Chapter 13: Introduction to Landform Study
... being pushed up or by being exposed by erosion c. granite: light colored, coarse-grained; most common of intrusive igneous rocks C. Sedimentary Rocks 1. sedimentary rock: rock formed by sediment that is consolidated by the combination of pressure and cementation a. mechanical and chemical processes ...
... being pushed up or by being exposed by erosion c. granite: light colored, coarse-grained; most common of intrusive igneous rocks C. Sedimentary Rocks 1. sedimentary rock: rock formed by sediment that is consolidated by the combination of pressure and cementation a. mechanical and chemical processes ...
Topdressed K for Last-Year Alfalfa May Not Pay
... an average soil test of exchangeable K that was in the medium range (<125 ppm K), indicating that the crop is likely to respond to K. University of Minnesota recommends applying 100-140 lb K2O/ac to alfalfa with these soil tests for a 6 ton/ac hay yield goal. Soils ranged from sandy to clay loams. O ...
... an average soil test of exchangeable K that was in the medium range (<125 ppm K), indicating that the crop is likely to respond to K. University of Minnesota recommends applying 100-140 lb K2O/ac to alfalfa with these soil tests for a 6 ton/ac hay yield goal. Soils ranged from sandy to clay loams. O ...
Abiotic Disorders of Trees
... Temperature Soil Extremes – hot and cold - roots are less cold hardy than stems (trees in containers more vulnerable) - hot, unmulched soil may lead to death of surface roots - affects growth, nutrient uptake, seed dormancy and germination ...
... Temperature Soil Extremes – hot and cold - roots are less cold hardy than stems (trees in containers more vulnerable) - hot, unmulched soil may lead to death of surface roots - affects growth, nutrient uptake, seed dormancy and germination ...
What-do-you-know-about-rocks
... bottoms of oceans, rivers, and streams, along with mud, clay, and sand. In some areas, sediment also includes small pieces of onceliving matter, such as shells, bones, and plant parts. ...
... bottoms of oceans, rivers, and streams, along with mud, clay, and sand. In some areas, sediment also includes small pieces of onceliving matter, such as shells, bones, and plant parts. ...
Chapter 22 REDOX
... 1 Balance the redox equation using the smallest wholenumber coefficients. [1] 2 As this voltaic cell operates, the mass of the Al(s) electrode decreases. Explain, in terms of particles, why this decrease in mass occurs. [1] ...
... 1 Balance the redox equation using the smallest wholenumber coefficients. [1] 2 As this voltaic cell operates, the mass of the Al(s) electrode decreases. Explain, in terms of particles, why this decrease in mass occurs. [1] ...
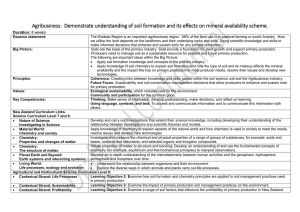
Demonstrate understanding of soil formation and its effects on
... we utilise the land depends on the landforms and their underlying rocks and soils. Using scientific knowledge and skills to make informed decisions that enhance and sustain soils for any primary production. Soils are the basis of the primary industry. Soils provide a foundation for plant growth and ...
... we utilise the land depends on the landforms and their underlying rocks and soils. Using scientific knowledge and skills to make informed decisions that enhance and sustain soils for any primary production. Soils are the basis of the primary industry. Soils provide a foundation for plant growth and ...
Elements, Compounds and Chemical Reactions
... element has an element cube that gives information about the element. The symbol is the short name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes f ...
... element has an element cube that gives information about the element. The symbol is the short name for the element. Notice that for an element, there is only ONE capital letter! Sometime the chemical symbol doesn’t look like it comes from the name of the element. This happens when the symbol comes f ...
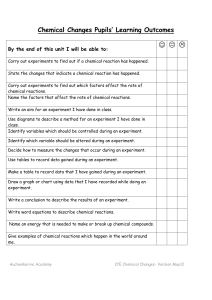
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Write an aim for an experiment I have done in class. Use diagrams to describe a method for an experiment I have done in class. Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that oc ...
... Write an aim for an experiment I have done in class. Use diagrams to describe a method for an experiment I have done in class. Identify variables which should be controlled during an experiment. Identify which variable should be altered during an experiment. Decide how to measure the changes that oc ...
Name - sfox4studentteacher
... The three main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle and core (inner and outer core layers). Temperature increases from the crust to the core. It is very hot inside Earth. Pressure also increases from the crust to the core. The crust is a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the o ...
... The three main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle and core (inner and outer core layers). Temperature increases from the crust to the core. It is very hot inside Earth. Pressure also increases from the crust to the core. The crust is a layer of solid rock that includes both dry land and the o ...
Unit 2
... • Make predictions based on data gathered over time in conjunction with various maps. EEn.2.1.3 • Recall that soil is the result of weathering of rocks and includes weathered particles: sand, silt and clay. • Explain differences in chemical and physical weathering and how weathering rates are affect ...
... • Make predictions based on data gathered over time in conjunction with various maps. EEn.2.1.3 • Recall that soil is the result of weathering of rocks and includes weathered particles: sand, silt and clay. • Explain differences in chemical and physical weathering and how weathering rates are affect ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Name__________________________________________
... recreation, subsidence, salt water intrusion. To access groundwater, ___________________ are dug into __________________. The primary use of groundwater by humans is for _____________________________. Issues with aquifers include ______________________________ __________________________ (sinking of ...
... recreation, subsidence, salt water intrusion. To access groundwater, ___________________ are dug into __________________. The primary use of groundwater by humans is for _____________________________. Issues with aquifers include ______________________________ __________________________ (sinking of ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... f. ___C7H16 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O g. ___C3H5OH + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O 4. Write and balance the following reactions: a. Zinc Carbonate can be heated to form Zinc Oxide and Carbon Dioxide ...
... f. ___C7H16 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O g. ___C3H5OH + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O 4. Write and balance the following reactions: a. Zinc Carbonate can be heated to form Zinc Oxide and Carbon Dioxide ...
chemical*equations
... When'a'chemical'reaction'occurs,'atoms'rearrange'to'form'new' compounds,'but'no'new'atoms'are'created'nor'are'any'destroyed.'This' concept'is'called'conservation'of'mass.'Mass'conservation'can'be'seen'in'a' balanced'chemical'equation,'where'the'numbers'of'each'kind'of'atom'are' the'same'on'both'side ...
... When'a'chemical'reaction'occurs,'atoms'rearrange'to'form'new' compounds,'but'no'new'atoms'are'created'nor'are'any'destroyed.'This' concept'is'called'conservation'of'mass.'Mass'conservation'can'be'seen'in'a' balanced'chemical'equation,'where'the'numbers'of'each'kind'of'atom'are' the'same'on'both'side ...
Rock Cycle Study Guide Key
... The lithosphere is the solid and rigid outer layer of our planet. It includes the crust and part of the upper mantle that contains rigid rocks. Beneath this layer is the asthenosphere where the rocks in this part of the upper mantle are not rigid. The rocks can flow like a liquid or break apart simi ...
... The lithosphere is the solid and rigid outer layer of our planet. It includes the crust and part of the upper mantle that contains rigid rocks. Beneath this layer is the asthenosphere where the rocks in this part of the upper mantle are not rigid. The rocks can flow like a liquid or break apart simi ...
Absorption of Water by Plants
... vascular plants. More than 90 percent of plants have a mycorrhizal symbiont that plays an important role in biochemical soil processes. ...
... vascular plants. More than 90 percent of plants have a mycorrhizal symbiont that plays an important role in biochemical soil processes. ...
Guidance for Soil Construction Standards and Testing Frequencies
... vegetative growth. A good vegetative cover will prevent erosion from occurring. Soils that enhance plant growth are well aerated and have the ability to hold moisture and nutrients for plant uptake. Rooting zone soils should be checked using the soil filter analysis described at the end of this fact ...
... vegetative growth. A good vegetative cover will prevent erosion from occurring. Soils that enhance plant growth are well aerated and have the ability to hold moisture and nutrients for plant uptake. Rooting zone soils should be checked using the soil filter analysis described at the end of this fact ...
An Introduction to Water Budget Equation
... more side is open, unconfined aquifer.Water table (3) is the upper level of the water stored in the aquifer.If water table is less than water level of the adjacent water body and if pores of sufficient size and frequency is available ground water will leech into the water body (Affluent) and if the ...
... more side is open, unconfined aquifer.Water table (3) is the upper level of the water stored in the aquifer.If water table is less than water level of the adjacent water body and if pores of sufficient size and frequency is available ground water will leech into the water body (Affluent) and if the ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... NaCl + KBr NaBr + KCl NO RXN 17. What is the % composition of each element in ammonium phosphate? ...
... NaCl + KBr NaBr + KCl NO RXN 17. What is the % composition of each element in ammonium phosphate? ...
Intro to Rocks & Igneous Rocks
... A group of minerals bound together. (See picture on pg. 118 in text) ...
... A group of minerals bound together. (See picture on pg. 118 in text) ...
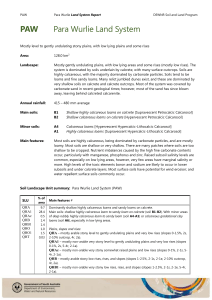
PAW Para Wurlie Land System
... Most soils are highly calcareous, being dominated by carbonate particles, and are mostly loamy. Most soils are shallow or very shallow. There are many patches where soils are too shallow to be cropped. Nutrient imbalances caused by the high fine carbonate contents occur, particularly with manganese, ...
... Most soils are highly calcareous, being dominated by carbonate particles, and are mostly loamy. Most soils are shallow or very shallow. There are many patches where soils are too shallow to be cropped. Nutrient imbalances caused by the high fine carbonate contents occur, particularly with manganese, ...
Keeping the soil healthy
... nitrogen and break down quickly, so the nutrients can soon be used by the following crop. Cover crops Plant these when they fit in your cropping system and allow them to grow and cover the soil. Slash them or kill them with herbicide just before planting the next crop and leave the dead material on ...
... nitrogen and break down quickly, so the nutrients can soon be used by the following crop. Cover crops Plant these when they fit in your cropping system and allow them to grow and cover the soil. Slash them or kill them with herbicide just before planting the next crop and leave the dead material on ...
Nursery Production and Management
... Startup cost is expensive largely due to field preparation and purchasing two containers for every plant as opposed to one. 15 to 25 gallon pots are more commonly used. ...
... Startup cost is expensive largely due to field preparation and purchasing two containers for every plant as opposed to one. 15 to 25 gallon pots are more commonly used. ...