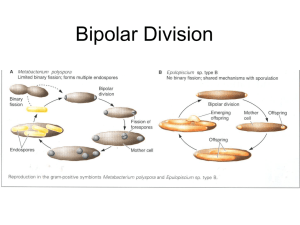
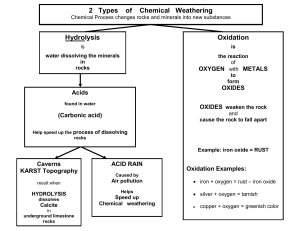
Reshaping the Land Unit Study Guide 1. What type of weathering
... 9. At what elevation would rocks be exposed to more wind, rain, and ice?__________________________________ 10. What type of weather would cause rapid chemical weathering?________________________________________ 11. Soil formation begins with the weathering of ________________________________________ ...
... 9. At what elevation would rocks be exposed to more wind, rain, and ice?__________________________________ 10. What type of weather would cause rapid chemical weathering?________________________________________ 11. Soil formation begins with the weathering of ________________________________________ ...
File
... 6. Which of these produces gas bubbles when it touches acid? a. shale b. all conglomerates c. humus d. limestone 7. What does the term permeability refer to? a. the hardness of soil b. the slope of soil c. the flow of water through soil d. the quality of the soil for use in farming 8. Which of the f ...
... 6. Which of these produces gas bubbles when it touches acid? a. shale b. all conglomerates c. humus d. limestone 7. What does the term permeability refer to? a. the hardness of soil b. the slope of soil c. the flow of water through soil d. the quality of the soil for use in farming 8. Which of the f ...
Soil Unit Terminology
... Soil Unit Terminology List ____________________________________________________________________________________ Required Terms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ Acid Precipitation: ...
... Soil Unit Terminology List ____________________________________________________________________________________ Required Terms: _____________________________________________________________________________________ Acid Precipitation: ...
APES Focus/Ch - cynthiaahmed
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
... Name some of the rare metals needed to produce electric or hybrid vehicles. Then, describe the process required to remove them. What are the consequences of this process? ...
Chapter 14 concept review
... h. the grinding and wearing away of rock surfaces through the mechanical action of other rock or sand particles i. the slow, downslope flow of soil saturated with water in areas surrounding glaciers at high elevations j. a horizontal layer of soil that can be distinguished from the layers above and ...
... h. the grinding and wearing away of rock surfaces through the mechanical action of other rock or sand particles i. the slow, downslope flow of soil saturated with water in areas surrounding glaciers at high elevations j. a horizontal layer of soil that can be distinguished from the layers above and ...
3D ROCKS AND SOILS
... soil, whether it allows water to pass through easily or not mineral – a substance which is taken out of the ground e.g. iron ore is mined and manufactured into metal products particles – very small pieces of a substance permeable – lets water through non-permeable – does not let water through sand – ...
... soil, whether it allows water to pass through easily or not mineral – a substance which is taken out of the ground e.g. iron ore is mined and manufactured into metal products particles – very small pieces of a substance permeable – lets water through non-permeable – does not let water through sand – ...
Soil and the Rhizosphere
... Organic matter and availability of alternate electron acceptors (e.g. nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide) will partly determine which anaerobic respiring bacteria thrive where. ...
... Organic matter and availability of alternate electron acceptors (e.g. nitrate, sulfate, carbon dioxide) will partly determine which anaerobic respiring bacteria thrive where. ...
Soil Science Big Ideas
... disintegrated rocks and living or dead organic matter. Organic matter is made of the organic compounds – carbon / oxygen / phosphorus / nitrogen / sulphur Soil composition is also dependent on weather elements such as temperature and rainfall. Within the soil there are ecosystems where the organisms ...
... disintegrated rocks and living or dead organic matter. Organic matter is made of the organic compounds – carbon / oxygen / phosphorus / nitrogen / sulphur Soil composition is also dependent on weather elements such as temperature and rainfall. Within the soil there are ecosystems where the organisms ...
SOIL COVER IN FLOODPLAINS OF SMALL RIVERS IN THE
... equilibrium and water exchange. Floodplains are the most productive landscapes, combining the high activity of biological and geological factors. Alluvial sedimentation in the territory of the reserve «Stolby» has certain unique features such as high degree of dismemberment of relief in conditions o ...
... equilibrium and water exchange. Floodplains are the most productive landscapes, combining the high activity of biological and geological factors. Alluvial sedimentation in the territory of the reserve «Stolby» has certain unique features such as high degree of dismemberment of relief in conditions o ...
ExamView - Weathering and Erosion Test_Review.tst
... 16. The decayed organic material in soil is called ______________. 17. As water moves slowly through a ____________, plants within it filter out waste materials. 18. The mixture of rock particles, minerals, decayed organic material, air, and water is called ____________. 19. A hot and wet climate ca ...
... 16. The decayed organic material in soil is called ______________. 17. As water moves slowly through a ____________, plants within it filter out waste materials. 18. The mixture of rock particles, minerals, decayed organic material, air, and water is called ____________. 19. A hot and wet climate ca ...
Answers
... Carbon dioxide is dissolved in water to form weak carbonic acid (H2CO3) Calcium carbonate present in limestone rocks react with carbonic acid This forms calcium BI-carbonate Calcium carbonate is not soluble in water but carbonic acid turns it to Soluble Calcium Bi-carbonate This soluble compound c ...
... Carbon dioxide is dissolved in water to form weak carbonic acid (H2CO3) Calcium carbonate present in limestone rocks react with carbonic acid This forms calcium BI-carbonate Calcium carbonate is not soluble in water but carbonic acid turns it to Soluble Calcium Bi-carbonate This soluble compound c ...
Earth Revealed - Weathering and Soils
... 1. What is the breakdown or fragmentation of rocks called? (a) erosion (b) mass wasting (c) weathering (d) deposition 2. With a release in confining pressure what process describes the shedding of granite layers? (a) compaction (b) cementation (c) lithification (d) exfoliation 3. What per cent does ...
... 1. What is the breakdown or fragmentation of rocks called? (a) erosion (b) mass wasting (c) weathering (d) deposition 2. With a release in confining pressure what process describes the shedding of granite layers? (a) compaction (b) cementation (c) lithification (d) exfoliation 3. What per cent does ...
Soil is - Amazon S3
... down rock through chemical changes. The causes of chemical weathering are ...
... down rock through chemical changes. The causes of chemical weathering are ...
Name: Date: Period: _____
... earthflow, or slump What is dark organic material found in topsoil? – humus, tephra, or talus What is primarily responsible for dissolving limestone & forming large caverns? – abrasion, carbonic acid or hydrolysis What is the break up of rock due to processes at the earth’s surface? – erosion or wea ...
... earthflow, or slump What is dark organic material found in topsoil? – humus, tephra, or talus What is primarily responsible for dissolving limestone & forming large caverns? – abrasion, carbonic acid or hydrolysis What is the break up of rock due to processes at the earth’s surface? – erosion or wea ...
Rocks and mineral monoliths lab
... Soil weathering profiles: Note soil color, structure, clay films and rock fragment content for the weathering profiles from the three different parent materials. How are soil properties affected by the properties of the parent material? What other kinds of information do you need to make interpretat ...
... Soil weathering profiles: Note soil color, structure, clay films and rock fragment content for the weathering profiles from the three different parent materials. How are soil properties affected by the properties of the parent material? What other kinds of information do you need to make interpretat ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil - a complex plant supporting system made up of disintegrated rock, remains and wastes of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Me ...
... About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil - a complex plant supporting system made up of disintegrated rock, remains and wastes of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Me ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... Affected by the surface area of the rock exposed to the weathering process ...
... Affected by the surface area of the rock exposed to the weathering process ...
The soil forming factors
... slopes and rapid drainage near the crest to more gentle slopes and less rapid (or even impeded) drainage near the foot of the slope and in the valley bottom. parent material ...
... slopes and rapid drainage near the crest to more gentle slopes and less rapid (or even impeded) drainage near the foot of the slope and in the valley bottom. parent material ...