Unit 3 Microorganisms Viruses Bacteria Protists Fungi PowerPoint
... bacterial cell. • Contains the cells genetic material and some of its cytoplasm. • Can survive freezing and boiling • Endospores are light, so they can be blown by the wind. ...
... bacterial cell. • Contains the cells genetic material and some of its cytoplasm. • Can survive freezing and boiling • Endospores are light, so they can be blown by the wind. ...
TAKS Review - Bowie Academic Chemistry Resources
... Enzymes allow viruses to insert their genetic material into the host cell’s DNA. The virus benefits from this action by — A acquiring the traits of the host cell B causing the host cell to produce viruses C introducing random deadly mutations into the host cell D turning the host cell into a virus ...
... Enzymes allow viruses to insert their genetic material into the host cell’s DNA. The virus benefits from this action by — A acquiring the traits of the host cell B causing the host cell to produce viruses C introducing random deadly mutations into the host cell D turning the host cell into a virus ...
Microorganisms: Viruses
... introduce the fundamentals of viruses, including the fact that they are composed of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA, but never both), proteins, and in some cases, lipids. The DNA or RNA includes just enough instructions (genes) to direct its host cell to make more viruses. Explain also that microbio ...
... introduce the fundamentals of viruses, including the fact that they are composed of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA, but never both), proteins, and in some cases, lipids. The DNA or RNA includes just enough instructions (genes) to direct its host cell to make more viruses. Explain also that microbio ...
Replication Patterns of Specific Viruses
... At the same time, the relative ease of maintaining the virus and replicating it in culture led to its early exploitation for molecular biological studies. It is still a favored model. Other closely related picornaviruses include rhinoviruses and hepatitis A virus. These replicate in a generally simi ...
... At the same time, the relative ease of maintaining the virus and replicating it in culture led to its early exploitation for molecular biological studies. It is still a favored model. Other closely related picornaviruses include rhinoviruses and hepatitis A virus. These replicate in a generally simi ...
Viral evolution and the emergence of SARS
... populations of DNA viruses are highly variable, which hints at higher mutation rates; Sanz et al. 1999). On average, RNA polymerases produce almost one error in each replication cycle (Drake et al. 1998; Malpica et al. 2002), thus when populations of RNA viruses are large, they will produce a myriad ...
... populations of DNA viruses are highly variable, which hints at higher mutation rates; Sanz et al. 1999). On average, RNA polymerases produce almost one error in each replication cycle (Drake et al. 1998; Malpica et al. 2002), thus when populations of RNA viruses are large, they will produce a myriad ...
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
... Each type of animal virus requires a different strategy for synthesis that depends on the kind of nucleic acid invol ed: DNA or RNA, and ds versus ss: • Synthesis of new dsDNA virions is similar to the normal replication of cellu lar DNA and translation of proteins. Each strand of viral DNA is use ...
... Each type of animal virus requires a different strategy for synthesis that depends on the kind of nucleic acid invol ed: DNA or RNA, and ds versus ss: • Synthesis of new dsDNA virions is similar to the normal replication of cellu lar DNA and translation of proteins. Each strand of viral DNA is use ...
What are viruses?
... Viroids, are infectious RNA molecules that cause diseases in various plants. Their genomes are much smaller than those of viruses (up to 400 nucleotides of circular single-stranded RNA) and do not code for any proteins. DEFINITION: A virus is a subcellular, submicroscopic, infectious obligate parasi ...
... Viroids, are infectious RNA molecules that cause diseases in various plants. Their genomes are much smaller than those of viruses (up to 400 nucleotides of circular single-stranded RNA) and do not code for any proteins. DEFINITION: A virus is a subcellular, submicroscopic, infectious obligate parasi ...
bacteriophage and viruses-study material-2012
... Nature of Viruses 1. Size. The size range of viruses is from about 20 to 300 nm. On the whole, viruses are much smaller than bacteria. Most animal viruses and all plant viruses and phages are invisible under the light microscope. 2. Simple structure. Viruses have very simple structures. The simplest ...
... Nature of Viruses 1. Size. The size range of viruses is from about 20 to 300 nm. On the whole, viruses are much smaller than bacteria. Most animal viruses and all plant viruses and phages are invisible under the light microscope. 2. Simple structure. Viruses have very simple structures. The simplest ...
ViRUSES AND PRiONS
... and certain cells within those hosts An important characteristic of a virus is its host range—the spectrum of hosts that it is able to infect. Some viruses infect only animals, while others infect only plants, fungi, and so forth. Even within a group such as animal viruses, however, a given virus ca ...
... and certain cells within those hosts An important characteristic of a virus is its host range—the spectrum of hosts that it is able to infect. Some viruses infect only animals, while others infect only plants, fungi, and so forth. Even within a group such as animal viruses, however, a given virus ca ...
Lesson Plan BISP Characterisation Clothes
... Go through worksheet answers as a way of recapping previous lesson. Tell them that this lesson we’ll be looking at the structure of viruses and how the structure is important for function. We’re going to make a model of a virus and we’ll use Dengue Virus as an example. What do viruses look like? (St ...
... Go through worksheet answers as a way of recapping previous lesson. Tell them that this lesson we’ll be looking at the structure of viruses and how the structure is important for function. We’re going to make a model of a virus and we’ll use Dengue Virus as an example. What do viruses look like? (St ...
viruses
... of the brain), small pox, and AIDS. Some viruses can even cause cancer by disrupting the normal cell cycle. Usually, a cell’s DNA contains information about when the cell should stay at rest and when it should replicate. Some cancer-causing viruses are able to direct the cell to keep dividing over a ...
... of the brain), small pox, and AIDS. Some viruses can even cause cancer by disrupting the normal cell cycle. Usually, a cell’s DNA contains information about when the cell should stay at rest and when it should replicate. Some cancer-causing viruses are able to direct the cell to keep dividing over a ...
18_Lectures_PPT Genetics of Viruses and
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Viral Genomes
... these genomes. Genome sequencing projects are uncovering many unique features of these that had been previously known. GENERAL FEATURES Currently over 4000 viruses have been described. These are classified into 71 families. Although viruses are generally the smallest genomes, as a collection of biol ...
... these genomes. Genome sequencing projects are uncovering many unique features of these that had been previously known. GENERAL FEATURES Currently over 4000 viruses have been described. These are classified into 71 families. Although viruses are generally the smallest genomes, as a collection of biol ...
Viruses
... cell or injects its genetic material into the cell (B.) The virus takes over the host cell and causes the cell to make viral proteins and genetic material. (C.) New virus particles are assembled (D.) Think of this process as similar to breaking into a car factory and using the machinery to make your ...
... cell or injects its genetic material into the cell (B.) The virus takes over the host cell and causes the cell to make viral proteins and genetic material. (C.) New virus particles are assembled (D.) Think of this process as similar to breaking into a car factory and using the machinery to make your ...
Fv1, the mouse retrovirus resistance gene
... sequence similarity is seen between different groups. There are between fifty and one hundred endogenous MLVs in mice (7). In the course of mapping one MLV sub-family, four proviruses, called Xmv8, Xmv9, X m v l 4 and Xmv44, were shown to be tightly linked to Fvl ( 1 5 ) . Since the Fv4 restriction ...
... sequence similarity is seen between different groups. There are between fifty and one hundred endogenous MLVs in mice (7). In the course of mapping one MLV sub-family, four proviruses, called Xmv8, Xmv9, X m v l 4 and Xmv44, were shown to be tightly linked to Fvl ( 1 5 ) . Since the Fv4 restriction ...
Physiological Factors in ill health (HIV / AIDS)
... • The major elements contained within the viral core are: - two single strands of HIV RNA - a protein p7 (nucleocapsid) - three enzyme proteins p51 (reverse transcriptase) p11 (protease) p32 (integrase) ...
... • The major elements contained within the viral core are: - two single strands of HIV RNA - a protein p7 (nucleocapsid) - three enzyme proteins p51 (reverse transcriptase) p11 (protease) p32 (integrase) ...
Enter Topic Title in each section above
... A. Act in one of four processes as helper T-cells, killer T-cells, suppressor T-cells or memory Tcells Q. Name the two main chemical components of a virus. ...
... A. Act in one of four processes as helper T-cells, killer T-cells, suppressor T-cells or memory Tcells Q. Name the two main chemical components of a virus. ...
Unit 4
... 12. Describe the process of translation including initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation – ribosomal subunits bind to mRNA and tRNA. They attach to the sequence on mRNA and the initiator tRNA (methionine) binds to the initiation codon. Proteins called initiation factors then bring toget ...
... 12. Describe the process of translation including initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation – ribosomal subunits bind to mRNA and tRNA. They attach to the sequence on mRNA and the initiator tRNA (methionine) binds to the initiation codon. Proteins called initiation factors then bring toget ...
الشريحة 1
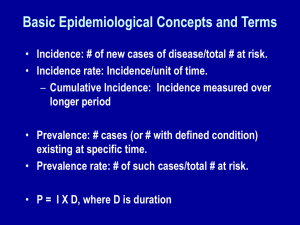
... •An outbreak of Avian Influenza H5N1 occurred in Hong Kong in 1997 where 18 persons were infected of which 6 died. •The source of the virus was probably from infected chickens and the outbreak was eventually controlled by a mass slaughter of chickens in the territory. •However, the strains involved ...
... •An outbreak of Avian Influenza H5N1 occurred in Hong Kong in 1997 where 18 persons were infected of which 6 died. •The source of the virus was probably from infected chickens and the outbreak was eventually controlled by a mass slaughter of chickens in the territory. •However, the strains involved ...
Student Worksheets
... a. A filter can be used to separate viruses from bacteria because of their different sizes. b. Bacteria are always smaller than viruses. c. Only bacteria infect plants. d. DNA can be used to identify the differences between viruses and bacteria. 2. What did Beijerinck conclude from his study of virus ...
... a. A filter can be used to separate viruses from bacteria because of their different sizes. b. Bacteria are always smaller than viruses. c. Only bacteria infect plants. d. DNA can be used to identify the differences between viruses and bacteria. 2. What did Beijerinck conclude from his study of virus ...
Viruses
... Serology: antigenic cross-reactivity Genetic material: form of nucleic acid ssDNA (+ or - strand) dsDNA ssRNA (+ or - strand) dsRNA segmented RNA genetic organization sequence homology DNA sequence Hybridization ...
... Serology: antigenic cross-reactivity Genetic material: form of nucleic acid ssDNA (+ or - strand) dsDNA ssRNA (+ or - strand) dsRNA segmented RNA genetic organization sequence homology DNA sequence Hybridization ...
Viruses Scavenger Hunt Guiding Worksheet
... Watch: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLoslN6d3Ec and Textbook Printout The Lysogenic Cycle is another type of viral reproductive cycle in which the genome of the phage is replicated without destroying the host. Phages capable of using both modes of reproduction (lytic and lysogenic) are referred to ...
... Watch: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLoslN6d3Ec and Textbook Printout The Lysogenic Cycle is another type of viral reproductive cycle in which the genome of the phage is replicated without destroying the host. Phages capable of using both modes of reproduction (lytic and lysogenic) are referred to ...