Microscopy - WordPress.com
... • Same principle as other acid-fast stains, except that fluorescent dyes (auramine and rhodamine) are used for primary stain • Modified acid-fast stain: • Weak decolorizing agent is used with any of three acid-fast stains listed. • Whereas mycobacteria are strongly acid-fast, other organisms stain w ...
... • Same principle as other acid-fast stains, except that fluorescent dyes (auramine and rhodamine) are used for primary stain • Modified acid-fast stain: • Weak decolorizing agent is used with any of three acid-fast stains listed. • Whereas mycobacteria are strongly acid-fast, other organisms stain w ...
Bacteria-eating viruses
... human pathogens. A lot of fundamental science needs to be carried out in order to ensure that we understand how to best exploit them.” ...
... human pathogens. A lot of fundamental science needs to be carried out in order to ensure that we understand how to best exploit them.” ...
Viruses - Sign In
... retroviruses. Retroviruses contain RNA as their genetic infor¬ mation. When retroviruses infect a cell, they produce a DNA copy of their RNA genes. This DNA, much like a prophage, is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. Retroviruses received their name from the fact that their genetic information ...
... retroviruses. Retroviruses contain RNA as their genetic infor¬ mation. When retroviruses infect a cell, they produce a DNA copy of their RNA genes. This DNA, much like a prophage, is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. Retroviruses received their name from the fact that their genetic information ...
Study Guide 4
... Symptoms and causative agent (microbe that causes a disease) for the following: Chlamydia, syphilis, Gonorrhea Human papilloma virus, the diseases it can cause, it’s transmission and vaccine HIV: The kind of virus HIV is The 3 major enzymatic activities of reverse polymerase The molecular mechanism ...
... Symptoms and causative agent (microbe that causes a disease) for the following: Chlamydia, syphilis, Gonorrhea Human papilloma virus, the diseases it can cause, it’s transmission and vaccine HIV: The kind of virus HIV is The 3 major enzymatic activities of reverse polymerase The molecular mechanism ...
3. Biological method (experimental infection)
... phage or some other tox+ phage. This is known as lysogenic or phage conversion. The toxigenicity remains only as long as the bacillus is lysogenic. The diphtheria toxin acts by inhibiting protein synthesis. Specifically, fragment A inhibiting polypeptide chain elongation in the presence of nicotinam ...
... phage or some other tox+ phage. This is known as lysogenic or phage conversion. The toxigenicity remains only as long as the bacillus is lysogenic. The diphtheria toxin acts by inhibiting protein synthesis. Specifically, fragment A inhibiting polypeptide chain elongation in the presence of nicotinam ...
MICROBIOLOGY
... The study of the resistance of the living body to disease producing organisms and the reactions of ...
... The study of the resistance of the living body to disease producing organisms and the reactions of ...
Modern Microbiology
... 1977, Holger Jannasch shows that microbial sulfur oxidation is a source of energy for dense animal colonies in the absence of light at deep sea hydrothermal vents. Jannasch and Wirsen use a device for sampling of microbial populations at depths of 6000 meters and then study the population without de ...
... 1977, Holger Jannasch shows that microbial sulfur oxidation is a source of energy for dense animal colonies in the absence of light at deep sea hydrothermal vents. Jannasch and Wirsen use a device for sampling of microbial populations at depths of 6000 meters and then study the population without de ...
Pathogenic Mechanisms
... • can be transmitted from one host to another (communicable) • some infections acquired from indigenous flora are categorized as communicable. ...
... • can be transmitted from one host to another (communicable) • some infections acquired from indigenous flora are categorized as communicable. ...
The Microbial World and You
... that microorganisms caused diseases Only specific microorganisms caused specific diseases Studied anthrax affects cattle & humans ...
... that microorganisms caused diseases Only specific microorganisms caused specific diseases Studied anthrax affects cattle & humans ...
DOL_Ch02_Transmittal_Final_CW
... protists cause most infectious diseases. Scientists also know that the simplest organisms are extremely abundant and play key roles in all ecosystems. Some of these organisms recycle nutrients, and others are important producers. Some can cause disease, and others ...
... protists cause most infectious diseases. Scientists also know that the simplest organisms are extremely abundant and play key roles in all ecosystems. Some of these organisms recycle nutrients, and others are important producers. Some can cause disease, and others ...
DNA / RNA Extraction - q
... Ophiostoma brunneo-ciliatum) associated to Ips acuminatus using LAMP technology ...
... Ophiostoma brunneo-ciliatum) associated to Ips acuminatus using LAMP technology ...
sample
... by endocytosis, while others enter by fusion. 10. In which of the following ways are prions believed to differ from all other infectious agents? a. Unlike any other infectious agents, they are acellular. b. Unlike any other infectious agents, they can infect many different species of hosts. c. Unlik ...
... by endocytosis, while others enter by fusion. 10. In which of the following ways are prions believed to differ from all other infectious agents? a. Unlike any other infectious agents, they are acellular. b. Unlike any other infectious agents, they can infect many different species of hosts. c. Unlik ...
Chapter 24
... • Viral pneumonia as a complication of influenza, measles, chickenpox • Viral etiology suspected if no cause determined • Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) • Common in infants; 4500 deaths annually • Causes cell fusion (syncytium) in cell culture • Symptoms: coughing • Diagnosis by serologic test fo ...
... • Viral pneumonia as a complication of influenza, measles, chickenpox • Viral etiology suspected if no cause determined • Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) • Common in infants; 4500 deaths annually • Causes cell fusion (syncytium) in cell culture • Symptoms: coughing • Diagnosis by serologic test fo ...
The Genetics of Viruses and Prokaryotes
... understood only within the last half century, but the first step on this path of discovery was taken by the Russian botanist Dmitri Ivanovsky in 1892. He was trying to find the cause of tobacco mosaic disease, which results in the destruction of photosynthetic tissues in plants and can devastate a t ...
... understood only within the last half century, but the first step on this path of discovery was taken by the Russian botanist Dmitri Ivanovsky in 1892. He was trying to find the cause of tobacco mosaic disease, which results in the destruction of photosynthetic tissues in plants and can devastate a t ...
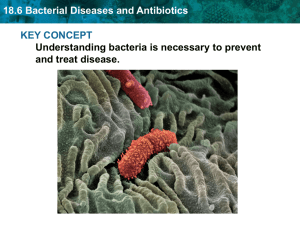
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics KEY CONCEPT
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
CHAPTER 5 REQUIREMENTS FOR INFECTION
... patients. • They produce common symptoms such as fever, shock, diarrhea, cardiac and neurological trauma, and the destruction of blood vessels. • There are 2 types of toxins: – Exotoxins – Endotoxins ...
... patients. • They produce common symptoms such as fever, shock, diarrhea, cardiac and neurological trauma, and the destruction of blood vessels. • There are 2 types of toxins: – Exotoxins – Endotoxins ...
Characterization of New Viruses from Hypersaline
... Viruses of Archaea are the least studied group of viruses. Fewer than 50 archaeal viruses have been reported which constitutes less than one percent of all the isolated prokaryotic viruses. Only about one third of the isolated archaeal viruses infect halophiles. The diversity of haloviruses, virus e ...
... Viruses of Archaea are the least studied group of viruses. Fewer than 50 archaeal viruses have been reported which constitutes less than one percent of all the isolated prokaryotic viruses. Only about one third of the isolated archaeal viruses infect halophiles. The diversity of haloviruses, virus e ...
Acute Gastroenteritis
... Pseudomembranous Colitis : Clostridium difficile is the causative bacteria It is found in colon as inactive spore form Antibiotics disrupt normal flora in intestine so ...
... Pseudomembranous Colitis : Clostridium difficile is the causative bacteria It is found in colon as inactive spore form Antibiotics disrupt normal flora in intestine so ...
Microbial Risk Levels
... Yellow fever virus some encephalitis viruses Serratia marcescens HIV Rabies Coccidiodes immitis Hepatitis A,B,C Prions Cryptococcus neoformans No parasitic agents Most parasitic agents The organisms found in Biosafety level 1 are often genetically unable to invade human hosts. To some extent these c ...
... Yellow fever virus some encephalitis viruses Serratia marcescens HIV Rabies Coccidiodes immitis Hepatitis A,B,C Prions Cryptococcus neoformans No parasitic agents Most parasitic agents The organisms found in Biosafety level 1 are often genetically unable to invade human hosts. To some extent these c ...
Presentation 8
... through organ transplantation usually from animal to human •Today, most of us are GM since we must have taken them in one way or the other as food or drug: “Take GM, become GM”. ...
... through organ transplantation usually from animal to human •Today, most of us are GM since we must have taken them in one way or the other as food or drug: “Take GM, become GM”. ...
The Prokaryotes, Viruses, and Protists
... strong and rigid. Some bacteria are also surrounded by a sticky capsule. The capsule reduces water loss, resists high temperatures, and helps keep out antibiotics and viruses. Bacteria cells vary considerably in shape. Three common shapes are coccus (plural: cocci), or round; bacillus (plural: bacil ...
... strong and rigid. Some bacteria are also surrounded by a sticky capsule. The capsule reduces water loss, resists high temperatures, and helps keep out antibiotics and viruses. Bacteria cells vary considerably in shape. Three common shapes are coccus (plural: cocci), or round; bacillus (plural: bacil ...
Microbiology - mypharmaguide.com
... composed of cellulose or plastic polymers Sizes of pores .01µm - .1mm .01µm can filter some viruses and proteins ...
... composed of cellulose or plastic polymers Sizes of pores .01µm - .1mm .01µm can filter some viruses and proteins ...
第4章 噬菌体
... Lysogenic or temperate phages are those that can either multiply via the lytic cycle or enter a quiescent state in the cell. In this quiescent state most of the phage genes are not transcribed; the phage genome exists in a repressed state. The phage DNA in this repressed state is called a prophage b ...
... Lysogenic or temperate phages are those that can either multiply via the lytic cycle or enter a quiescent state in the cell. In this quiescent state most of the phage genes are not transcribed; the phage genome exists in a repressed state. The phage DNA in this repressed state is called a prophage b ...
Microbial Pathogenesis and infection
... bacteria are non-invasive, but multiply at site of adherence. Invasive bacteria secrete several invasive factors (spreading factors) that result in degrading tissue and facilitate the pathogen spreading through human body. Evasion of host defense: Generally, Some mechanisms that play important role ...
... bacteria are non-invasive, but multiply at site of adherence. Invasive bacteria secrete several invasive factors (spreading factors) that result in degrading tissue and facilitate the pathogen spreading through human body. Evasion of host defense: Generally, Some mechanisms that play important role ...
World_AIDS_Day
... AIDS occurs when HIV has severely damaged the immune system. When AIDS sets in, the body stops being able to fight off illnesses. ...
... AIDS occurs when HIV has severely damaged the immune system. When AIDS sets in, the body stops being able to fight off illnesses. ...