animal cells have a plasma membrane
... Viruses are found in plants, animals and bacteria and are Associated with diseases in all 3. Viruses have an RNA or DNA genome, but THEY ONLY REPRODUCE BY USING THE METABOLIC MACHINERY OF A HOST CELL ...
... Viruses are found in plants, animals and bacteria and are Associated with diseases in all 3. Viruses have an RNA or DNA genome, but THEY ONLY REPRODUCE BY USING THE METABOLIC MACHINERY OF A HOST CELL ...
Viral Structure Virion, protein capsid, some have lipid envelope
... • Nucleocapsid, or genome with some associated proteins targeted to nucleus • Conversion of ssDNA to dsDNA • Transcription of viral DNA by host RNA polymerase • Transport of viral mRNA to cytoplasm and translation by host cell ribosomes • Replication of viral DNA in nucleus of host cell • Combinat ...
... • Nucleocapsid, or genome with some associated proteins targeted to nucleus • Conversion of ssDNA to dsDNA • Transcription of viral DNA by host RNA polymerase • Transport of viral mRNA to cytoplasm and translation by host cell ribosomes • Replication of viral DNA in nucleus of host cell • Combinat ...
Name
... 7. List and describe three ways that ordinary bacteria can get antibiotic-resistant genes from other bacteria, and turn into “superbugs.” 1. Antibiotic-resistant genes are often found on plasmids (circular DNA). Plasmids can transfer from one type of bacteria to a different kind, as long as the germ ...
... 7. List and describe three ways that ordinary bacteria can get antibiotic-resistant genes from other bacteria, and turn into “superbugs.” 1. Antibiotic-resistant genes are often found on plasmids (circular DNA). Plasmids can transfer from one type of bacteria to a different kind, as long as the germ ...
HOW HIV INFECTS CELLS
... In general, viruses have very small genomes. This means they can encode a very limited number of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteins provided by their host in order to reproduce (make more viruses). In a way, viruses act like parasites. They bring very little with ...
... In general, viruses have very small genomes. This means they can encode a very limited number of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteins provided by their host in order to reproduce (make more viruses). In a way, viruses act like parasites. They bring very little with ...
The Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
... It reproduces within the cell nucleus using viral and cellular enzymes to replicate and transcribe it’s DNA Herpesvirus DNA may become integrated into the cell’s genome as a provirus The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the gen ...
... It reproduces within the cell nucleus using viral and cellular enzymes to replicate and transcribe it’s DNA Herpesvirus DNA may become integrated into the cell’s genome as a provirus The provirus remains latent within the nucleus until triggered by physical or emotional stress to leave the gen ...
Ebola strain variation in outbreaks
... outbreaks occurred. Zaire EBOV (ZEBOV) has the highest fatality rate (83% fatality over 27 years) and can infect humans as well as primates. Sudan EBOV (SEBOV) affects only humans and has a fatality rate ranging from 53-68%. Reston EBOV (REBOV) was found more recently in Reston, VA, and infected pri ...
... outbreaks occurred. Zaire EBOV (ZEBOV) has the highest fatality rate (83% fatality over 27 years) and can infect humans as well as primates. Sudan EBOV (SEBOV) affects only humans and has a fatality rate ranging from 53-68%. Reston EBOV (REBOV) was found more recently in Reston, VA, and infected pri ...
bacteriophage and viruses-study material-2012
... now known to be a bacteriophage could pass through a Chamberland filter. He accurately diluted a suspension of these viruses and discovered that the highest dilutions (lowest virus concentrations), rather than killing all the bacteria, formed discrete areas of dead organisms. Counting these areas an ...
... now known to be a bacteriophage could pass through a Chamberland filter. He accurately diluted a suspension of these viruses and discovered that the highest dilutions (lowest virus concentrations), rather than killing all the bacteria, formed discrete areas of dead organisms. Counting these areas an ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... in the are twocalled Located in which the cytoplasm tinysoil, structures During a process called conjugation, one bacterium cells. decomposers—organisms thatwhere break proteins down large ribosomes, chemical factories are transfers some of its genetic material to another chemicals produced. in dead ...
... in the are twocalled Located in which the cytoplasm tinysoil, structures During a process called conjugation, one bacterium cells. decomposers—organisms thatwhere break proteins down large ribosomes, chemical factories are transfers some of its genetic material to another chemicals produced. in dead ...
02EDU02B-Fea17Edu (Amaravathi).qxd
... The chapter on Bacteria is almost a repetition of information given elsewhere in second year and first year. In first year 9th chapter structure of bacteria is given under prokaryotic cell. In addition to that only little information is added here. Explanation is given on sexual reproduction and nut ...
... The chapter on Bacteria is almost a repetition of information given elsewhere in second year and first year. In first year 9th chapter structure of bacteria is given under prokaryotic cell. In addition to that only little information is added here. Explanation is given on sexual reproduction and nut ...
HOW HIV INFECTS CELLS
... In general, viruses have very small genomes. This means they can encode a very limited number of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteins provided by their host in order to reproduce (make more viruses). In a way, viruses act like parasites. They bring very little with ...
... In general, viruses have very small genomes. This means they can encode a very limited number of their own proteins. For this reason, most viruses must use the proteins provided by their host in order to reproduce (make more viruses). In a way, viruses act like parasites. They bring very little with ...
Exam 3 BIO 308 Spring 2014
... C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa D. Corynebacterium diphtheria* E. Mycoplasma pneumonia 38. Which of the organisms listed in question 37 is responsible for primary atypical pneumonia? A. Streptococcus pyogenes B. Streptococcus pneumonia C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa D. Corynebacterium diphtheria E. Mycoplasma ...
... C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa D. Corynebacterium diphtheria* E. Mycoplasma pneumonia 38. Which of the organisms listed in question 37 is responsible for primary atypical pneumonia? A. Streptococcus pyogenes B. Streptococcus pneumonia C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa D. Corynebacterium diphtheria E. Mycoplasma ...
viruses - Images
... They can be spread via objects such as eating utensils Drinking from a cup used by an infected person can spread diseases such as strep throat and mononucleosis ...
... They can be spread via objects such as eating utensils Drinking from a cup used by an infected person can spread diseases such as strep throat and mononucleosis ...
IRRN 1984 9 (6) - James Litsinger
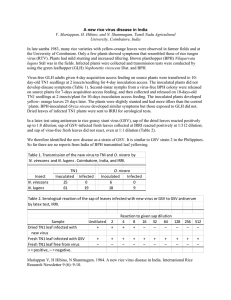
... Virus-free GLH adults given 4-day acquisition access feeding on source plants were transferred to 10day-old TN1 seedlings at 2 insects/seedling for 4-day inoculation access. The inoculated plants did not develop disease symptoms (Table 1). Second-instar nymphs from a virus-free BPH colony were relea ...
... Virus-free GLH adults given 4-day acquisition access feeding on source plants were transferred to 10day-old TN1 seedlings at 2 insects/seedling for 4-day inoculation access. The inoculated plants did not develop disease symptoms (Table 1). Second-instar nymphs from a virus-free BPH colony were relea ...
eprint_5_13643_353
... genomic-size transcript because the virus is able to replicate in enucleated cells. Class III (e.g. paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses.) The genome is of -ve polarity to the messenger. A virion RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase first transcribes the genomes into separate monocistronic messengers initiatin ...
... genomic-size transcript because the virus is able to replicate in enucleated cells. Class III (e.g. paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses.) The genome is of -ve polarity to the messenger. A virion RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase first transcribes the genomes into separate monocistronic messengers initiatin ...
Influenza virus:
... Spiked: 2 types of proteins:H(Hemagglutinin) and N( Neuraminidase). Classification and nomenclature: Influenza virus classified into three types according to group-specific antigens (nucleocapsid antigens): influenza A, B and C. Influenza type A and B contain 8 segments, while influenza type C has ...
... Spiked: 2 types of proteins:H(Hemagglutinin) and N( Neuraminidase). Classification and nomenclature: Influenza virus classified into three types according to group-specific antigens (nucleocapsid antigens): influenza A, B and C. Influenza type A and B contain 8 segments, while influenza type C has ...
ig{@mg@+l72$
... d. All of the choices. a. Blood agar. b. MacConkey agar. 70. In eukaryotic cells, the secretion protein was: a. synthesized at smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. transported from trans face to cis faces of Golgi apparatus. c. modified and packed as secretory vesicle at Golgi apparatus. d. marked by ubi ...
... d. All of the choices. a. Blood agar. b. MacConkey agar. 70. In eukaryotic cells, the secretion protein was: a. synthesized at smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. transported from trans face to cis faces of Golgi apparatus. c. modified and packed as secretory vesicle at Golgi apparatus. d. marked by ubi ...
2017 List of Reportable Diseases in Tennessee For Healthcare
... 2017 List of Reportable Diseases in Tennessee For Laboratories The diseases, events, and conditions reportable to Tennessee Department of Health (TDH) by laboratories, including laboratories in healthcare facilities, are listed below for 2017. Refer to Page 1 of this document for a list of diseases ...
... 2017 List of Reportable Diseases in Tennessee For Laboratories The diseases, events, and conditions reportable to Tennessee Department of Health (TDH) by laboratories, including laboratories in healthcare facilities, are listed below for 2017. Refer to Page 1 of this document for a list of diseases ...
"HIV" in plasma - The Perth Group
... “Viruses in search of Diseases”, during which many viruses, undisputedly demonstrated by electron microscopy, had no known infectivity”. LINK Everybody, including the HIV experts, some of them in sworn testimony in court (see addendum), agree that to prove a particle is a virus, i.e. infectious, one ...
... “Viruses in search of Diseases”, during which many viruses, undisputedly demonstrated by electron microscopy, had no known infectivity”. LINK Everybody, including the HIV experts, some of them in sworn testimony in court (see addendum), agree that to prove a particle is a virus, i.e. infectious, one ...
Overview and History
... prevent surgical wound infections after looking at Pasteur’s work showing microbes are in the air, can spoil food, and cause animal diseases. • 1876: Robert Koch provided proof that a bacterium causes anthrax and provided the experimental steps, Koch’s postulates, used to prove that a specific micro ...
... prevent surgical wound infections after looking at Pasteur’s work showing microbes are in the air, can spoil food, and cause animal diseases. • 1876: Robert Koch provided proof that a bacterium causes anthrax and provided the experimental steps, Koch’s postulates, used to prove that a specific micro ...
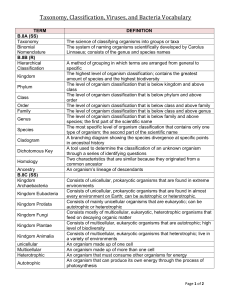
Biology First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... An organism in which a parasite derives nutrients from Anything capable of causing infectious disease A chemical substance that kills bacteria cells A virus that infects bacteria A common childhood disease caused by the varicella virus A virus that contains reverse transcriptase and RNA A poisonous ...
... An organism in which a parasite derives nutrients from Anything capable of causing infectious disease A chemical substance that kills bacteria cells A virus that infects bacteria A common childhood disease caused by the varicella virus A virus that contains reverse transcriptase and RNA A poisonous ...
History of virology

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitry Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a ""virus"" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. By the 20th century many viruses were discovered.