive and used to show clusters of similar taxa (classification). • Trees are also used as evolutionary models for phylogenies. ...
B 262, F 2008
... Tuberculosis kills 5% of its sufferers within a year, the other 95% do not show disease symptoms for 2-50 years. The tuberculosis bacterium eventually kills all (100%) infected persons who do not die of other causes, and caused about 20% of all deaths during the Middle Ages in Europe. Black plague i ...
... Tuberculosis kills 5% of its sufferers within a year, the other 95% do not show disease symptoms for 2-50 years. The tuberculosis bacterium eventually kills all (100%) infected persons who do not die of other causes, and caused about 20% of all deaths during the Middle Ages in Europe. Black plague i ...
Plant Viruses
... Molecular Approaches for the control of plant viruses Pathogen-derived resistance - gene silencing ...
... Molecular Approaches for the control of plant viruses Pathogen-derived resistance - gene silencing ...
Report for week ending March 2, 2013
... Wadsworth Center, the NYSDOH public health laboratory, tests specimens from sources including, but not limited to, outpatient healthcare providers (ILINet program) and hospitals (EIP program). ...
... Wadsworth Center, the NYSDOH public health laboratory, tests specimens from sources including, but not limited to, outpatient healthcare providers (ILINet program) and hospitals (EIP program). ...
Student Worksheet Hands-on Activity Viral DNA Integration
... T cells. Over time, HIV infection weakens a person’s ability to fight other infections and some diseases. The advanced stage of HIV infection is termed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). An individual with AIDS has a severely impaired immune system. Although there is no cure for AIDS, HIV ...
... T cells. Over time, HIV infection weakens a person’s ability to fight other infections and some diseases. The advanced stage of HIV infection is termed acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). An individual with AIDS has a severely impaired immune system. Although there is no cure for AIDS, HIV ...
Microevolution - cloudfront.net
... 2) What are the three aspects in a population we examine in order to understand how evolution is occurring in a population. 3) If a population had 2500 individuals that are diploid, how many total alleles would be present? 4) In a population of 1000 humans, 840 possess the ability to roll their tong ...
... 2) What are the three aspects in a population we examine in order to understand how evolution is occurring in a population. 3) If a population had 2500 individuals that are diploid, how many total alleles would be present? 4) In a population of 1000 humans, 840 possess the ability to roll their tong ...
Acute retroviral syndrome - UCLA Program in Global Health
... Recent Infection: considered the phase up to 6 months after infected during which anti-HIV antibodies are detectable. Early HIV: either acute or recent HIV infection Acute retroviral syndrome: patient w/ acute HIV infection w/ ...
... Recent Infection: considered the phase up to 6 months after infected during which anti-HIV antibodies are detectable. Early HIV: either acute or recent HIV infection Acute retroviral syndrome: patient w/ acute HIV infection w/ ...
Lecture 6
... Protein-‐coding sequences present opportunities to study differential rates • A nonsynonymous substitution is a nucleotide mutation that alters the amino acid sequence of a protein. • Synonymous substitutions do not alter amin ...
... Protein-‐coding sequences present opportunities to study differential rates • A nonsynonymous substitution is a nucleotide mutation that alters the amino acid sequence of a protein. • Synonymous substitutions do not alter amin ...
05 Lecture Evolution 09
... LECTURE 05 EVOLUTION Read CH6: 113-123; see also parts of CH 13 MAJOR CONCEPTS 1) Organisms facing a changing environment can evolve only if genetic variation exists in population and natural selection favors alleles suitable for new environment. 2) The sources of genetic variation are mutation and ...
... LECTURE 05 EVOLUTION Read CH6: 113-123; see also parts of CH 13 MAJOR CONCEPTS 1) Organisms facing a changing environment can evolve only if genetic variation exists in population and natural selection favors alleles suitable for new environment. 2) The sources of genetic variation are mutation and ...
Viral phylodynamics
Viral phylodynamics is defined as the study of how epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes act and potentially interact to shape viral phylogenies.Since the coining of the term in 2004, research on viral phylodynamics has focused on transmission dynamics in an effort to shed light on how these dynamics impact viral genetic variation. Transmission dynamics can be considered at the level of cells within an infected host, individual hosts within a population, or entire populations of hosts.Many viruses, especially RNA viruses, rapidly accumulate genetic variation because of short generation times and high mutation rates.Patterns of viral genetic variation are therefore heavily influenced by how quickly transmission occurs and by which entities transmit to one another.Patterns of viral genetic variation will also be affected by selection acting on viral phenotypes.Although viruses can differ with respect to many phenotypes, phylodynamic studies have to date tended to focus on a limited number of viral phenotypes.These include virulence phenotypes, phenotypes associated with viral transmissibility, cell or tissue tropism phenotypes, and antigenic phenotypes that can facilitate escape from host immunity.Due to the impact that transmission dynamics and selection can have on viral genetic variation, viral phylogenies can therefore be used to investigate important epidemiological, immunological, and evolutionary processes, such as epidemic spread, spatio-temporal dynamics including metapopulation dynamics, zoonotic transmission, tissue tropism, and antigenic drift.The quantitative investigation of these processes through the consideration of viral phylogenies is the central aim of viral phylodynamics.























