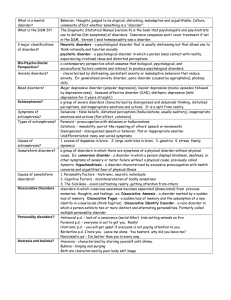
Abnormal Psychology
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
... What is the DSM-IV? How is the DSM-IV used by psychologists? Why the DSM-IV only bases diagnoses on observable patterns of behavior? self-fulfilling prophecies What is the difference between neurotic disorders and psychotic disorders? The negative effects of diagnostic labels The relationship betwee ...
DSM-5 – The First 17 Pages This is the first of what I am hoping will
... High comorbidity Shared treatment response ...
... High comorbidity Shared treatment response ...
PSYCHOLOGY (9th Edition) David Myers
... Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters, before committing a crime, respond with lower levels of stress hormones than others do at their age. ...
... Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters, before committing a crime, respond with lower levels of stress hormones than others do at their age. ...
Hypochondria - Cloudfront.net
... fear of having a serious disease. This preoccupation is based on misinterpretation of physical symptoms or sensations. Appropriate medical evaluation and reassurance that there is no illness present do not eliminate the preoccupation. Fear of illness must not be of delusional intensity. Delusional h ...
... fear of having a serious disease. This preoccupation is based on misinterpretation of physical symptoms or sensations. Appropriate medical evaluation and reassurance that there is no illness present do not eliminate the preoccupation. Fear of illness must not be of delusional intensity. Delusional h ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Somatic Symptom Disorder (new!) Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
... Somatic Symptom Disorder (new!) Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
Somatoform Disorders
... somatoform disorder in which a person appears to be, but is not, blind, deaf, paralyzed or insensitive to pain in various parts of the body. – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in ...
... somatoform disorder in which a person appears to be, but is not, blind, deaf, paralyzed or insensitive to pain in various parts of the body. – The person will not be able to move their arms, see, feel, etc. but there is no biological cause – The diagnosis of conversion disorder is rare, occurring in ...
Mental Disorders, Basic Concepts
... Multiple Causation Maintaining causes consequences of the disorder keep disorder going once it begins sometimes positive consequences (e.g., extra attention) often negative consequences (e.g., lack of friends) ...
... Multiple Causation Maintaining causes consequences of the disorder keep disorder going once it begins sometimes positive consequences (e.g., extra attention) often negative consequences (e.g., lack of friends) ...
psychology - TeacherWeb
... – 2. Hypochondriasis (hypochondriac) – excessive concerns about health ...
... – 2. Hypochondriasis (hypochondriac) – excessive concerns about health ...
AP Psych 15 sq AP Psych-Psychological Disorders-SQ
... 2. What effects do psychiatric labeling have on social and self-perceptions? 3. What is a phobia, and what are the three major types of phobias? 4. Differentiate between obsessions and compulsions. How are they typically related? 5. Describe four common features of PTSD. 6. How does psychoanalytic t ...
... 2. What effects do psychiatric labeling have on social and self-perceptions? 3. What is a phobia, and what are the three major types of phobias? 4. Differentiate between obsessions and compulsions. How are they typically related? 5. Describe four common features of PTSD. 6. How does psychoanalytic t ...