Decontamination Procedures for Medical Equipment
... is shared between them unless it is decontaminated between use. They can also be carried on the skin surface which is why hand washing between examining patients is important. Microbes gain access to the body, through open wounds, inhalation of infected secretions or by close contact with mucous mem ...
... is shared between them unless it is decontaminated between use. They can also be carried on the skin surface which is why hand washing between examining patients is important. Microbes gain access to the body, through open wounds, inhalation of infected secretions or by close contact with mucous mem ...
Chapter 10 Microbiology
... Pathogens that cause body to produce antibodies. Allergen An antigen that causes an over-reaction Can cause anaphylactic shock. ...
... Pathogens that cause body to produce antibodies. Allergen An antigen that causes an over-reaction Can cause anaphylactic shock. ...
Best practice guide for the control of bovine respiratory disease
... Some calves will need re-treatment, which will push costs up even further. It’s not just a calf disease - pneumonia in adult cattle can lead to reduced fertility and productivity which can also cause grave financial losses in the long term. ...
... Some calves will need re-treatment, which will push costs up even further. It’s not just a calf disease - pneumonia in adult cattle can lead to reduced fertility and productivity which can also cause grave financial losses in the long term. ...
Chapter 34
... – the pathogen could be transmitted in sap – even when precipitated in ethanol the pathogen was still capable of causing an infection – it was capable of passing through filters with pores so small they filtered out bacteria ...
... – the pathogen could be transmitted in sap – even when precipitated in ethanol the pathogen was still capable of causing an infection – it was capable of passing through filters with pores so small they filtered out bacteria ...
Viral adaptation to host - Molecular Systems Biology
... tested the codon usage adaptation for over 100 bacteriophages infecting 10 different bacterial hosts, it was shown that the bacteriophage genomes are under codon-selective pressure imposed by the translational biases of their respective hosts (Carbone, 2008). The reasoning underlying this codon sele ...
... tested the codon usage adaptation for over 100 bacteriophages infecting 10 different bacterial hosts, it was shown that the bacteriophage genomes are under codon-selective pressure imposed by the translational biases of their respective hosts (Carbone, 2008). The reasoning underlying this codon sele ...
Lyme Disease
... Acute urethral syndrome: No active UTI, but irritative voiding symptoms. Vaginitis: May cause symptoms similar to UTI. Prostatitis: Acute bacterial, Chronic bacterial, Chronic nonbacterial ...
... Acute urethral syndrome: No active UTI, but irritative voiding symptoms. Vaginitis: May cause symptoms similar to UTI. Prostatitis: Acute bacterial, Chronic bacterial, Chronic nonbacterial ...
Henry Potosnak
... The purpose of this investigation is to attempt to discover a never- before-classified bacteriophage. The research involves finding a novel bacteriophage and then characterizing it. The techniques employed to characterize the identified phage include electron microscopy; sequencing, annotating, and ...
... The purpose of this investigation is to attempt to discover a never- before-classified bacteriophage. The research involves finding a novel bacteriophage and then characterizing it. The techniques employed to characterize the identified phage include electron microscopy; sequencing, annotating, and ...
Review Sheet for 2nd Midterm Exam
... the highest fish production (size of phytoplankton, number of trophic levels, food capture efficiency) What factors are not taken into account in the Ryther model? What are the main uses of the logged marine fish catch? What makes up the un-logged marine fish catch? Discuss 5 complications of fishin ...
... the highest fish production (size of phytoplankton, number of trophic levels, food capture efficiency) What factors are not taken into account in the Ryther model? What are the main uses of the logged marine fish catch? What makes up the un-logged marine fish catch? Discuss 5 complications of fishin ...
Virulence factor Bacterial
... component of LPS has toxic properties.The LPS is a very potent antigen and, as a result, stimulates an intense host immune response. As part of this immune response cytokines are released; these can cause the fever and other symptoms seen during disease. If a high amount of LPS is present then septi ...
... component of LPS has toxic properties.The LPS is a very potent antigen and, as a result, stimulates an intense host immune response. As part of this immune response cytokines are released; these can cause the fever and other symptoms seen during disease. If a high amount of LPS is present then septi ...
Medical Microbiology short answer questions
... What is the difference between prevalence and incidence of an infectious disease? It can be differentiated in chronic diseases. Prevalence: total number of diseases (per 100,000 people). Incidence: number of new cases in a year (per 100,000 people). ...
... What is the difference between prevalence and incidence of an infectious disease? It can be differentiated in chronic diseases. Prevalence: total number of diseases (per 100,000 people). Incidence: number of new cases in a year (per 100,000 people). ...
(PHAB2HH1) Module Contact: Dr Sheng Qi, PHA Copyright of the
... Endogenous retroviruses are derived from ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates Human endogenous retroviruses comprise around 5-8% of the human genome They are passed on to the next generation in the form of proviruses Endogenous retroviruses have been linked with ...
... Endogenous retroviruses are derived from ancient infections of germ cells in humans, mammals and other vertebrates Human endogenous retroviruses comprise around 5-8% of the human genome They are passed on to the next generation in the form of proviruses Endogenous retroviruses have been linked with ...
Chapter 18: Infectious Diseases Affecting the Skin and Eyes
... 2. Begins as a reddish rash on the face resulting in a “slapped-cheek” appearance 3. The rash then spreads over the body but is most prominent on arms, legs, and trunk 4. Rash may last for days to weeks and can recur during times of stress K. Roseola 1. Primarily caused by Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6 ...
... 2. Begins as a reddish rash on the face resulting in a “slapped-cheek” appearance 3. The rash then spreads over the body but is most prominent on arms, legs, and trunk 4. Rash may last for days to weeks and can recur during times of stress K. Roseola 1. Primarily caused by Human Herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6 ...
Lower Respiratory System a. larynx (voice box)
... causes inflammation of joints, skin, brain, heart valves (endocarditis); leading cause of heart disease among children in developing countries; bacteria have an Ag similar to that on heart cells – wbc’s become sensitized to the bacterial Ag, then attack the heart cells; disease can be prevented if s ...
... causes inflammation of joints, skin, brain, heart valves (endocarditis); leading cause of heart disease among children in developing countries; bacteria have an Ag similar to that on heart cells – wbc’s become sensitized to the bacterial Ag, then attack the heart cells; disease can be prevented if s ...
COMMISSION DECISION of 27 February 2004 on measures to
... Article 13(1)(ii) of Directive 2000/29/EC, stating that they have been obtained by means of an appropriate acid extraction method, and: (a) that they originate in areas in which Pepino mosaic virus is known not to occur; or (b) that no symptoms of Pepino mosaic virus have been observed on the plants ...
... Article 13(1)(ii) of Directive 2000/29/EC, stating that they have been obtained by means of an appropriate acid extraction method, and: (a) that they originate in areas in which Pepino mosaic virus is known not to occur; or (b) that no symptoms of Pepino mosaic virus have been observed on the plants ...
Host Parasite Relationship OBJECTIVES
... Having low pathogenecity and infect people with low immunity. e.g. Pseudomonas ...
... Having low pathogenecity and infect people with low immunity. e.g. Pseudomonas ...
Mechanisms of Multi-strain Coexistence in Host
... mortality, by delineating the specific phage types capable of infecting and lysing specific host types and, potentially, the taxonomic and biogeographic drivers of cross-infection [10]. Although predictive models of cross-infection remain elusive, it is evident that a single virus can infect multipl ...
... mortality, by delineating the specific phage types capable of infecting and lysing specific host types and, potentially, the taxonomic and biogeographic drivers of cross-infection [10]. Although predictive models of cross-infection remain elusive, it is evident that a single virus can infect multipl ...
Description of the Infectious Diseases & Biodefense program
... anthrax, tularemia, legionella, pertussis, yersinia, community-acquired MRSA, Ps. aeruginosa, H. pylori, Salmonella ...
... anthrax, tularemia, legionella, pertussis, yersinia, community-acquired MRSA, Ps. aeruginosa, H. pylori, Salmonella ...
Outpacing Infectious Diseases - Complex Adaptive Systems Initiative
... profile the host body defense systems as exquisite sentinel of ...
... profile the host body defense systems as exquisite sentinel of ...
Molecular Diagnostics
... The four main mechanisms by which microorganisms exhibit resistance to antimicrobials are: 1. Drug inactivation or modification: e.g. enzymatic deactivation of Penicillin G in some penicillin-resistant bacteria through the production of β-lactamases. 2. Alteration of target site : e.g. alteration of ...
... The four main mechanisms by which microorganisms exhibit resistance to antimicrobials are: 1. Drug inactivation or modification: e.g. enzymatic deactivation of Penicillin G in some penicillin-resistant bacteria through the production of β-lactamases. 2. Alteration of target site : e.g. alteration of ...
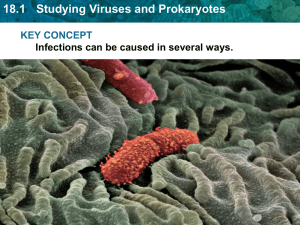
18.1 Studying Viruses and Prokaryotes
... • Virus - recognize and attach to a receptor site on the plasma membrane of host • Protein on capsid locks with receptor site • Each virus has a specifically shaped attachment protein ...
... • Virus - recognize and attach to a receptor site on the plasma membrane of host • Protein on capsid locks with receptor site • Each virus has a specifically shaped attachment protein ...
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
... plant cell, the protein coat falls away and nucleic acid portion directs the plant cell to produce more virus nucleic acid and virus protein, disrupting the normal activity of the cell. TMV can multiply only inside a living cell but it can survive in a dormant state in dead tissue, retaining its abi ...
... plant cell, the protein coat falls away and nucleic acid portion directs the plant cell to produce more virus nucleic acid and virus protein, disrupting the normal activity of the cell. TMV can multiply only inside a living cell but it can survive in a dormant state in dead tissue, retaining its abi ...
Concepts of Infectious Diseases
... Latency: The pathogen remains viable but is dormant within the host. It however remains capable of causing disease at a later date (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis or herpes viruses). The Infectious Disease Cycle: Reservoirs: Reservoirs for bacterial pathogens are generally divided into the followi ...
... Latency: The pathogen remains viable but is dormant within the host. It however remains capable of causing disease at a later date (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis or herpes viruses). The Infectious Disease Cycle: Reservoirs: Reservoirs for bacterial pathogens are generally divided into the followi ...
Concepts of Infectious Diseases
... Latency: The pathogen remains viable but is dormant within the host. It however remains capable of causing disease at a later date (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis or herpes viruses). The Infectious Disease Cycle: Reservoirs: Reservoirs for bacterial pathogens are generally divided into the followi ...
... Latency: The pathogen remains viable but is dormant within the host. It however remains capable of causing disease at a later date (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis or herpes viruses). The Infectious Disease Cycle: Reservoirs: Reservoirs for bacterial pathogens are generally divided into the followi ...